Fact Sheets - Invasive Species
For more invasive species information, reference the First Detector Guide to Invasive Insects, Invasive Fruit Pest Guide for Utah, Invasive Insect Field Guide for Utah, and Invasive Pests of Landscape Trees in Utah
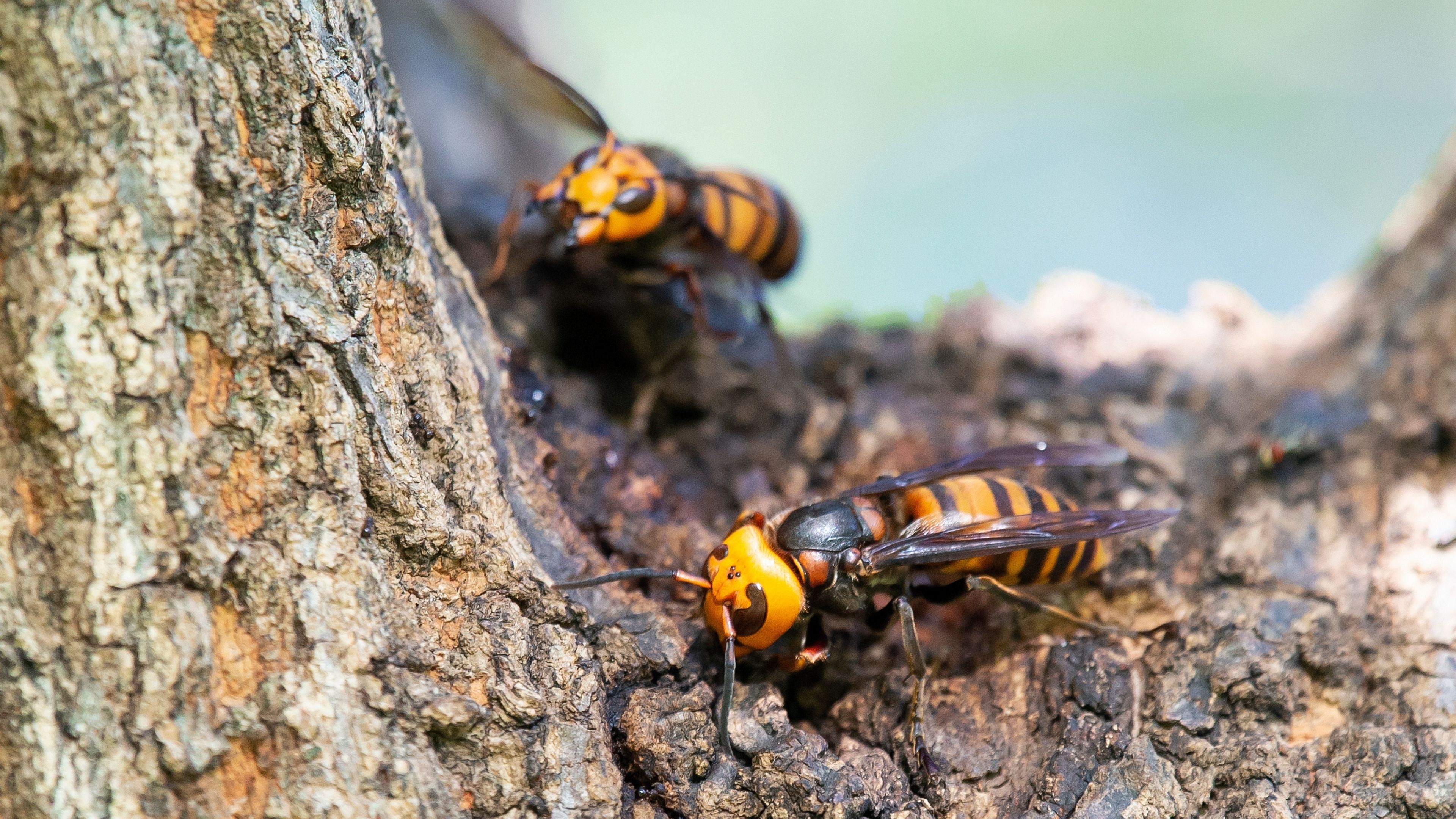
Northern Giant Hornet
Northern giant hornet (also known as the Asian giant hornet, AGH) is an invasive wasp native to Southeast Asia. AGH was recently detected in a small area of North America but is not known to be established in that region. This insect is a concern to beekeepers because it can quickly destroy honey bee colonies. Stings can cause pain and swelling and are a health concern for people with bee or wasp allergies. At roughly 2 inches in length, AGH is the world's largest hornet.
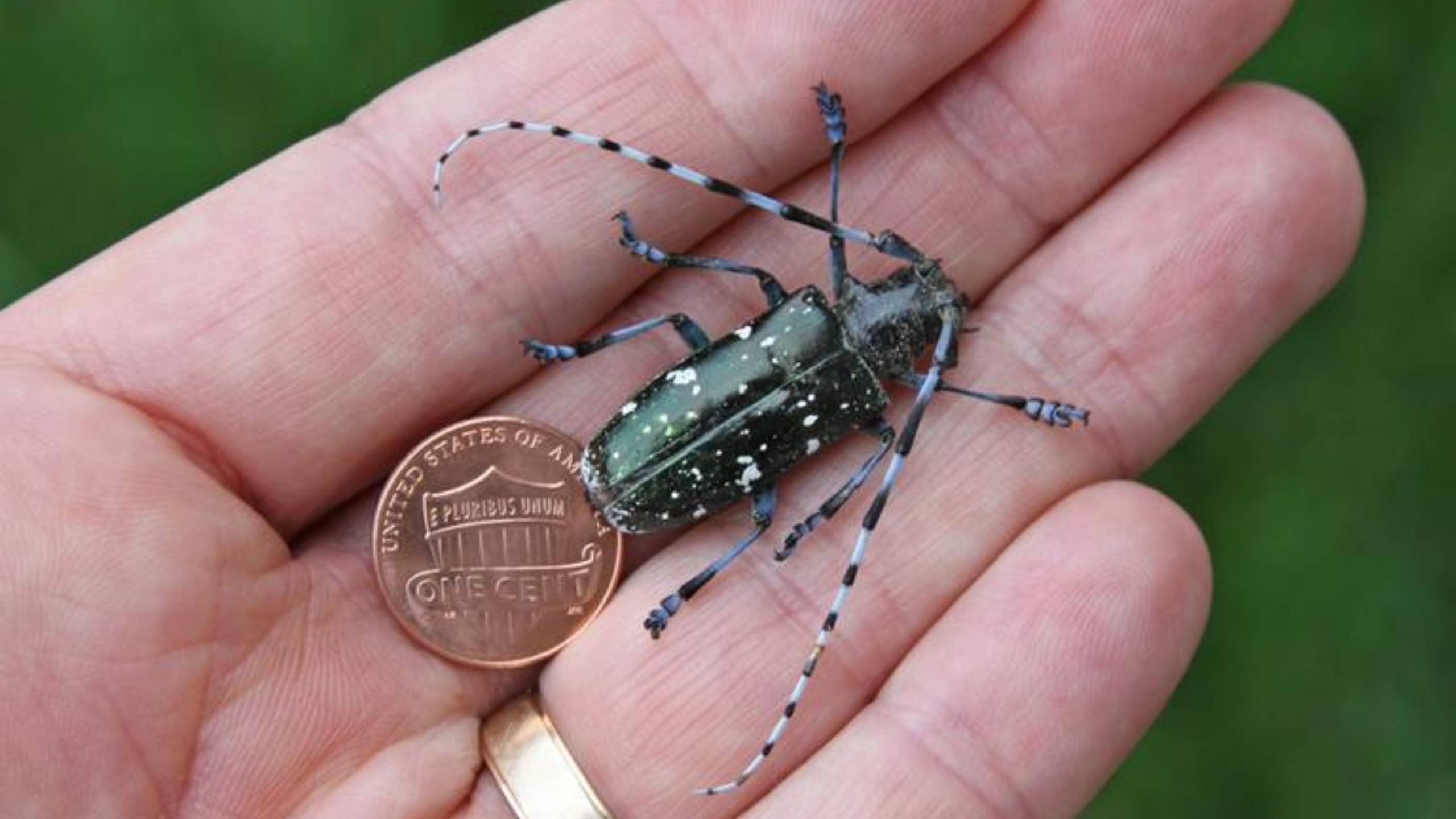
Asian Longhorned Beetle
Asian longhorned beetle (ALB) is an invasive wood-boring pest that threatens over 100 hardwood tree species and maple syrup production. ALB is currently known to occur in Massachusetts, New York, South Carolina, and Ohio. Citizen reports of this pest have been critical in restricting the movement of this pest, which has no known enemies in North America.
Balsam Woolly Adelgid
In the U.S., BWA is a serious pest of true firs in forests, landscapes, and in seed and Christmas tree production. In some areas of North America, BWA has completely removed true firs from forest stands. In Utah, subalpine fir is a highly susceptible host tree; white fir is also a host but is more tolerant.
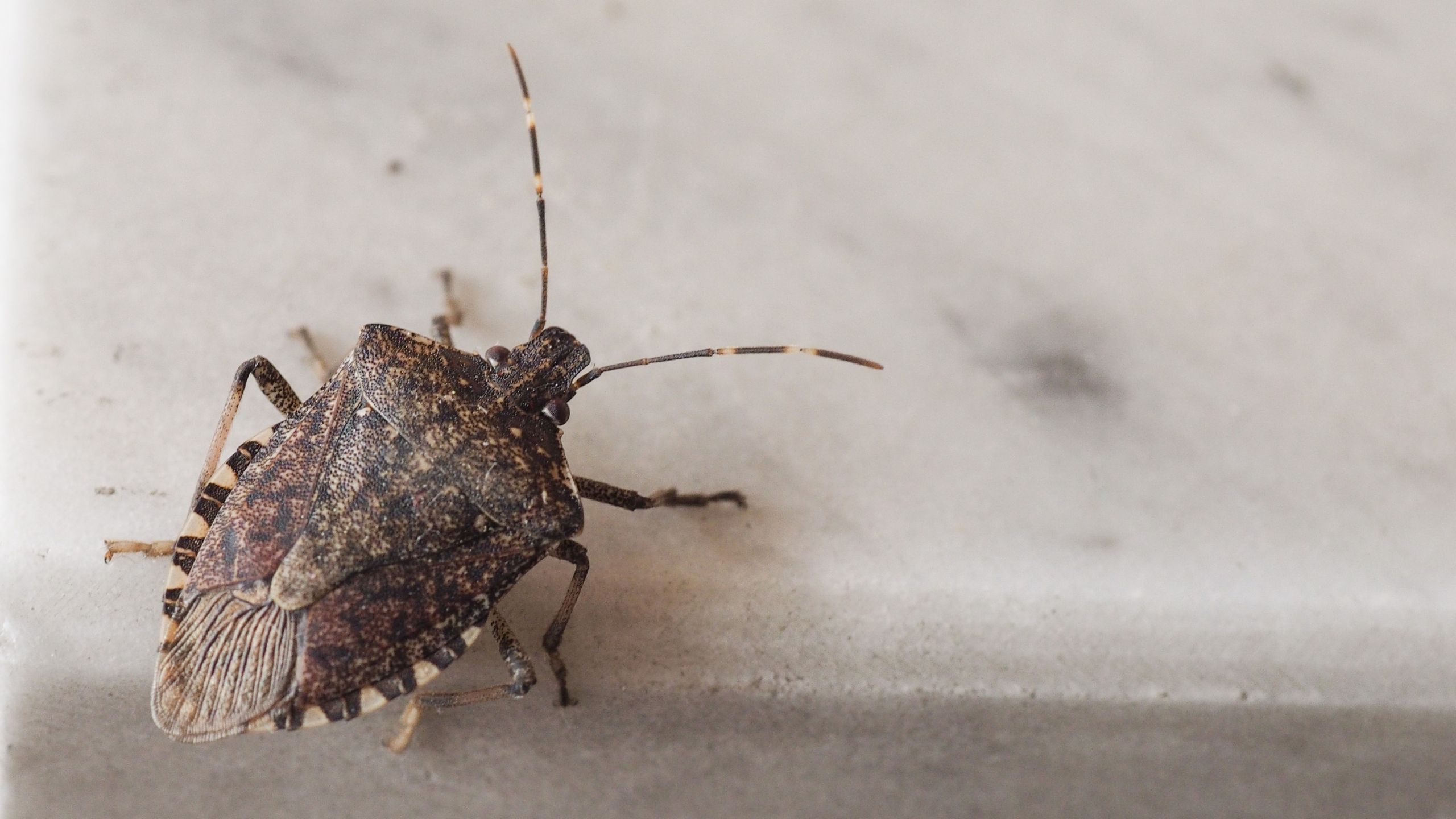
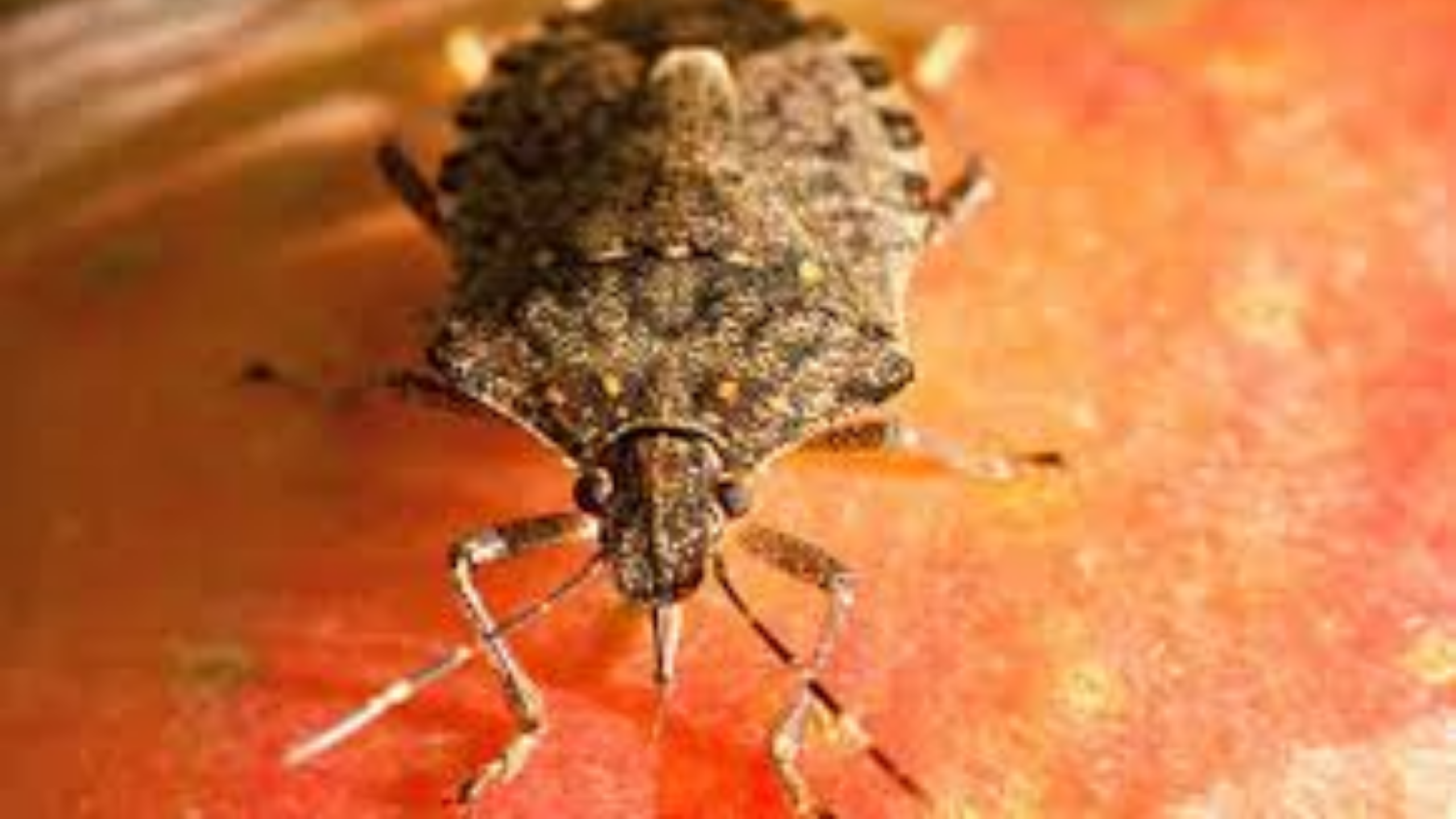
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug
The brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) was accidentally introduced into the eastern U.S. from Asia in the late 1990s and was first detected in Utah in 2012. BMSB now occurs in several northern Utah counties. BMSB can be a nuisance pest as it aggregates in large numbers, and it has a broad host range that includes fruit, vegetable, ornamental, and field crop plants.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug Management for Fruits And Vegetables
Brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) is an invasive insect that attacks fruit and vegetable crops in Utah. BMSB was first detected in Utah in 2012, and since 2017 it has caused damage to fruits and vegetables in some Northern Utah counties. More detailed monitoring and management strategies are included here.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug - Parasitoids
Parasitoid wasps that sting and kill brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) eggs are the most promising type of biological control for this invasive pest. Parasitoid wasps found in Utah that can affect BMSB are discussed here, including the highly specialized samurai wasp, Trissolcus japonicus, that is native to BMSB’s home range and was detected in Utah in June 2019.
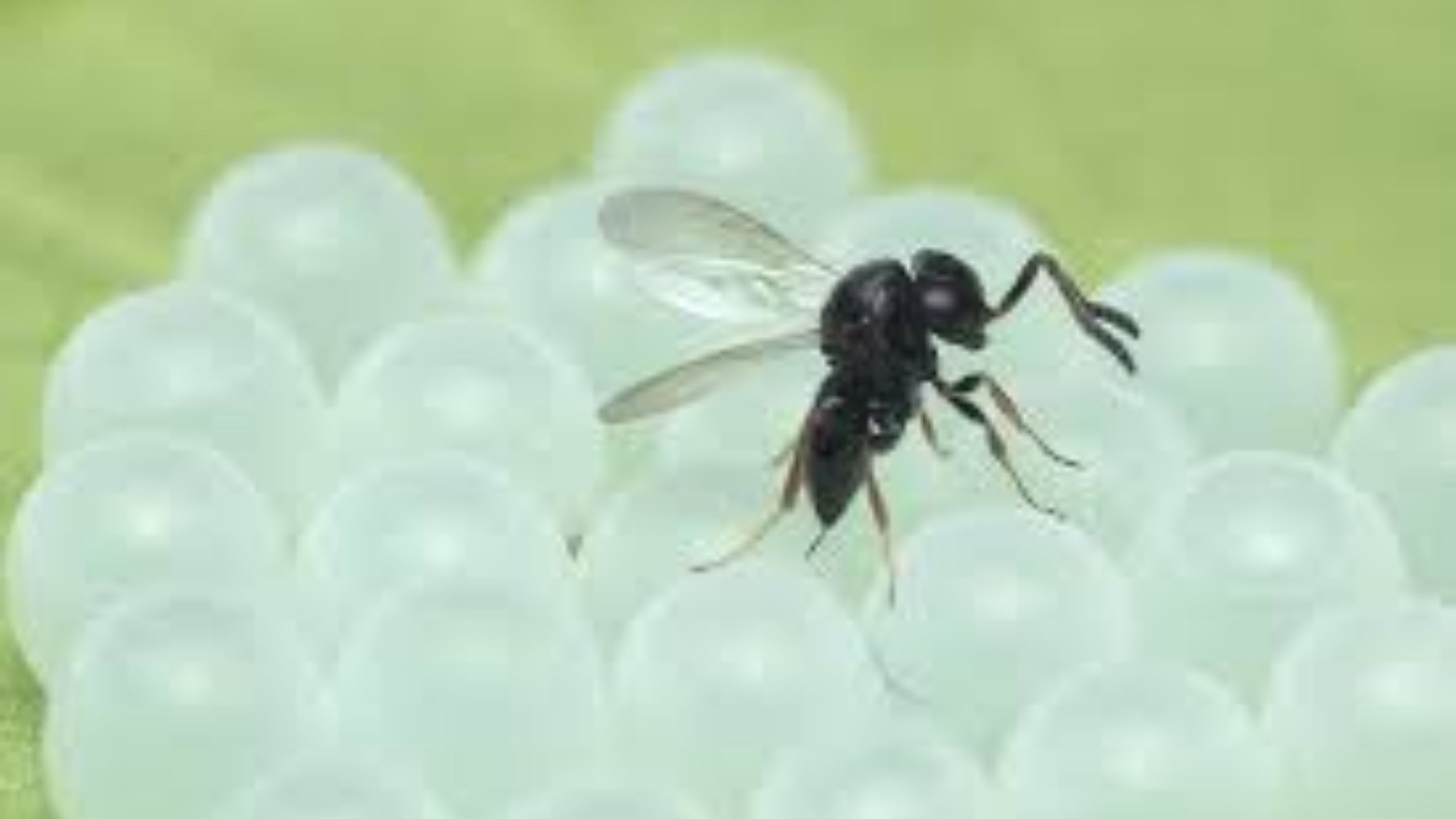
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug - Predatory Samurai Wasp in Utah
In June 2019, the exotic parasitoid "samurai wasp" (Trissolcus japonicus) was discovered in Salt Lake City. This wasp targets the brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) in its native Asia and is currently the most promising biological control agent for BMSB.Elm Seed Bug
The elm seed bug (ESB) was first discovered in the U.S. in Idaho in 2012. In Utah, ESB is now a nuisance pest as it enters homes and buildings in great numbers, similar to the boxelder bug's behavior. ESB is now widely distributed along the Wasatch Front and within Cache County as well as other counties in Utah.
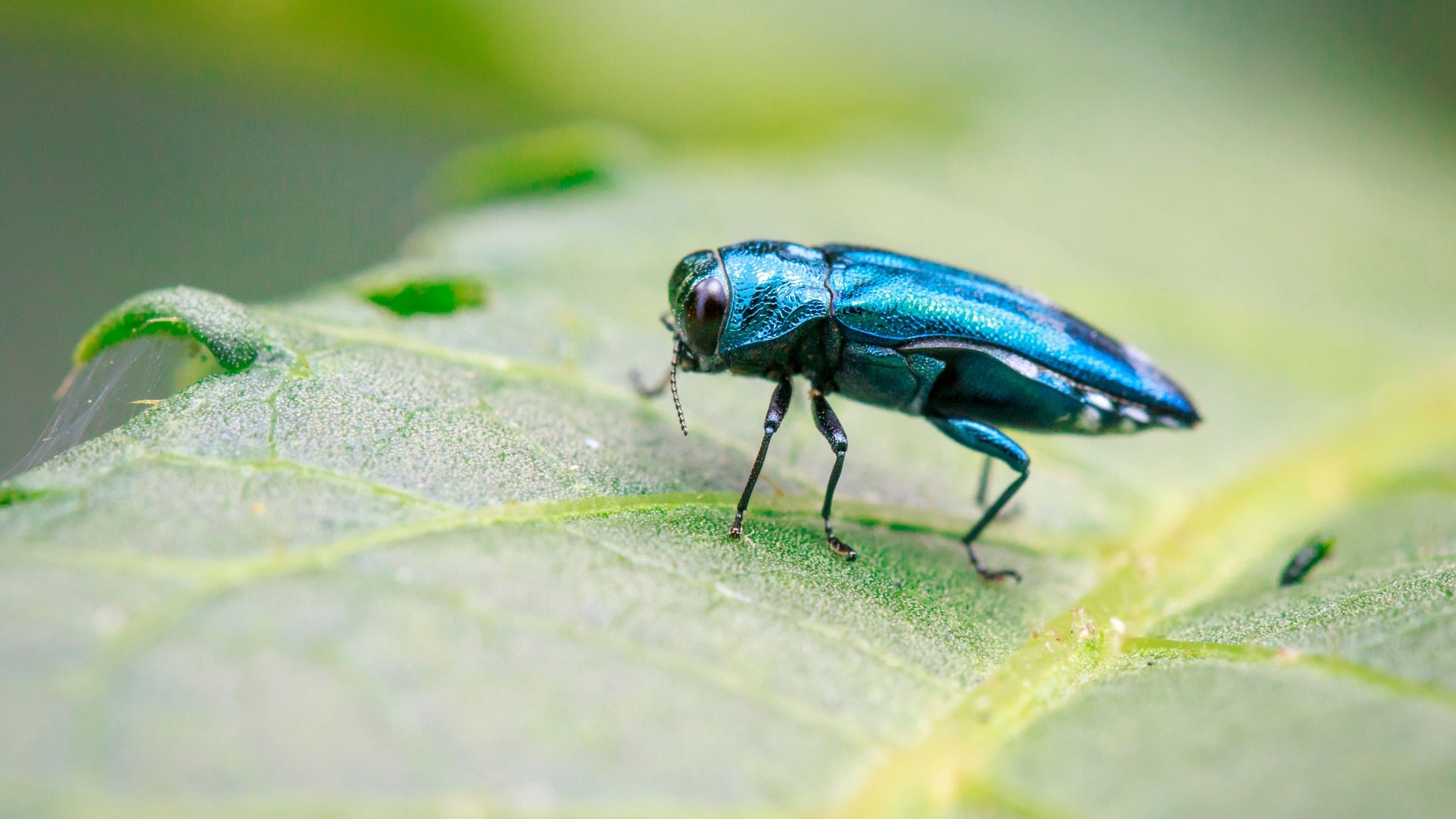
Emerald Ash Borer
The invasive and highly destructive emerald ash borer (EAB) has caused extensive damage to ash trees where it has established in North America. EAB is now established most closely in Colorado where it is causing extensive damage to ash trees. EAB initially infests tree crowns, and emerging adults leave distinctive D-shaped exit holes on the tree trunk. Larvae create twisting excrement-filled channels visible on peeled bark. EAB has not been detected in UT.
European Cherry Fruit Fly
The European cherry fruit fly (ECFF) is a new invasive pest from Europe that infests cherry fruit. It was first detected in North America in Ontario (2016). Larvae are the damaging life stage as they feed within fruits, causing them to rot and fall off the tree. In Europe, heavy infestations have resulted in 100% fruit loss. Spread occurs primarily through movement of infested fruit.
Imported Fire Ants
The red and black imported fire ants (IFA) are an invasive and aggressive pest from South America. IFA are not known to occur in Utah, but parts of southern Utah may be suitable for colony establishment, particularly in areas that have accessible water from irrigation or natural sources. IFA cause agricultural, ecological, economical, nuisance, and public health issues.
Invasive Insect Look-Alikes
Learn how to identify some invasive insects and their look-alikes. Here, we provide a quick identification guide for brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) and Japanese beetle (JB)--both of which currently occur in Utah--as well as emerald ash borer (EAB) and Asian longhorned beetle (ALB).
Japanese Beetle
Japanese beetle was initially detected in Orem, Utah, in July 2006. Past eradication efforts were highly successful. However, constant pressure from travel and trade has resulted in a few additional captures in monitoring traps in recent years. Adults have a broad host range of more than 300 plant species and can cause significant damage.
Lily Leaf Beetle
The lily leaf beetle (LLB) is a an important pest from Eurasia that threatens native and cultivated true lilies and fritillaries. LLB adults and larvae create large holes as they feed, and all parts of host plants can be consumed. LLB has not been detected in Utah, but it is likely capable of establishing throughout most of the U.S. where plants in the Liliaceae family occur, which includes Utah.
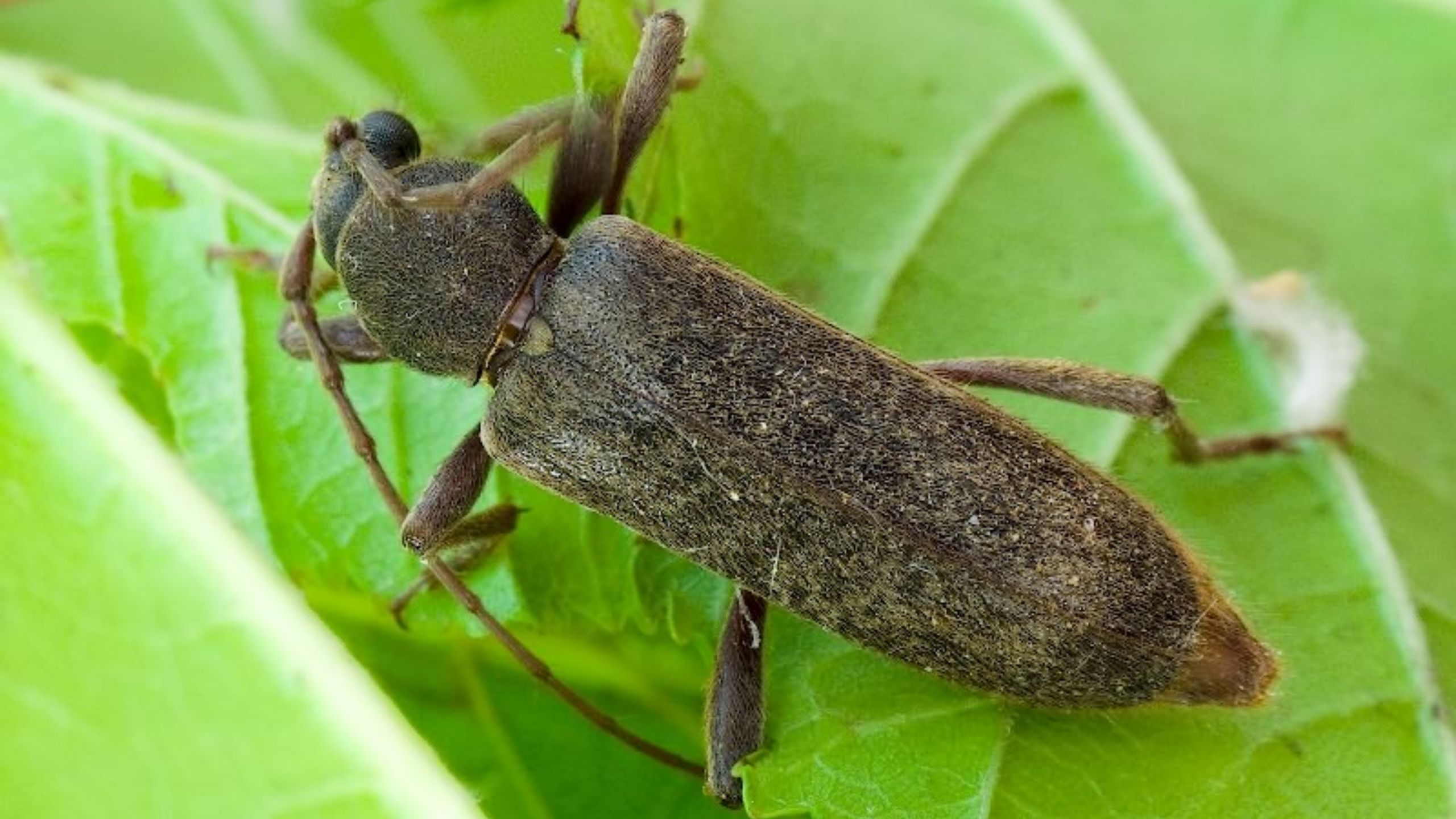
Plum Curculio
Plum curculio is a small brown weevil (beetle with a snout) native to eastern North America where it is a major pest of pome and stone fruits. Plum curculio was detected in Box Elder County, Utah, in the early 1980s, and this population remains the only known infestation in western North America, where it is occasionally found in residential and wild fruit trees.
Quagga Mussel and Zebra Mussel
Quagga and zebra mussel are native to eastern Europe and western Asia that cause severe disruptions of aquatic ecosystems and critical water infrastructure systems. The quagga mussel was detected in Lake Powell in 2012 and quickly infested the reservoir. Zebra mussel is not known to occur in Utah, but it was detected in aquarium "moss balls" sold in Utah in 2021. Important disposal details are included here.
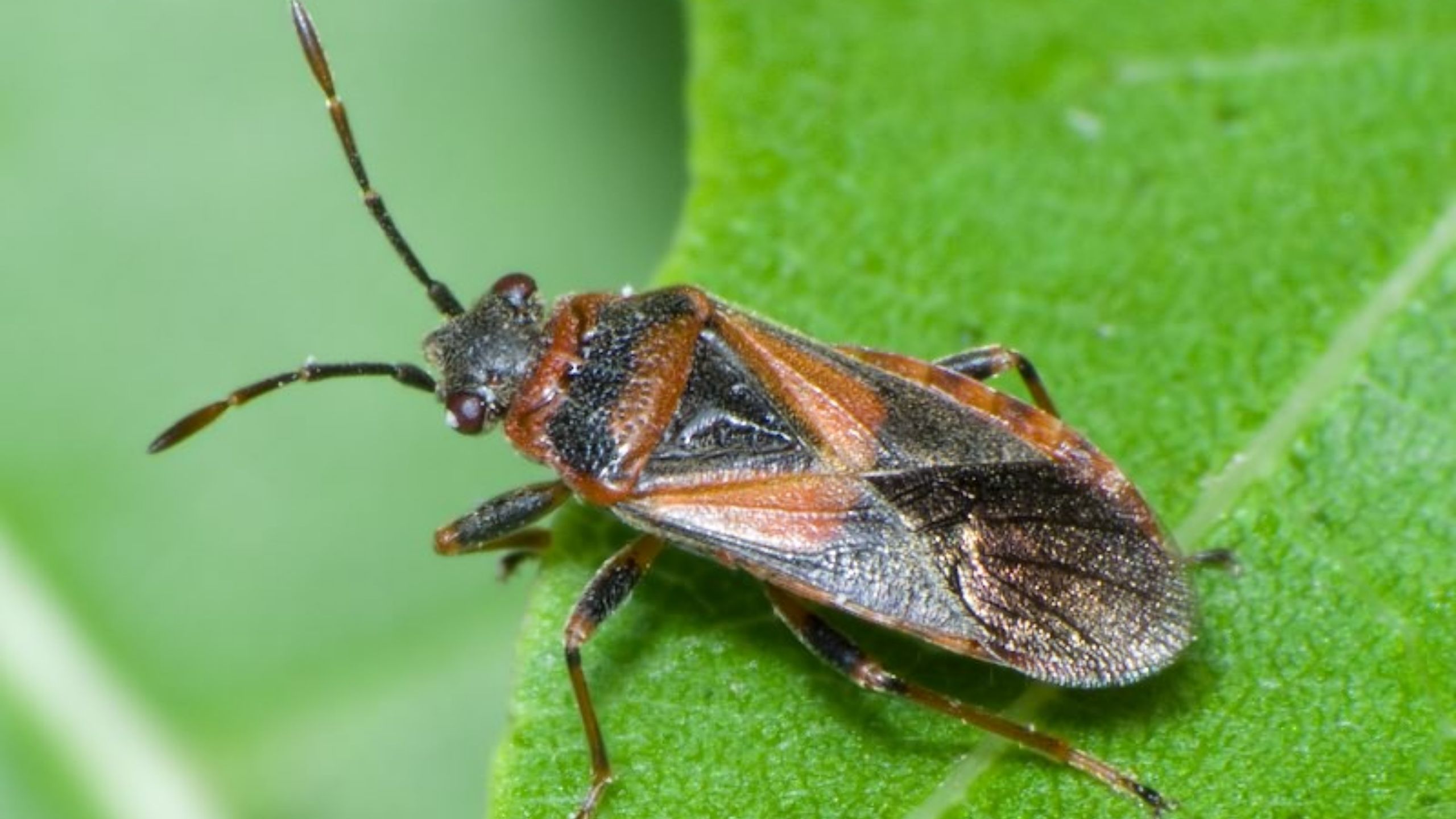
Red Firebug
Red Firebugs were first discovered in North America in Salt Lake City, Utah in 2008. These insects are seed feeders on a wide range of plants, including linden and mallow.
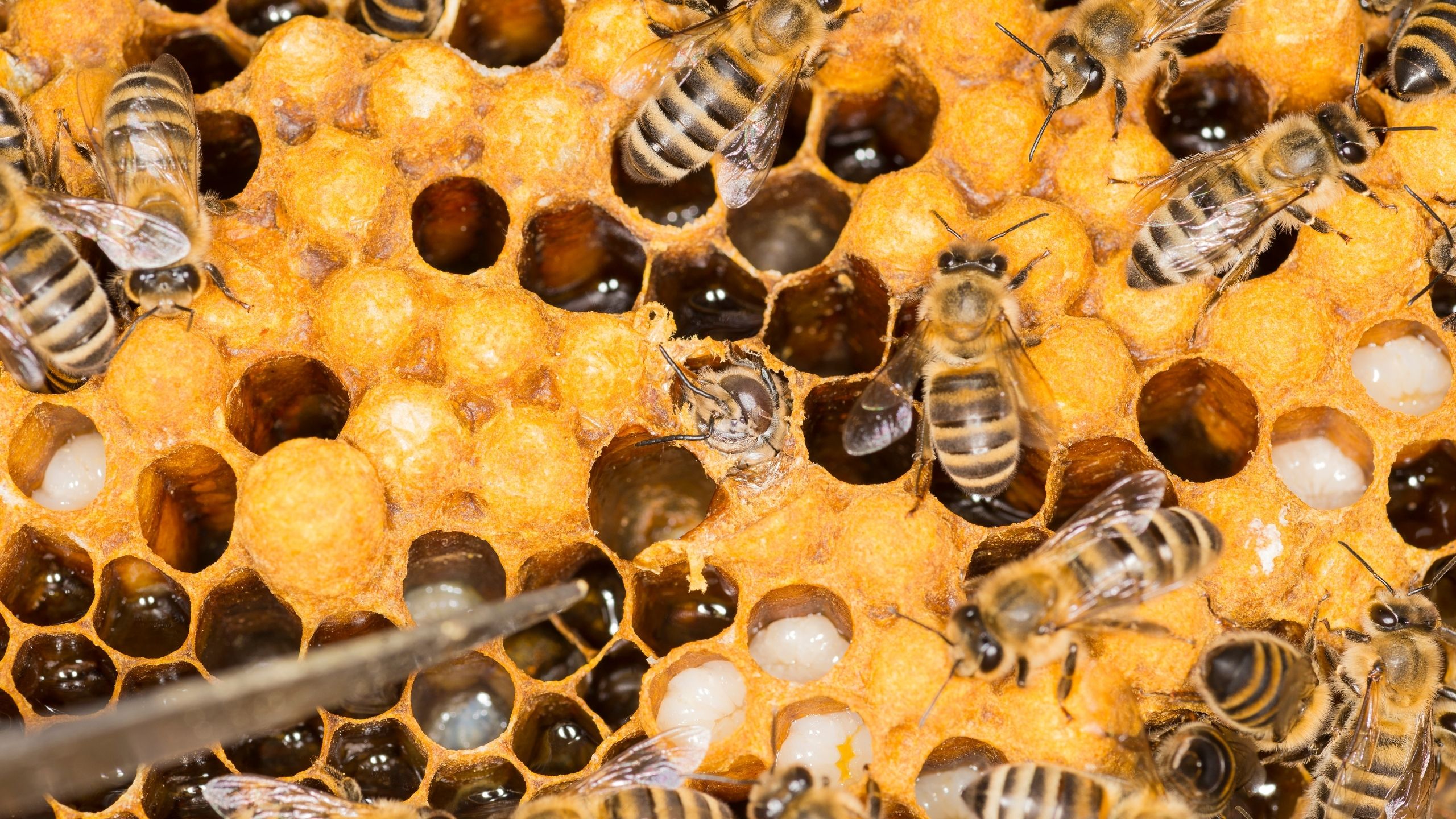
Small Hive Beetle
The small hive beetle (SHB) is a pest of honey and bumble bee colonies and was first detected in Utah in 2016. SHB is now confirmed in Washington and Davis counties. SHB native feeds on pollen and honey, kills bee brood and workers, and causes honey to discolor and ferment.
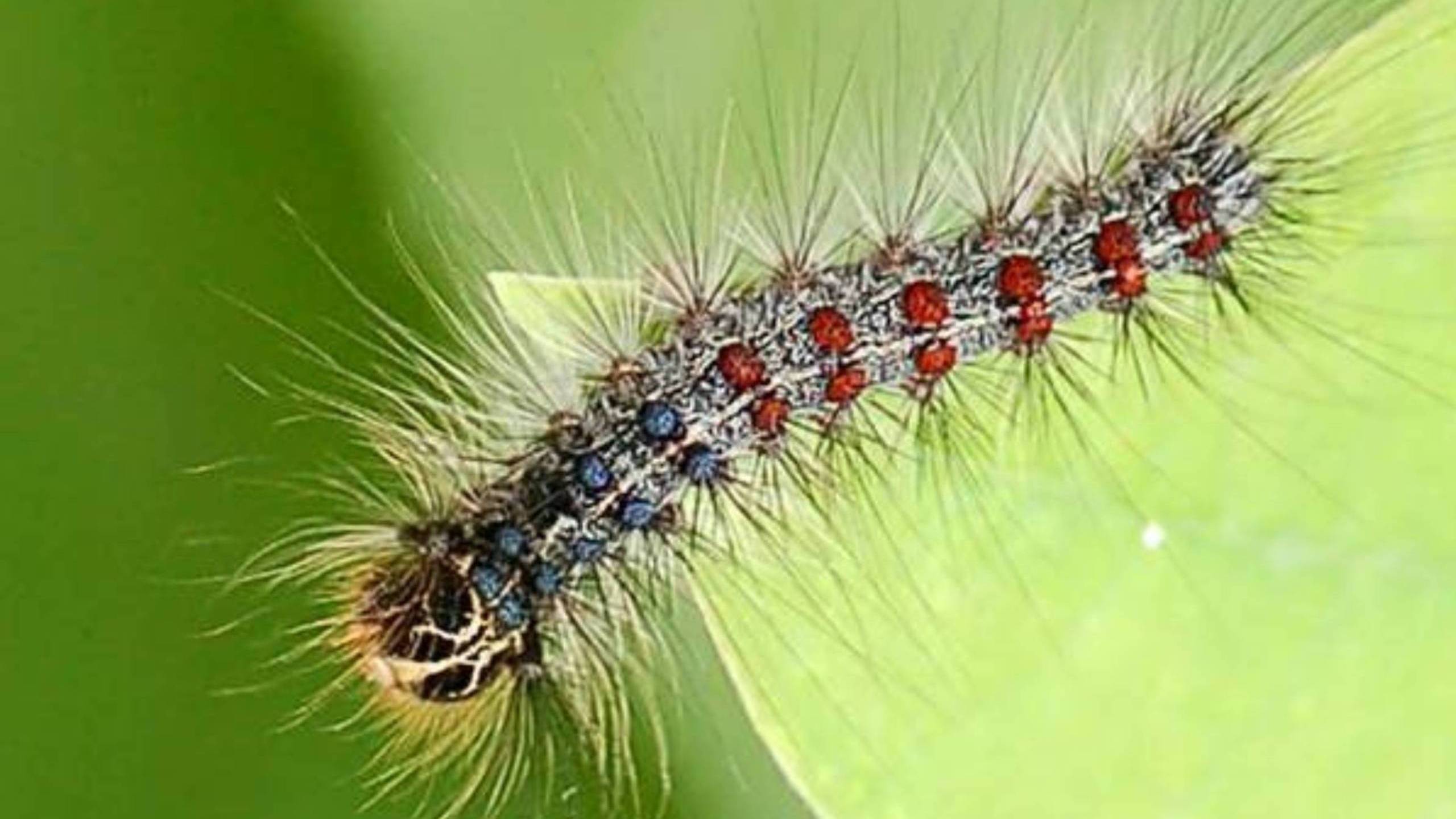
Spongy Moth
Spongy moth is the new name for the European gypsy moth, whose name was officially changed in 2022 to respect cultural sensitivity. This pest has ravaged parts of the eastern U.S. The threat of an Asian subspecies with the added "super power" of flight is also addressed in this fact sheet.
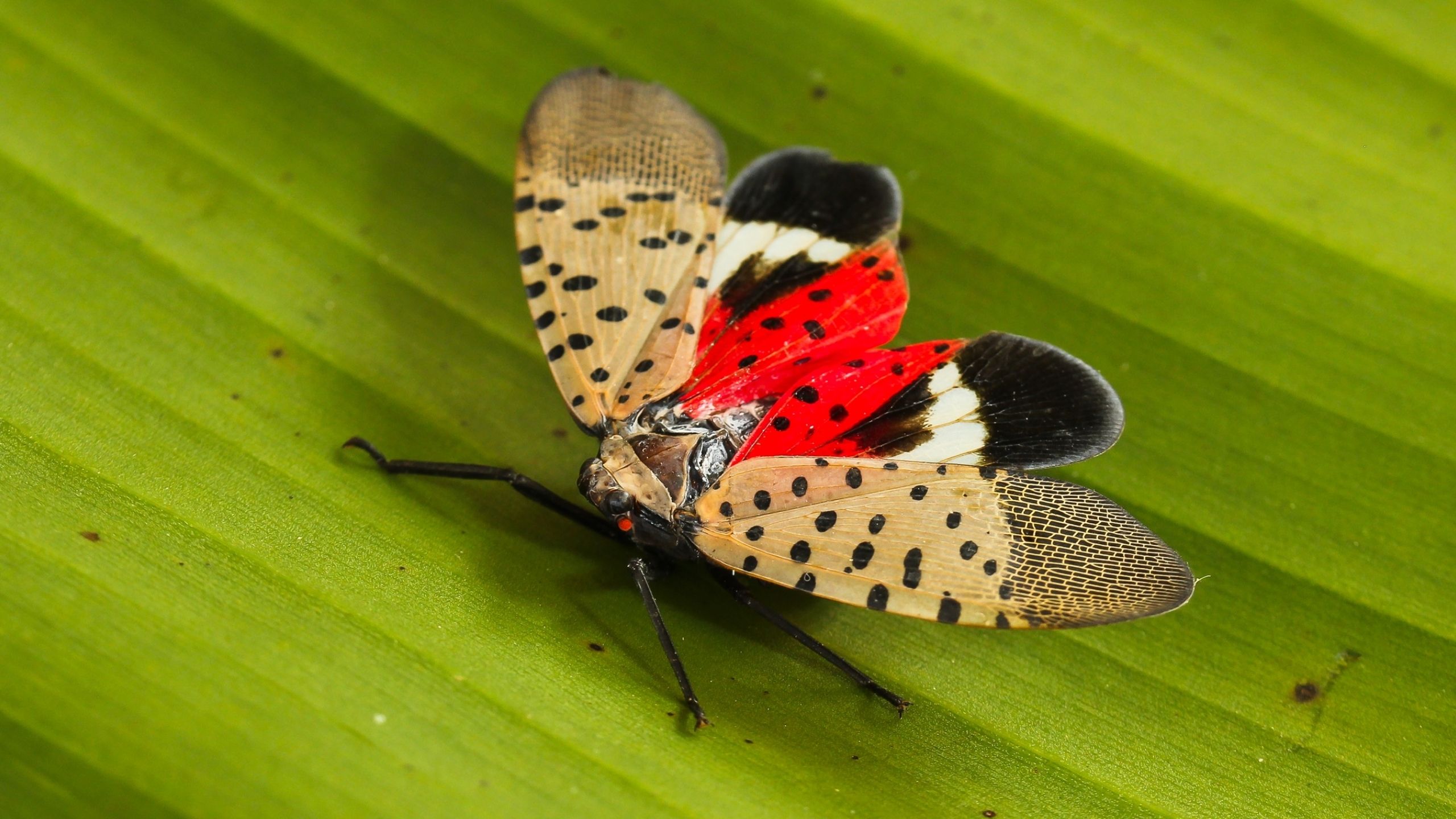
Spotted Lanternfly
Spotted Lanternfly (SLF) is a new invasive pest from China that was first detected in the U.S. in Pennsylvania in 2014. SLF attacks more than 70 host plants, including some fruit and hardwood ornamental trees.
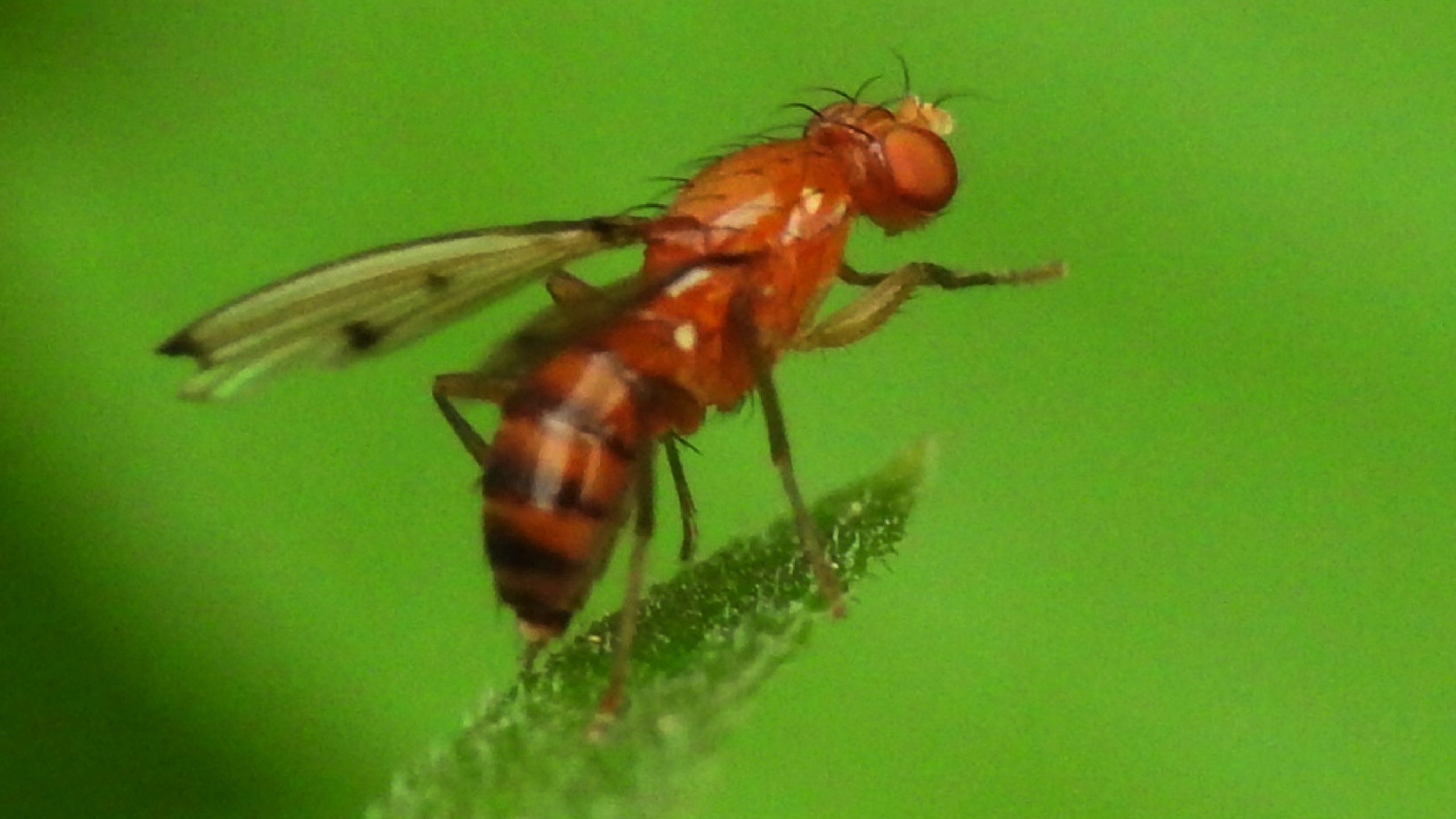
Spotted Wing Drosophila
The spotted wing drosophila (SWD) is an invasive pest from Asia that has been detected in many counties in northern Utah. SWD can be controlled using insecticides common in fruit integrated pest management plants. If SWD is caught in monitoring traps, insecticide applications must be used during the unripe fruit stage to prevent damage.
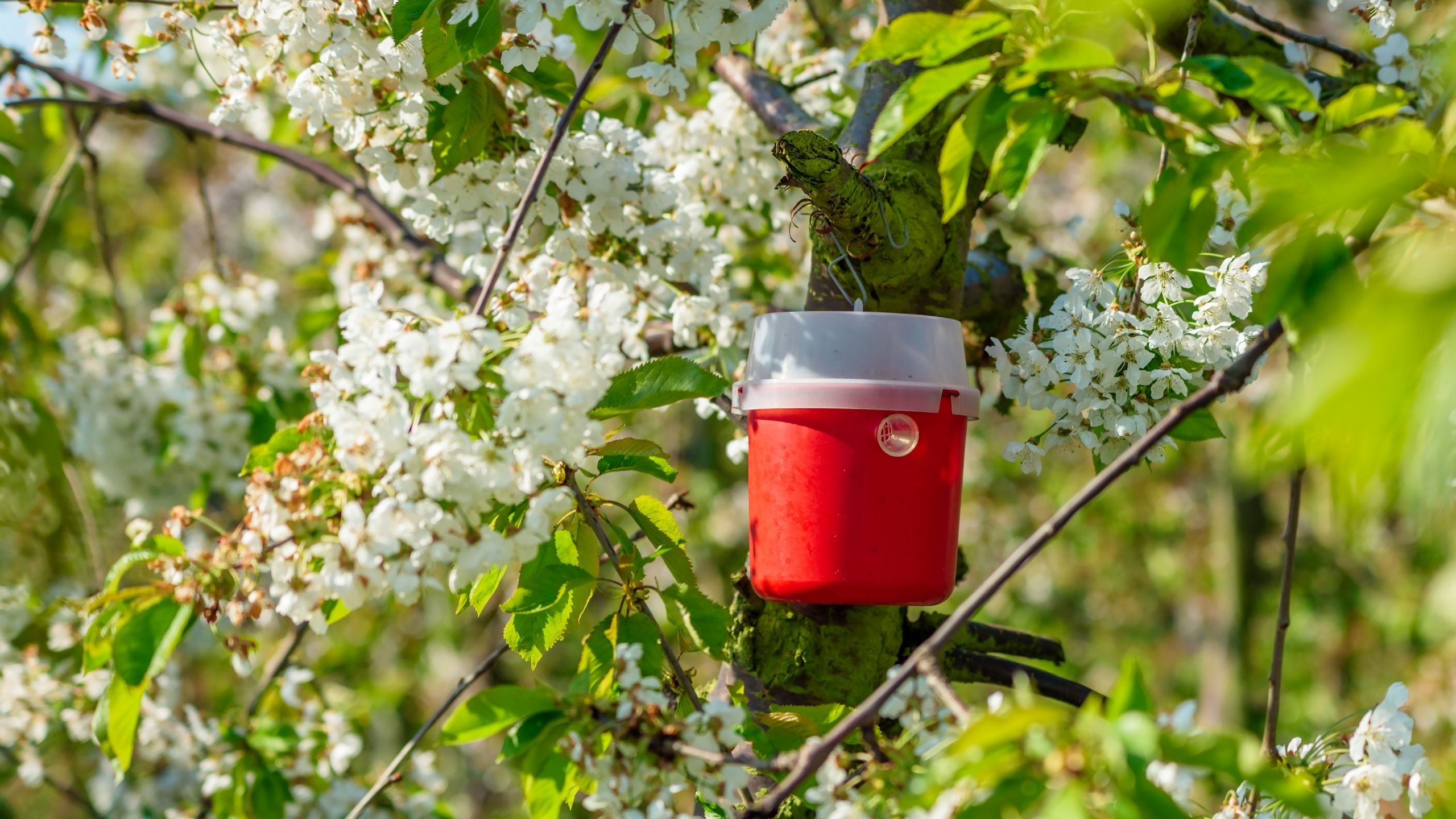
Spotted Wing Drosophila - Monitoring
Monitoring is a crucial first step for managing the invasive spotted wing drosophila (SWD). Methods for monitoring and diagnosing SWD are discussed here. Suspected SWD caught in monitoring traps can be sent to the Utah Plant Pest Diagnostic Lab (UPPDL) for identification before applying an insecticide.
Velvet Longhorned Beetle
The velvet longhorned beetle (VLB) is an invasive wood-boring beetle native to Asia and Russia that was first detected in Utah in 2010. VLB will attack living and dying trees, as well as green and dried wood; it can infest apple, cherry, mulberry, peach, and a number of deciduous and conifer tree species. Fruit yield, tree longevity, and wood marketability can all be negatively impacted by VLB.