Fact Sheets - Tree Fruit Insects
For more tree fruit insect information reference the Intermountain Commercial Tree Fruit Production Guide and Utah Home Orchard Pest Management GuideApple and Pear Insect Control For Homeowners (Codling Moth)
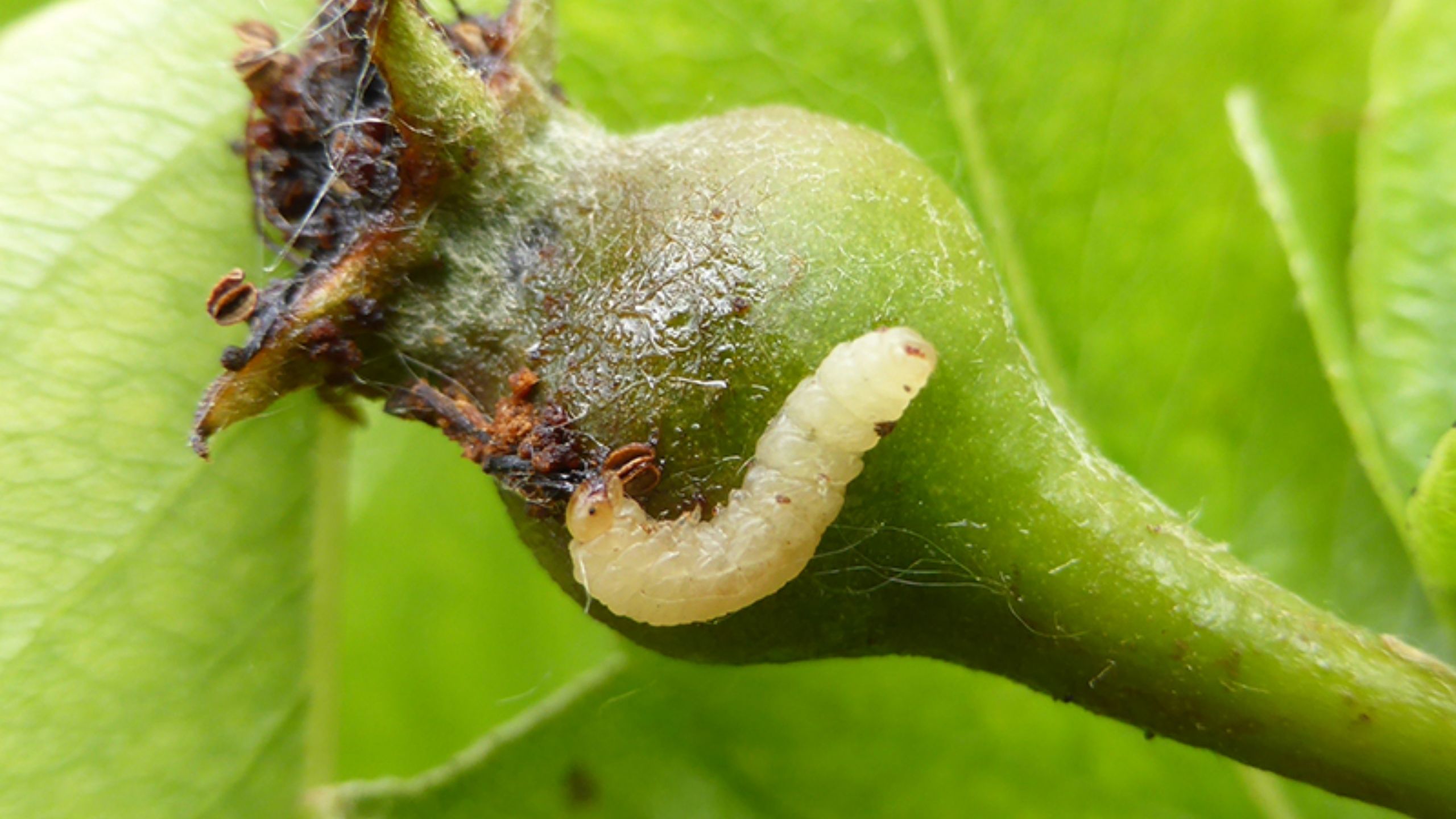
There are few experiences that equal biting into a crisp, flavorful apple; few worse than finding half a worm in the remaining portion. Worms infesting apples and pears are immature larvae of codling moth.
Apple Aphids
Aphids are common, secondary pests of apples, but infestations resulting in economic loss are uncommon, except for woolly apple aphid. Aphids overwinter as eggs on tree limbs, or as nymphs on roots and/or limbs.
Apple Maggot
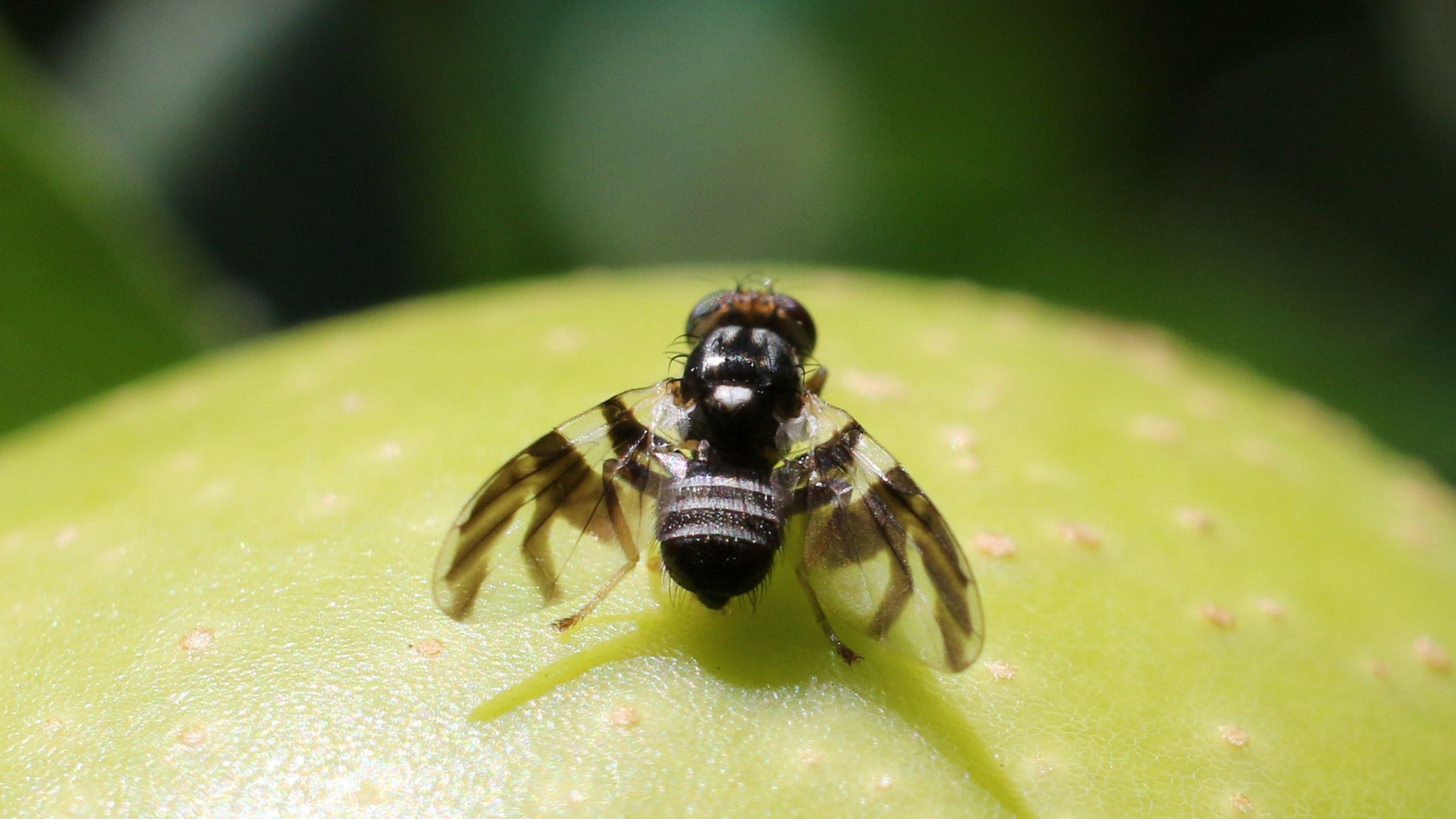

The fruit fly, apple maggot, primarily infests native hawthorn in Utah, but recently has been found in home garden plums. Apple maggot is a quarantine pest; its presence can restrict export markets for commercial fruit.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug
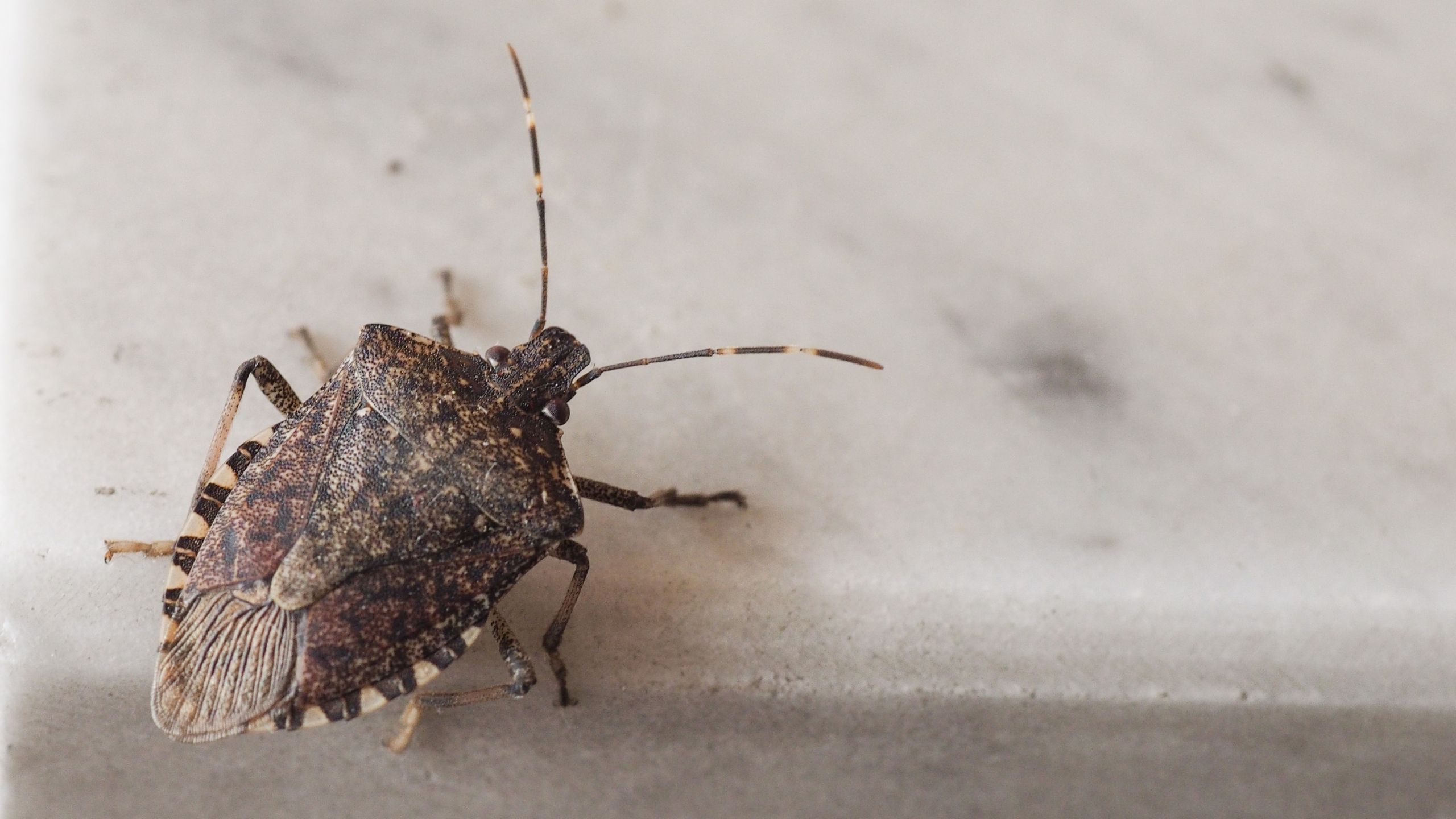

Brown marmorated stink bug feeds on a broad range of plants including fruits, vegetables, field crops, ornamentals, weeds, and native species. Adult- and nymph-feeding causes light-colored stippling and lesions on leaves, necrotic lesions and scars on fruits, and deformed pods and seeds on legumes.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug Management for Fruits And Vegetables

It is important to accurately identify and monitor brown marmorated stink bug and feeding damage before making any treatment. This fact sheet emphasizes identification, monitoring, and management of this pest.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug - Parasitoids

The brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) is an invasive pest that damages fruit, vegetable, and nut crops in the U.S. Parasitoid wasps that sting and kill BMSB eggs are the most promising biological control method. This fact sheet describes some of the parasitoid wasps that have been found in Utah, as well as Trissolcus japonicus, a very effective parasitoid wasp that is native to BMSB’s home range and has been found in the U.S., but has not yet been detected in Utah.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug - Samurai Wasp Parasitoid
Brown marmorated stink bug is an invasive insect that first invaded Utah in 2012. It has since caused urban nuisance problems for northern Utah residents and poses a serious threat to various commerical fruit and vegetable crops. In June 2019, the samurai wasp was discovered in Salt Lake City. This exotic parasitoid wasp is the most promising agent for biological control of BMSB and is uniquely evolved to lay its eggs inside of BMSB eggs.
Bumble Flower Beetle
Bumble flower beetles are common throughout the growing season on flowers, oozing sap, and other sweet, overripe, or fermenting matter. Bumble flower beetles seldom warrant the use of chemicals for control.
Campylomma Bug

A new pest to Utah apples; controls are recommended only if there has been a history of damage. Damaging stage: first generation nymphs feed on developing fruit. Monitor nymphs in the spring from pink through petal fall.
Cankerworms
Both spring and fall cankerworms occur sporadically in Utah, typically on a five to seven year cycle. Larvae feed for six weeks in the spring and cause heavy defoliation in outbreak years.
Cat-facing Insects
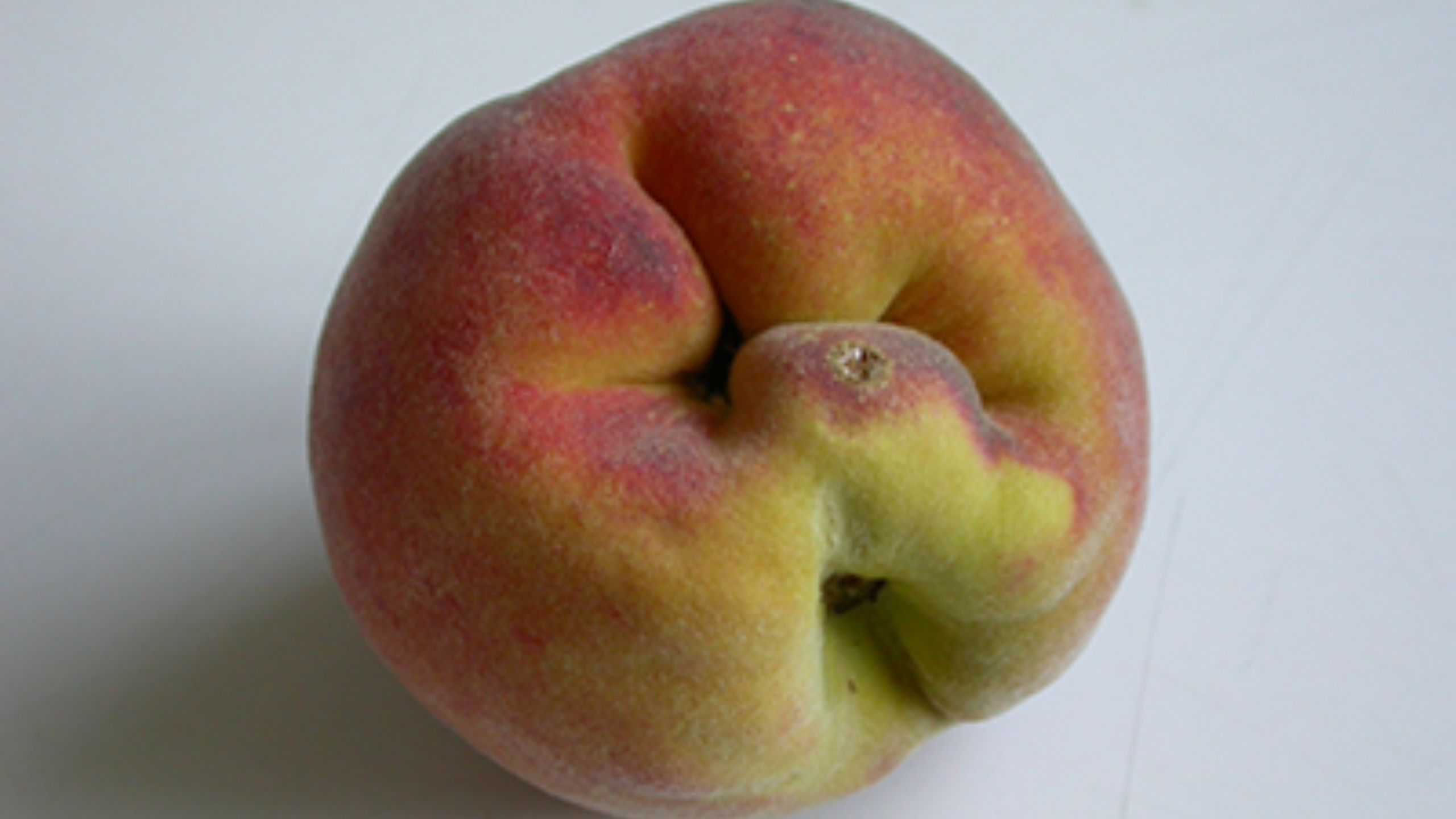

Cat-facing insects are sporadic pests in orchards, but can cause severe fruit injury when populations are high. Cat-facing adults and nymphs feed on the surface of fruit causing unsightly dimpling, deformity, and scarring.
Codling Moth
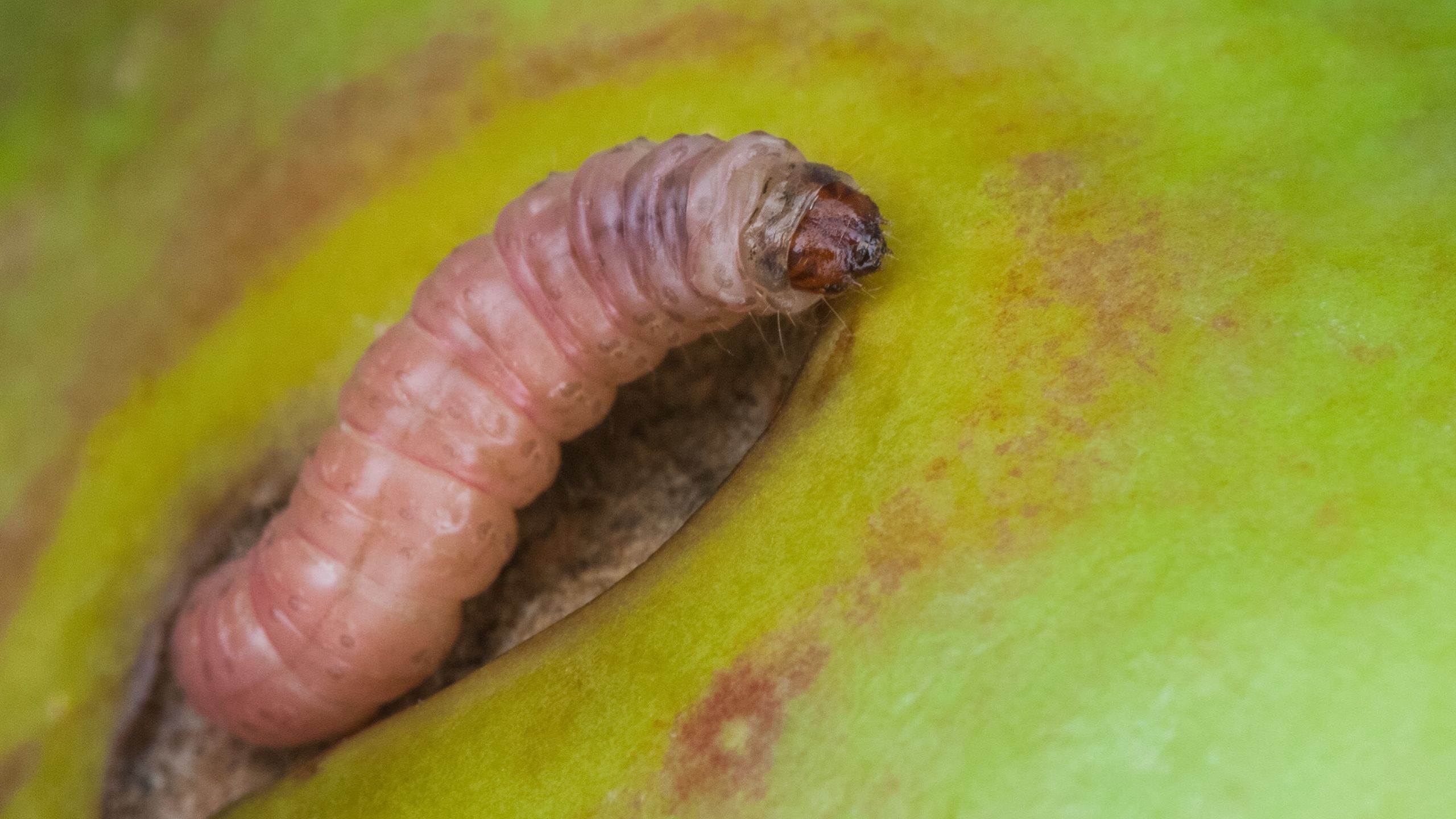

Codling moth is the major pest of apple and pear in Utah. Damaging stage: larva tunnels into fruit. Monitoring stage: adult moth. Use of pheromone traps and the degree-day model (based on daily temperatures) are critical for determining optimal treatment timings.
Codling Moth - An Alternate Biofix-Setting Method

Codling moth, Cydia pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), is the key insect pest of apple, pear, and walnut throughout the world, including Utah (apple and pear).
Codling Moth Mating Disruption
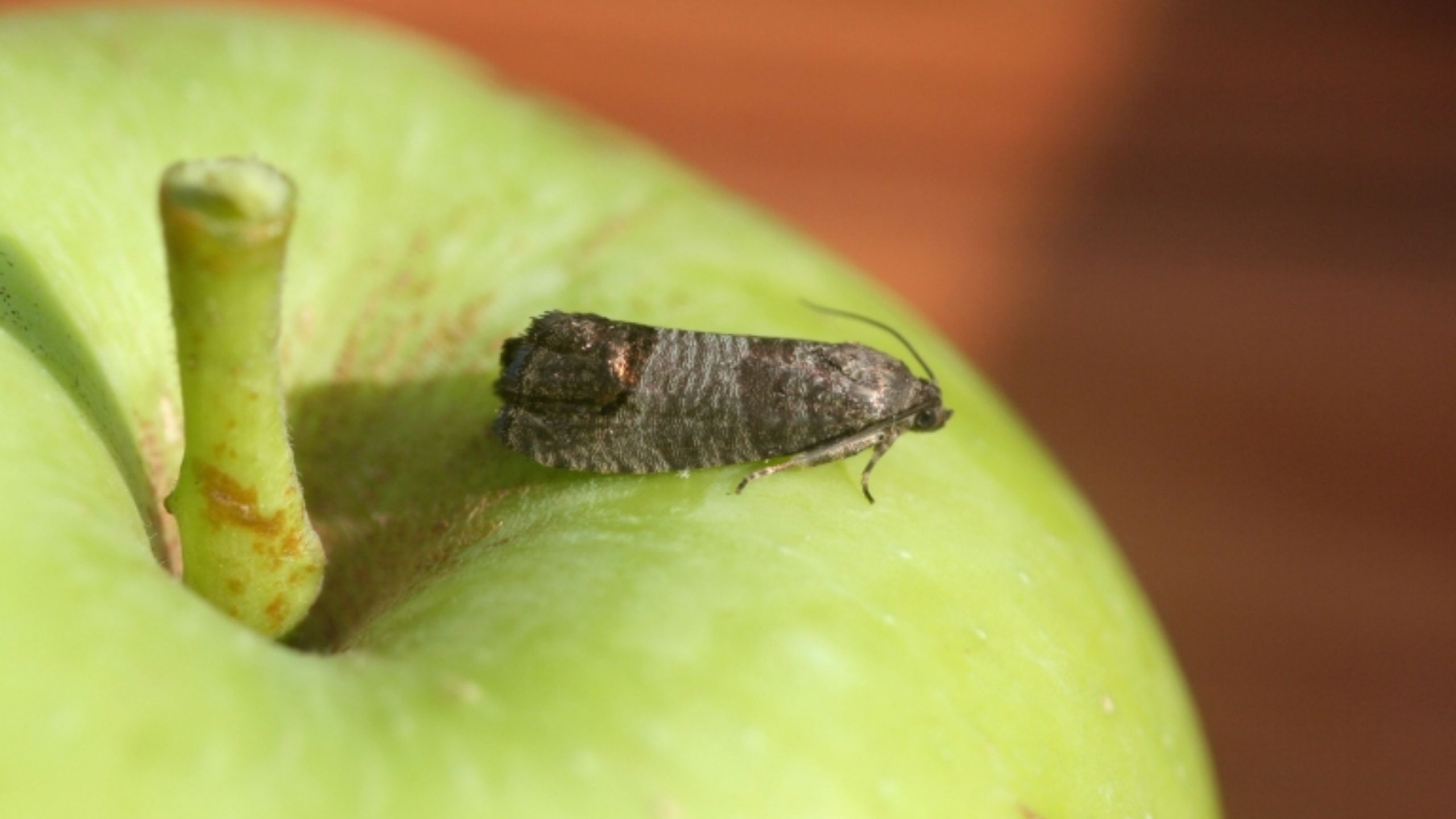

Codling moth is a key pest of apples and pears. Mating disruption does not kill insects; it saturates the orchard with the female moth sex pheromone to delay or prevent mating. At least 10 contiguous acres are required for codling moth mating disruption to be effective.
Common Stink Bugs of Utah
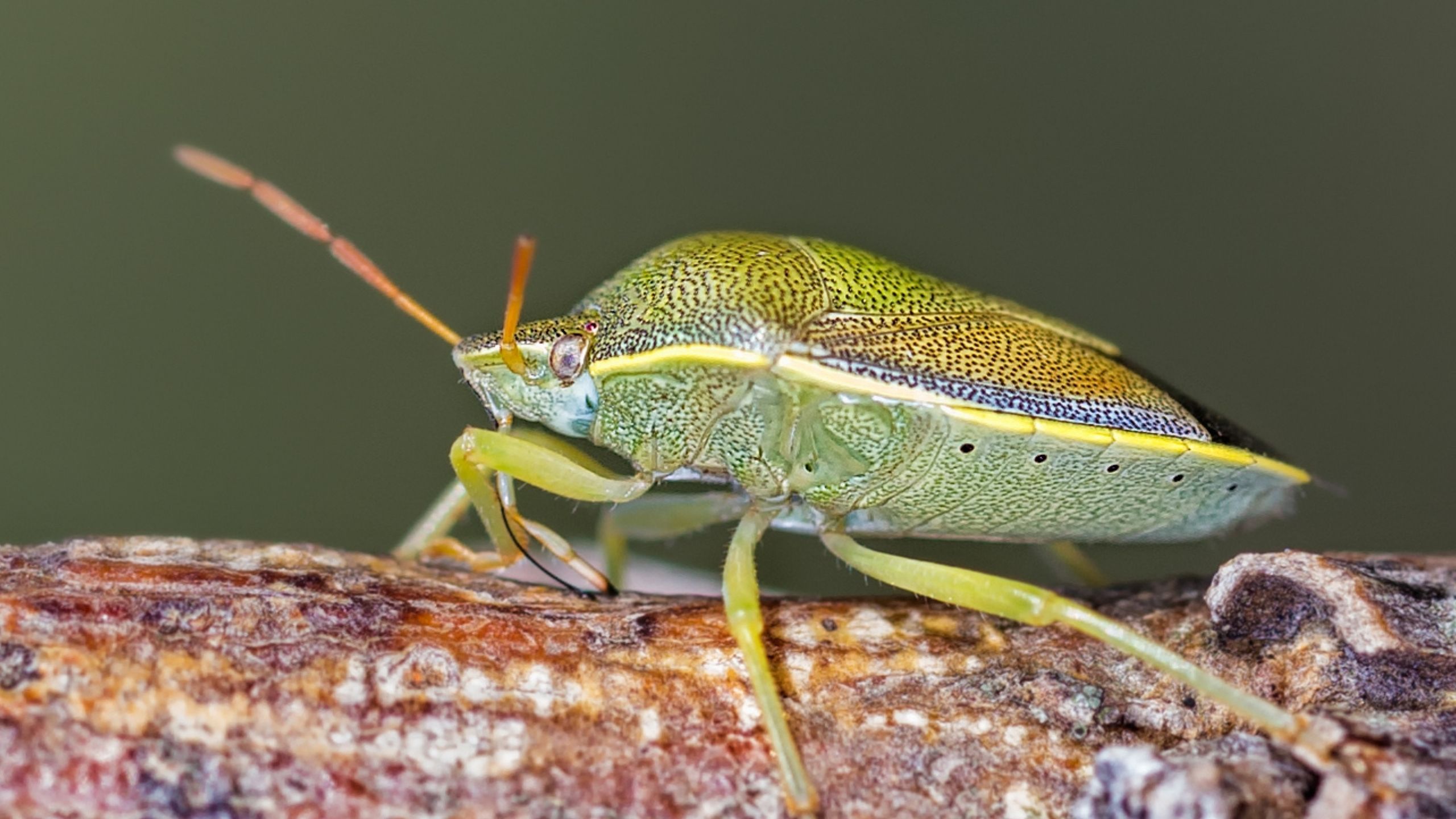

This fact sheet provides descriptions and images of stink bugs, including the adult and immature stages, that are commonly encountered in gardens and farms in Utah.
Eriophyid Mites: Bud, Blister, Gall, and Rust Mites
Eriophyid mites cannot be seen without a 20x hand lens or greater magnification. Eriophyid mites seldom cause serious injury or stress to plants; damage is normally aesthetic.
European Cherry Fruit Fly
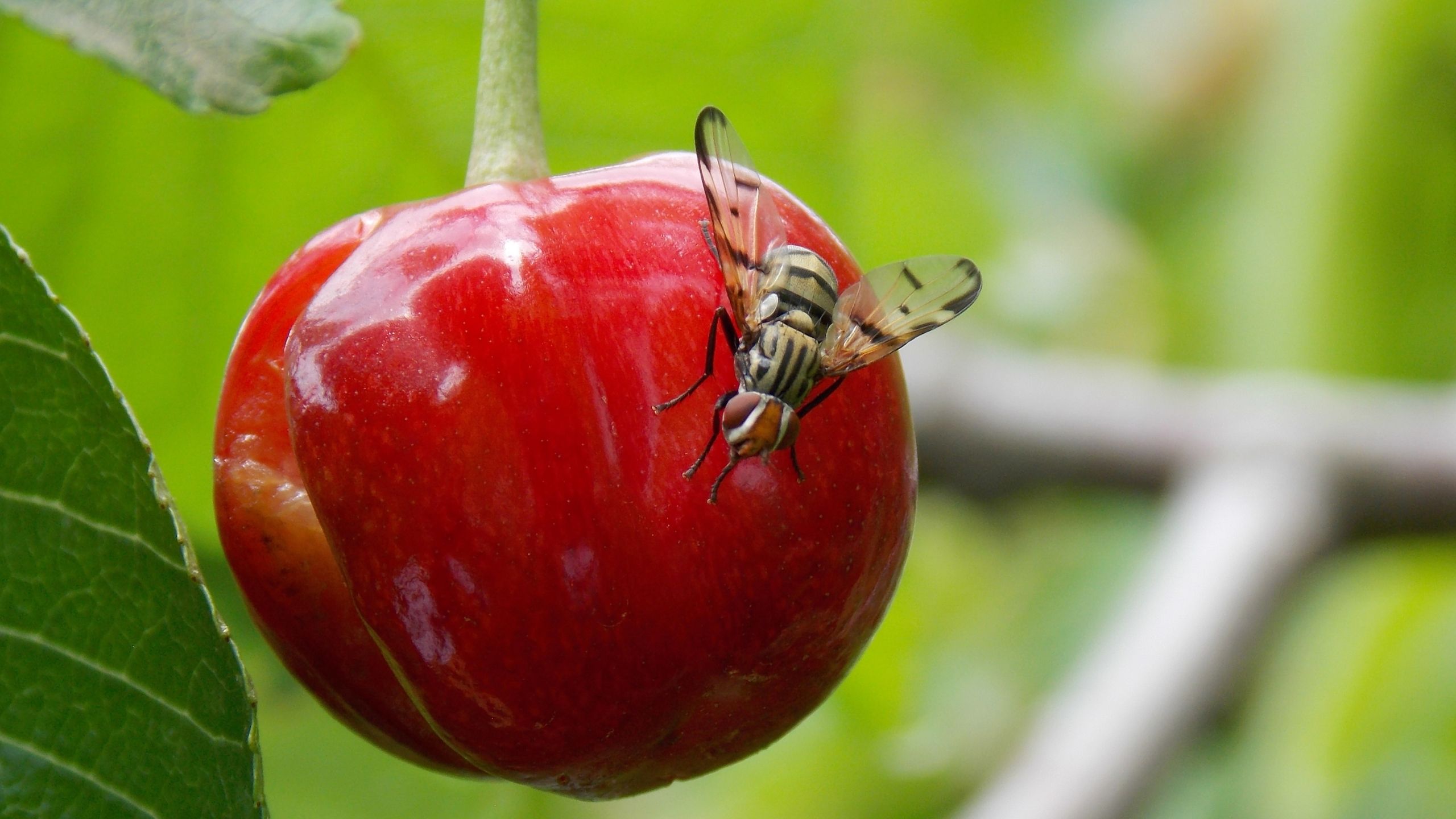

European Cherry Fruit Fly (ECFF) is a new invasive cherry-infesting pest from Europe. It was first detected in the U.S. in New York in 2017. Larvae feed exclusively within fruits, causing them to rot and fall off the tree. In Europe, heavy infestations have resulted in 100% fruit loss. Since adults fly only short distances, spread occurs primarily through movement of infested fruit.
European Earwig
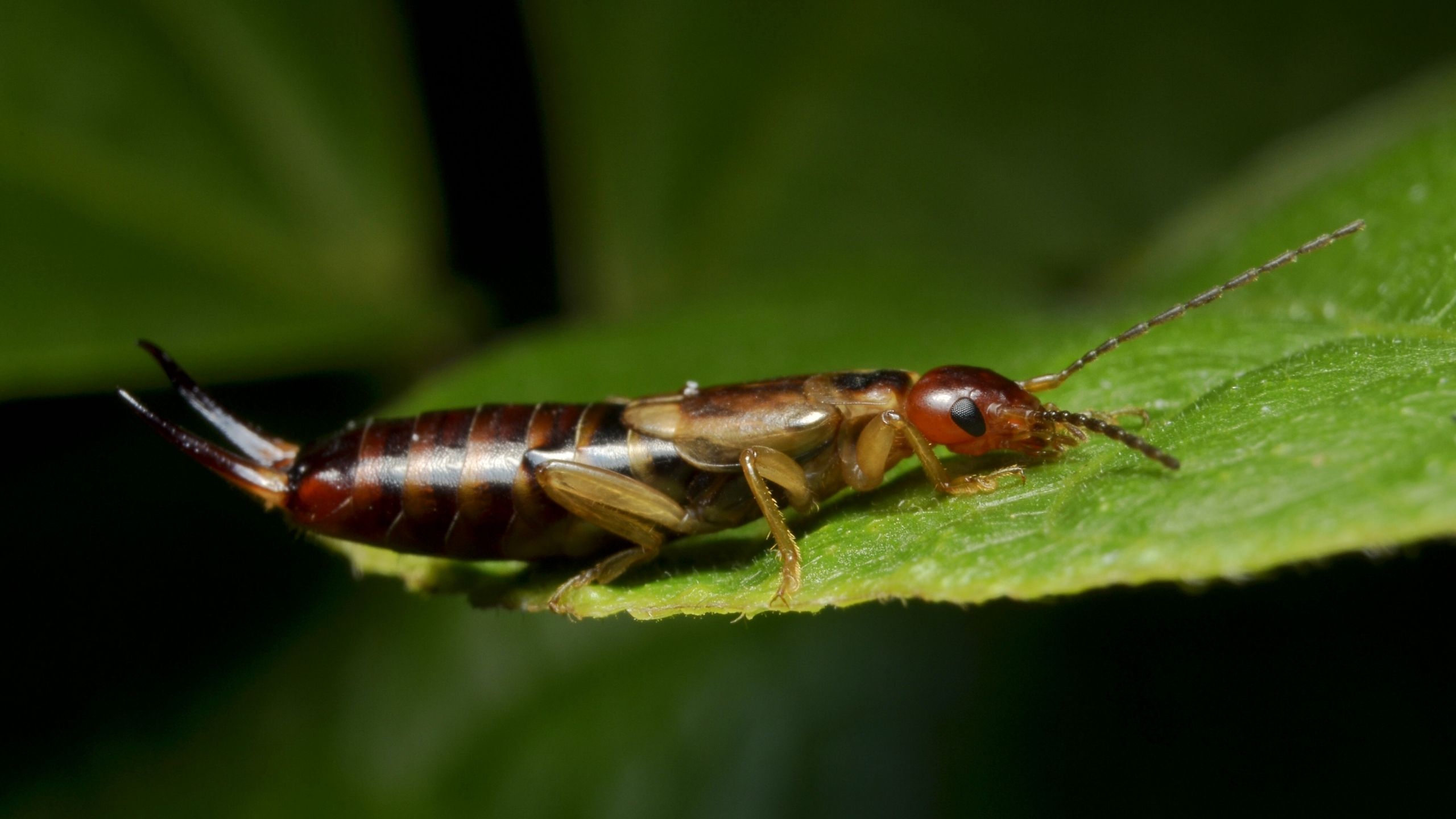

The European earwig is an omnivore; it feeds on detritus, fungi, plants, and insects. Earwigs can injure the buds, leaves, flowers, and fruits of a broad range of plants, including fruits, vegetables, and ornamentals; they can be a nuisance pest by entering buildings.
European Red Mite
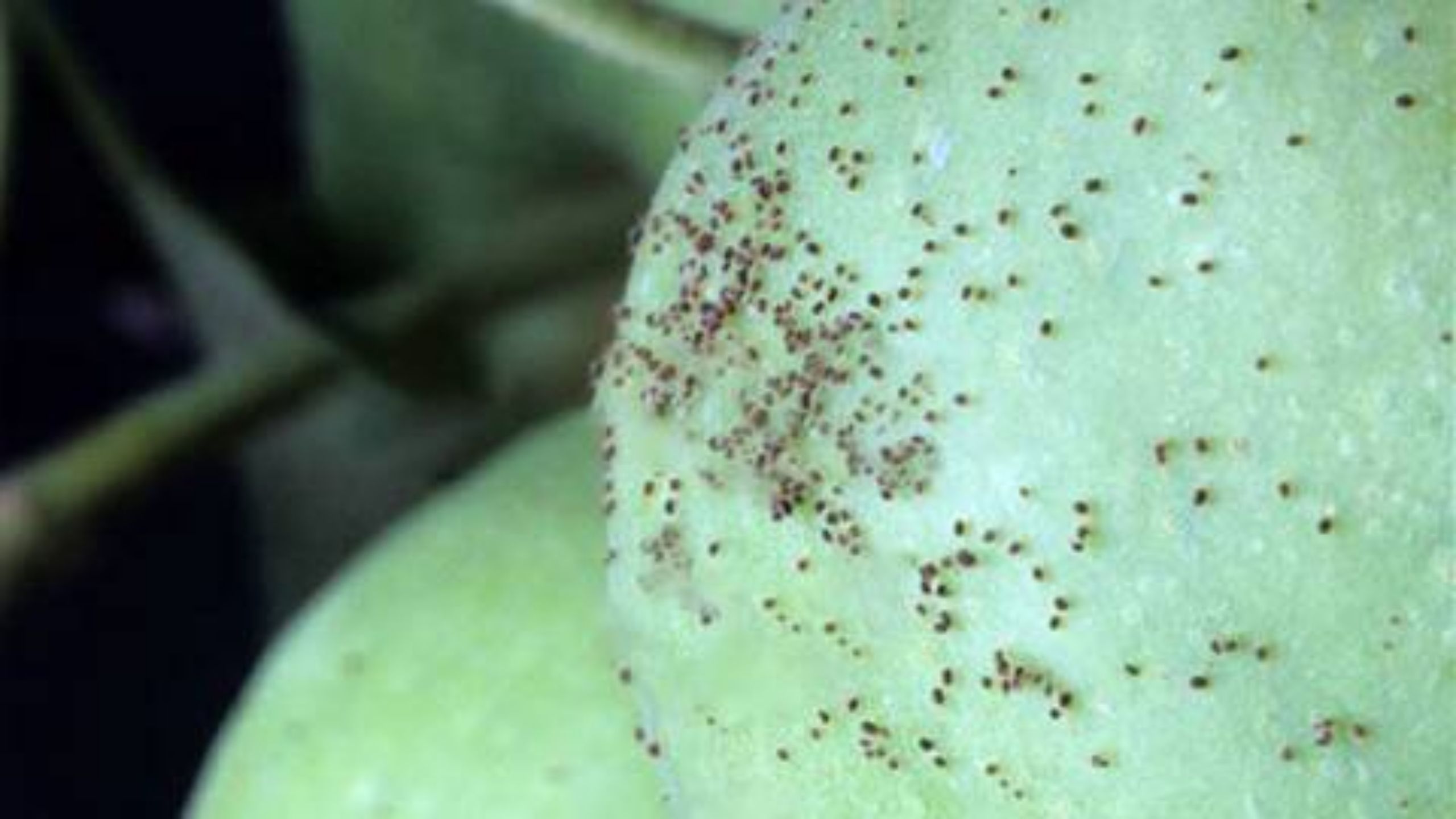

European red mite infestations are sporadic in Utah orchards, but injury can be severe when populations are high. Adult and immature mites feed on leaves causing white stippling, bronzing, and defoliation. Tree vigor and fruit color, size, and production.
Flatheaded Borers (Pacific, Appletree)

Pacific flatheaded and flatheaded appletree borers are two wood-boring pests of many fruit and ornamental trees. The most susceptible trees are drought-stressed, newly planted, or those with trunk or limb wounds.
Greater Peachtree Borer

Greater peachtree borer is an important pest of peach, nectarine, apricot, cherry, and plum. Adults are clearwing moths and larvae are caterpillars that burrow and feed in the cambium beneath the bark near or just below the soil line.
Invasive Insect Look-Alikes
Pest identification is the cornerstone of integrated pest management, but is a skill that can be difficult to master. Mistakes in identification are common, as many insects look and act alike, and/or can cause similar injury.
Japanese Beetle
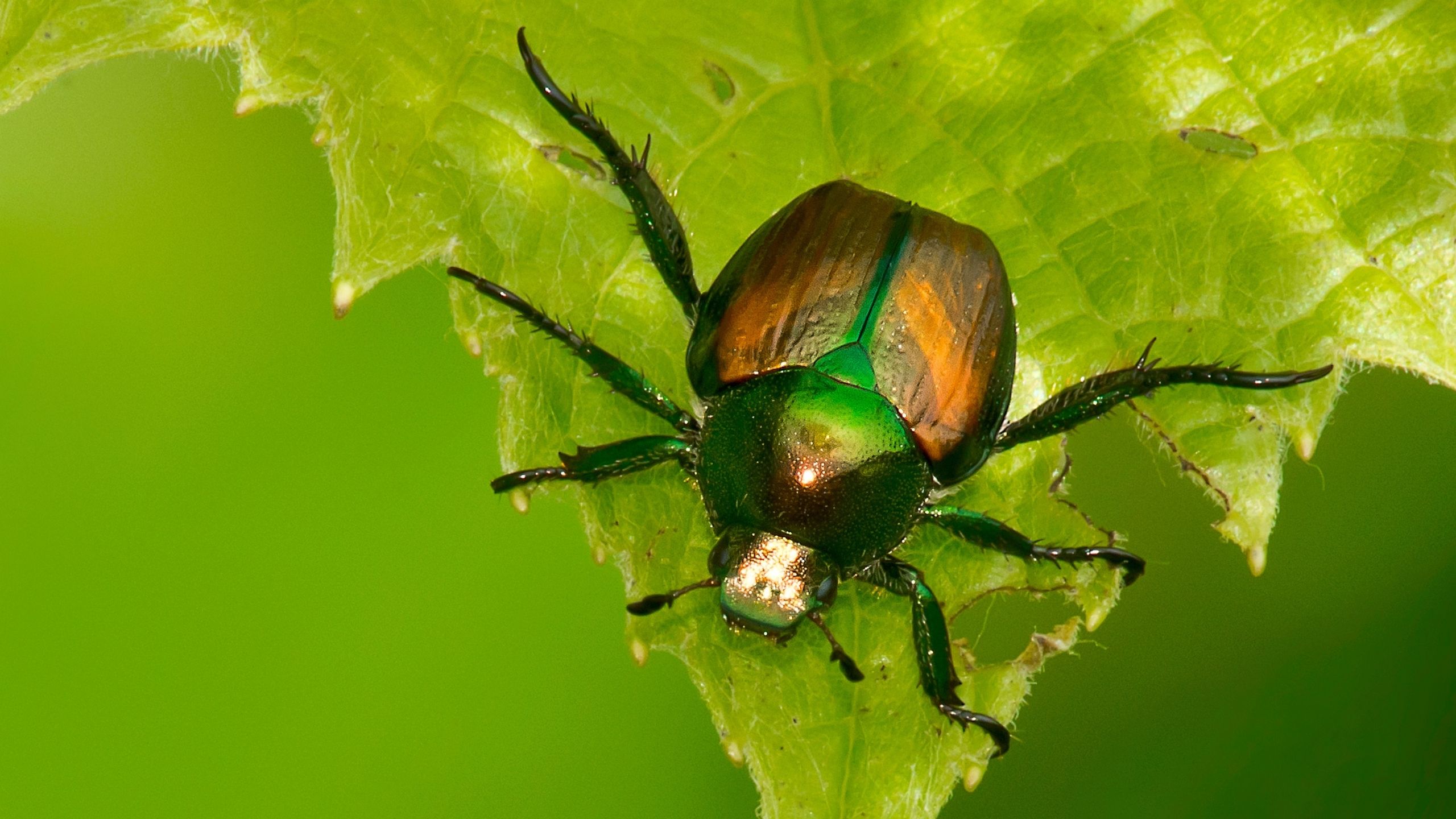

Japanese beetle was initially detected in Orem, Utah, in July 2006. Past eradication efforts were highly successful. However, constant pressure from travel and trade has resulted in a few additional captures in monitoring traps in recent years. Adults have a broad host range of more than 300 plant species and can cause significant damage.
Leafrollers in Fruit Orchards
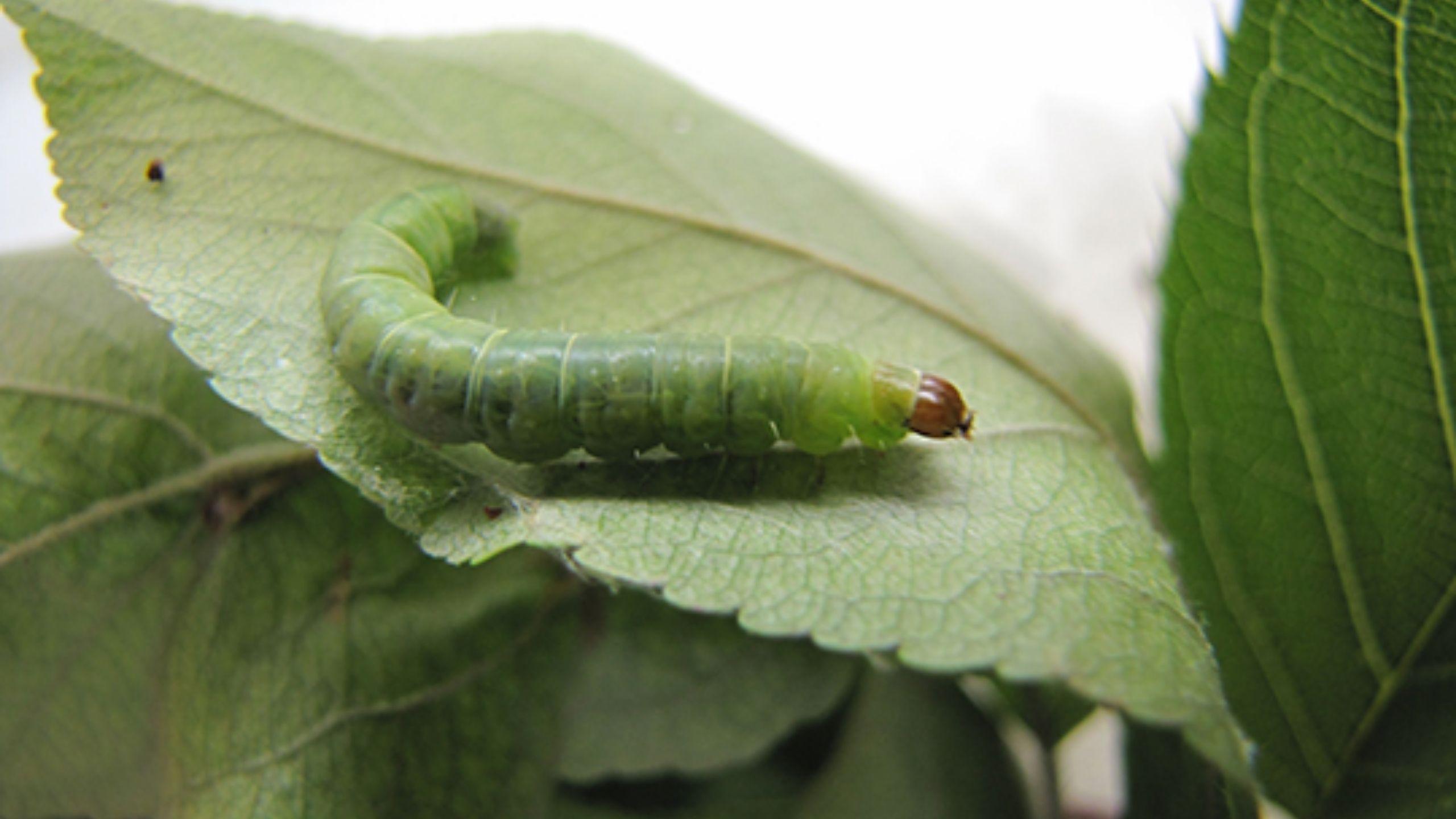

Several species of leafrollers are economically important pests of tree fruits in North America. In Utah, injury to tart cherry crops from leafroller caterpillars prompted a 4 year survey for five species that are known to occur in the western U.S.
Peach Twig Borer
Peach twig borer is a major pest of peach, nectarine and apricot in Utah. There are multiple generations each year. Spring and early summer generations of larvae bore into and kill new shoots while later summer larvae attack fruit, typically entering fruit near the stem end.
Peach Twig Borer Mating Disruption
Peach twig borer is a key pest of peach, nectarine, and apricot. Mating disruption does not kill insects; it saturates the orchard with the female moth sex pheromone to delay or prevent mating.
Pear Fruit Sawfly
Pear fruit sawfly (Hoplocampa brevis) was first identified in Utah in 2015. It is different from another pest of the same name that feeds on foliage--also known as pear slug (Caliroa cerasi)--and feeds exclusively within pear fruitlets in early spring.
Pear Psylla
Pear psylla is an important pest of pear in Utah. Young and adult psylla feed in leaf phloem tissues, producing sticky honeydew. Psylla can cause fruit russetting and stunt trees; psylla shock and transmission of pear decline can kill trees.
Pear Sawfly
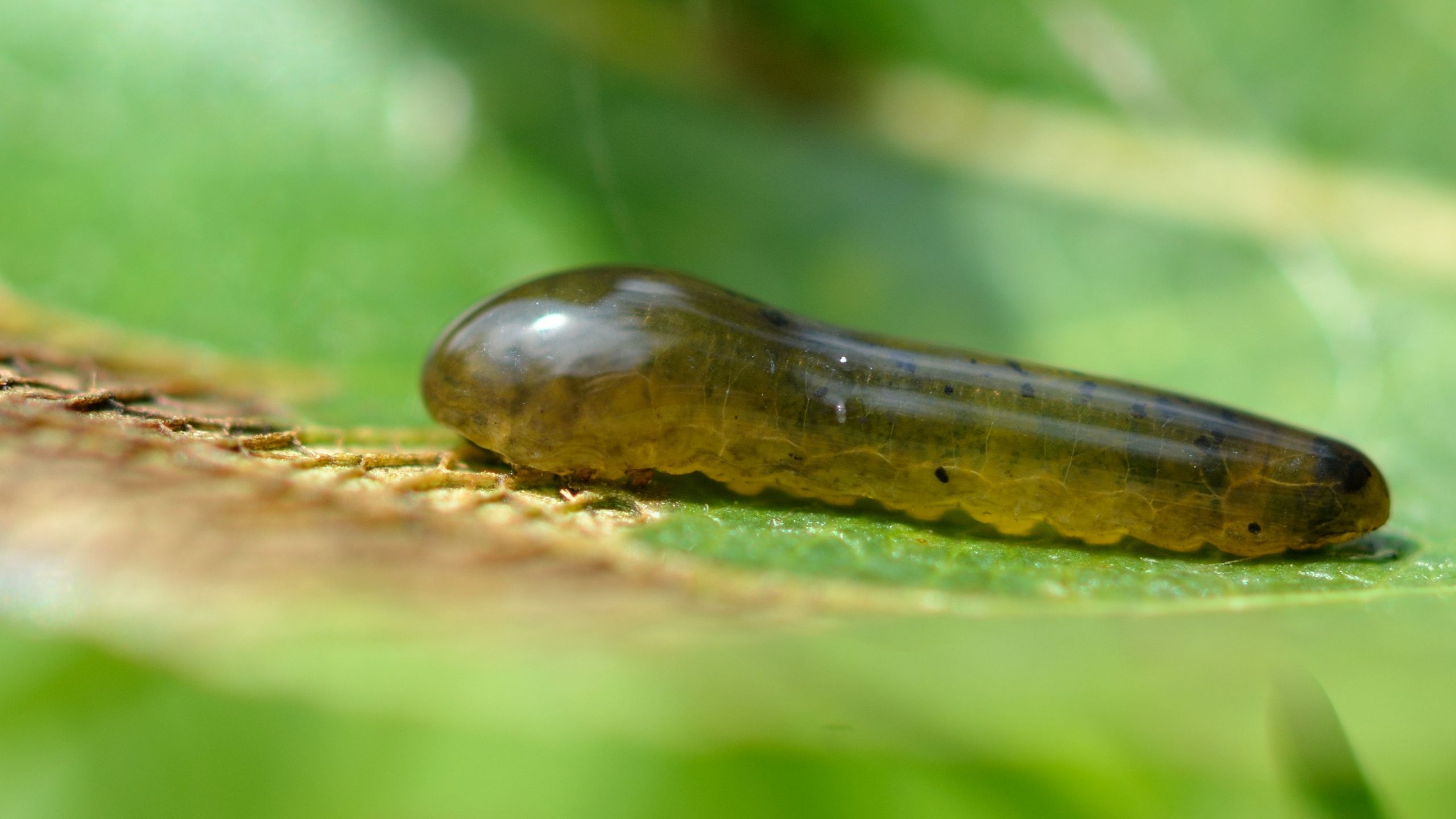

Pear sawfly hosts include pear, cherry, hawthorn, plum, buttonbrush, Juneberry, mountain ash, cotoneaster, and quince. There are 2 generations of pear sawfly each year; second generation larvae cause the majority of the damage.
Plum Curculio
Plum curculio is a small brown weevil (beetle with a snout) native to eastern North America where it is a major pest of pome and stone fruits. Plum curculio was detected in Box Elder County, Utah, in the early 1980s, and this population remains the only known infestation in western North America, where it is occasionally found in residential and wild fruit trees.
Prionus Root Borer

This long-horned beetle is native to western North America and lives for 3 years or more underground, feeding on tree roots. Severe infestations can cause the death of stone fruit trees.
San Jose Scale
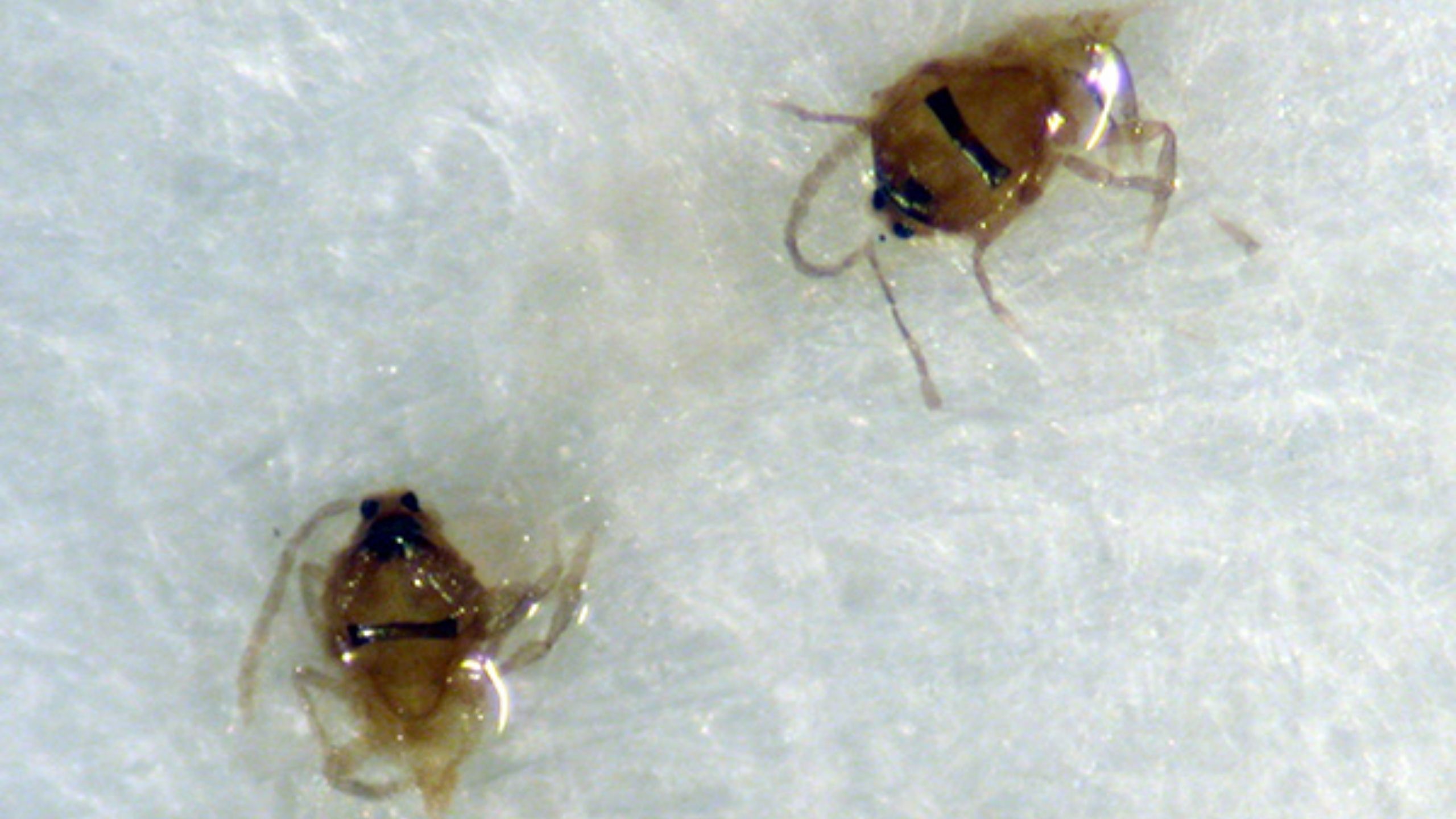

San Jose scale is a sporadic pest in well maintained commercial fruit orchards. Severe infestations can kill limbs, cause deformed and poor colored fruit, reduce yields, and eventually kill trees.
Shothole Borer
Shothole borers can cause damage to ornamental and fruit trees in Utah and adults are present from spring to early fall. Stressed or injured trees are more prone to attack.
Soft Scale in Utah
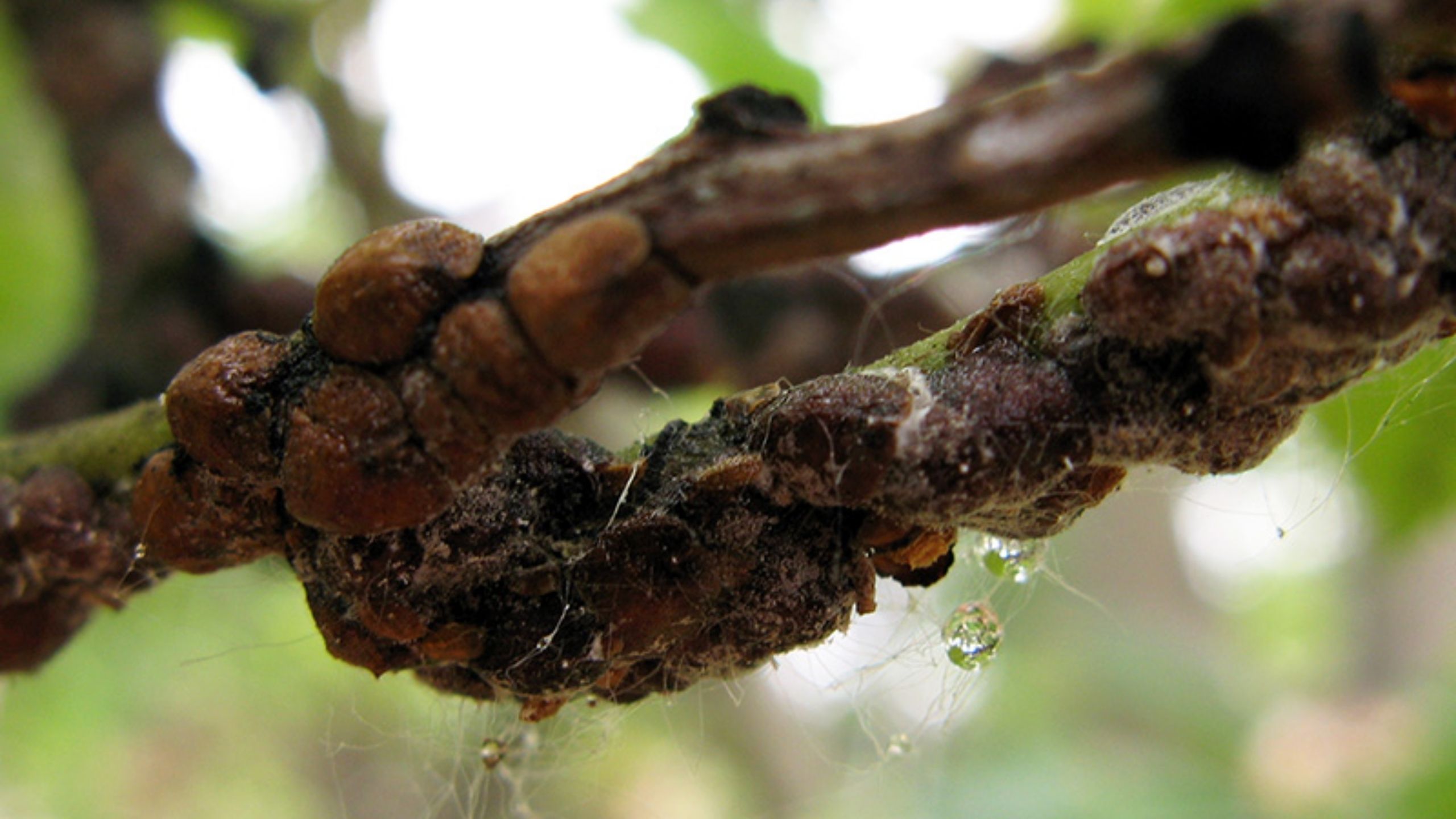

There are more than 1,000 different species of soft scales found throughout the world. Less than 5% are considered serious pests.
Speckled Green Fruitworm
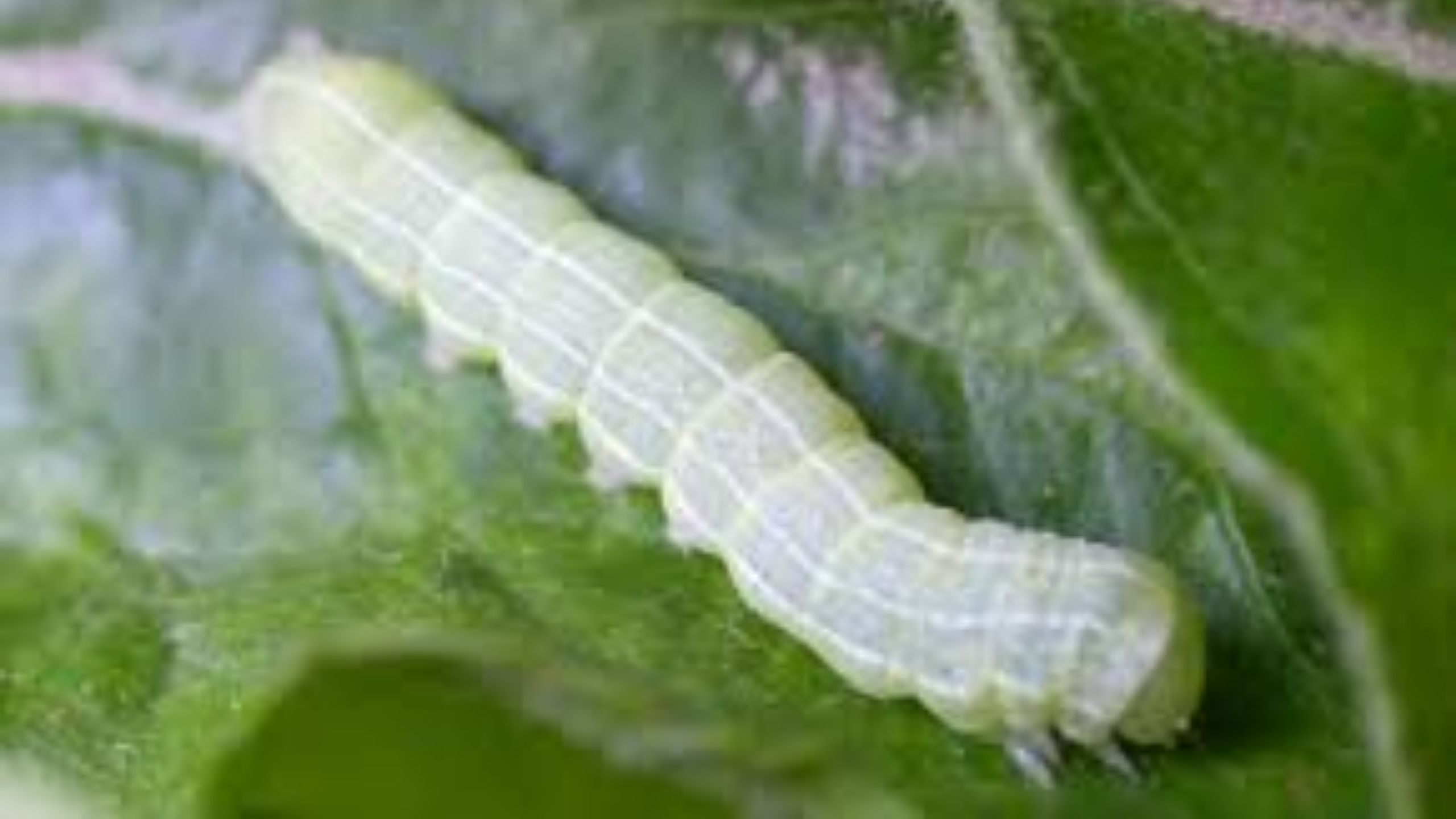

Fruitworms chew holes in fruits and leaves, and can cause localized defoliation of fruit trees. Fruitworms can be monitored with beat-samples (abrupt shaking of tree branches over a tray).
Spongy Moth
Spongy moth is formerly known as European gypsy moth, whose name was changed in 2022 to remove a culturally insensitive term. Spongy moth is among the topmost devastating pests in North America. It has previously been detected and eradicated in Utah.
Spotted Lanternfly
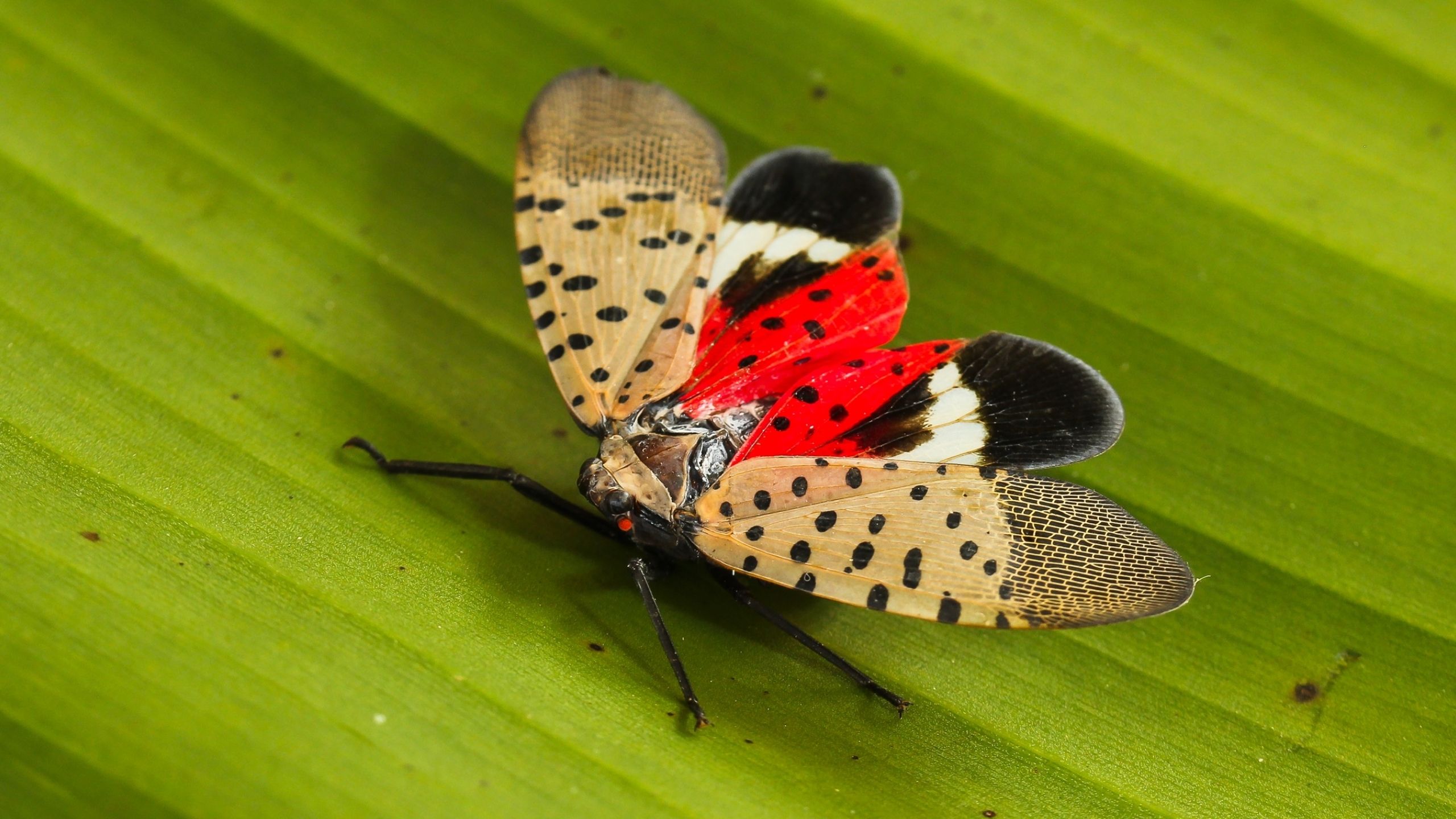

SLF is a new invasive pest from China first detected in the U.S. in Pennsylvania in 2014. SLF attacks more than 70 host plants that include grapes, fruit trees, hops, and hardwood ornamental trees. Extensive feeding by SLF can impact plant vigor and crop yield.
Spotted Wing Drosophila
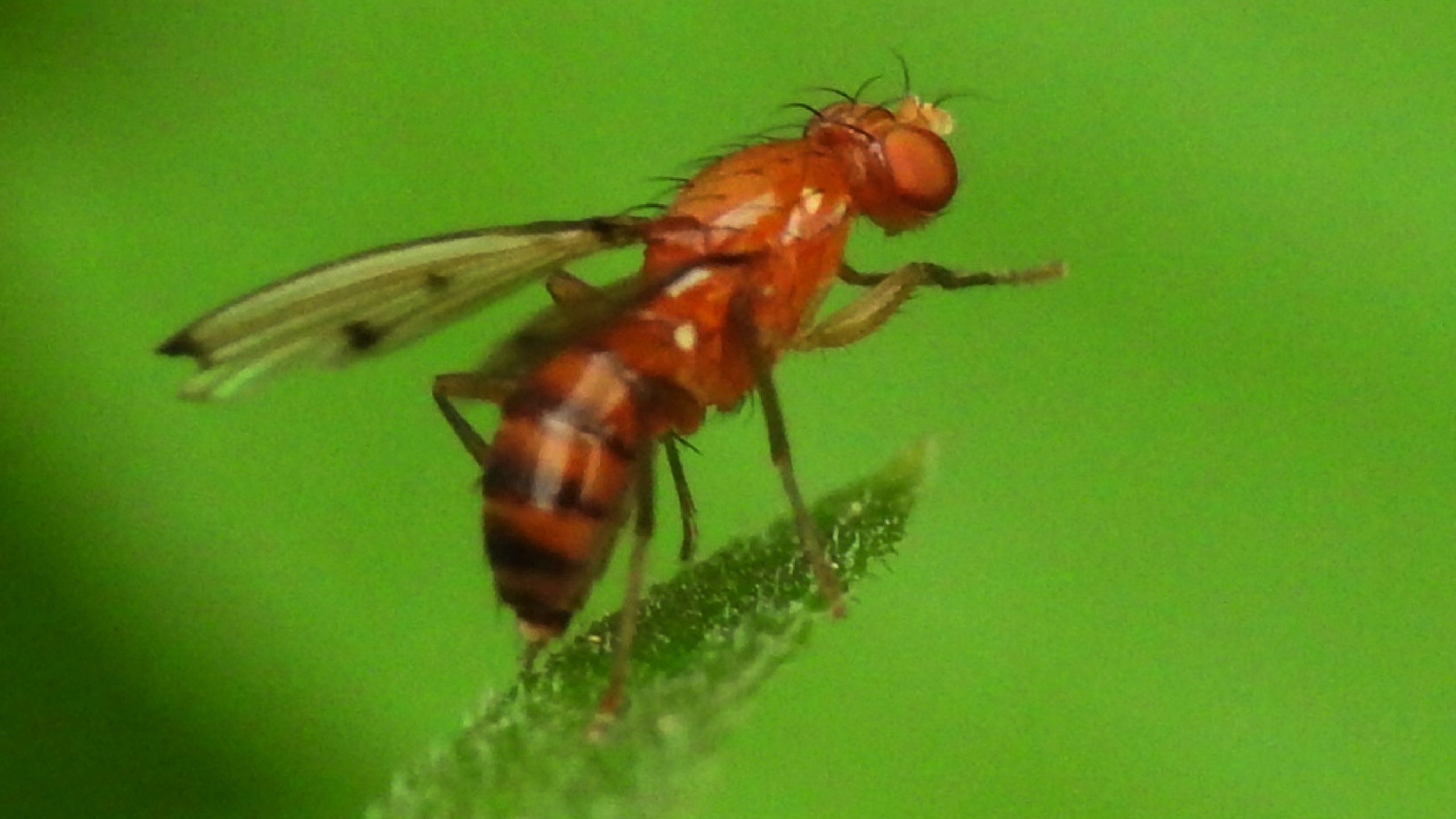

Spotted Wing Drosophila (SWD) is a new Utah pest (first found August, 2010) that can infest un-ripened (pre-harvest), ripe, over-ripe, and spoiled fruits. SWD attacks a broad range of fruits, including tree fruits, berry fruits, and vegetable fruits.
The Backyard Orchard - Apple Pests

A short summary of the main pests of apples and how they are managed by the backyard fruit grower.
The Backyard Orchard - Apricot Pests

A short summary of the main pests of apricots and how they are managed by the backyard fruit grower.
The Backyard Orchard - Cherry Pests

A short summary of the main pests of cherries and how they are managed by the backyard fruit grower.
The Backyard Orchard - Peach and Nectarine Pests

A short summary of the main pests of peaches and nectarines and how they are managed by the backyard fruit grower.
The Backyard Orchard - Pear Pests

A short summary of the main pests of pears and how they are managed by the backyard fruit grower.
The Backyard Orchard - Plum Pests

A short summary of the main pests of plums and how they are managed by the backyard fruit grower.
Velvet Longhorned Beetle
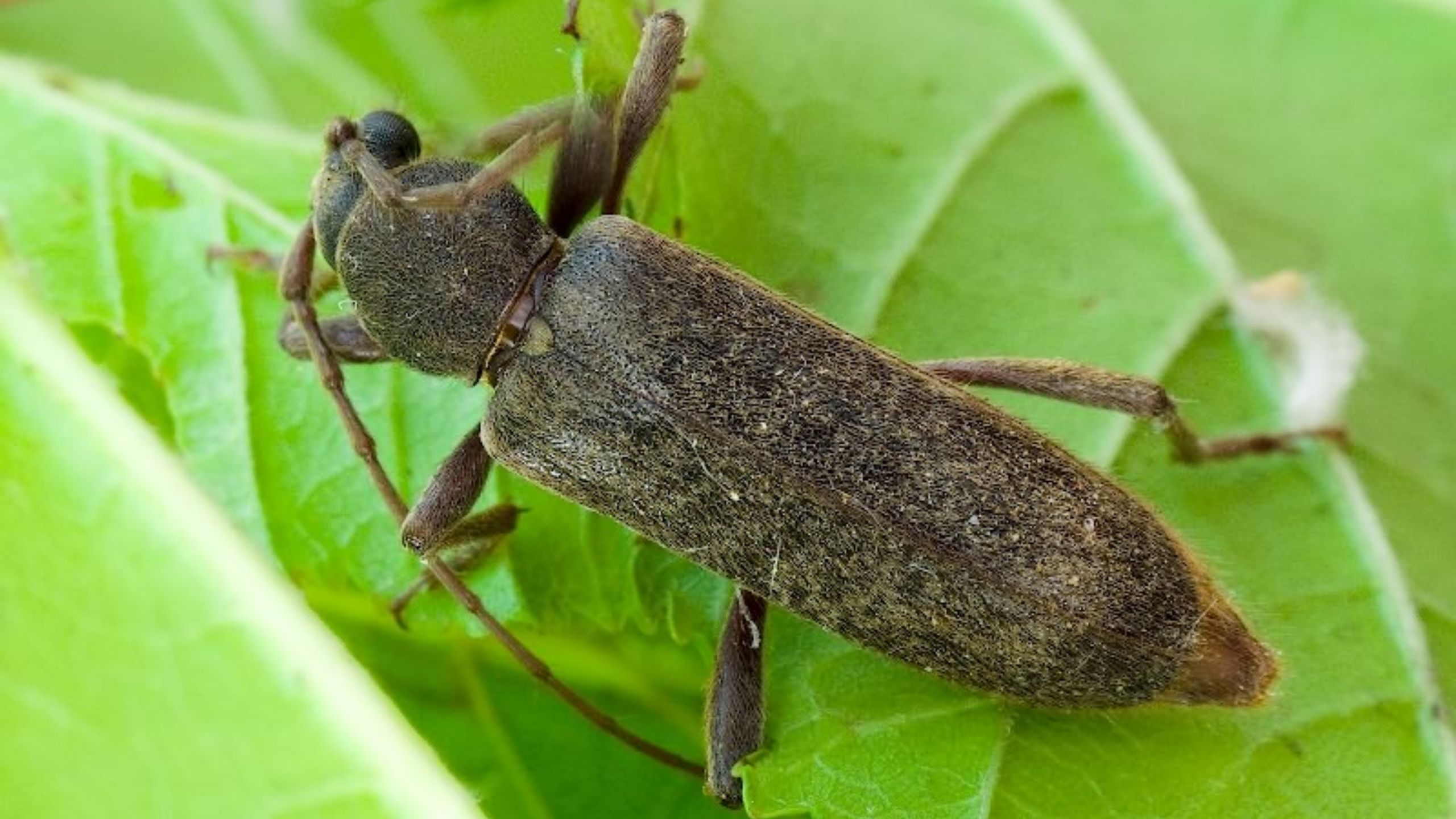

Velvet Longhorned Beetle (VLB) is an invasive wood-boring beetle that is native to Asia and Russia. It was first detected in Utah in 2010. VLB will attack living and dying trees, as well as green and dried wood; it can infest apple, cherry, mulberry, peach, and a number of deciduous and conifer tree species. Fruit yield, tree longevity, and wood marketability can all be negativly impacted by VLB.
Walnut Husk Fly

Walnut husk fly infests black and English walnuts, and late-maturing apricot and peach fruits when infested walnuts are nearby. Damage is caused by egg-laying punctures and larvae developing inside husks and fruits.
Web Spinning Spider Mites
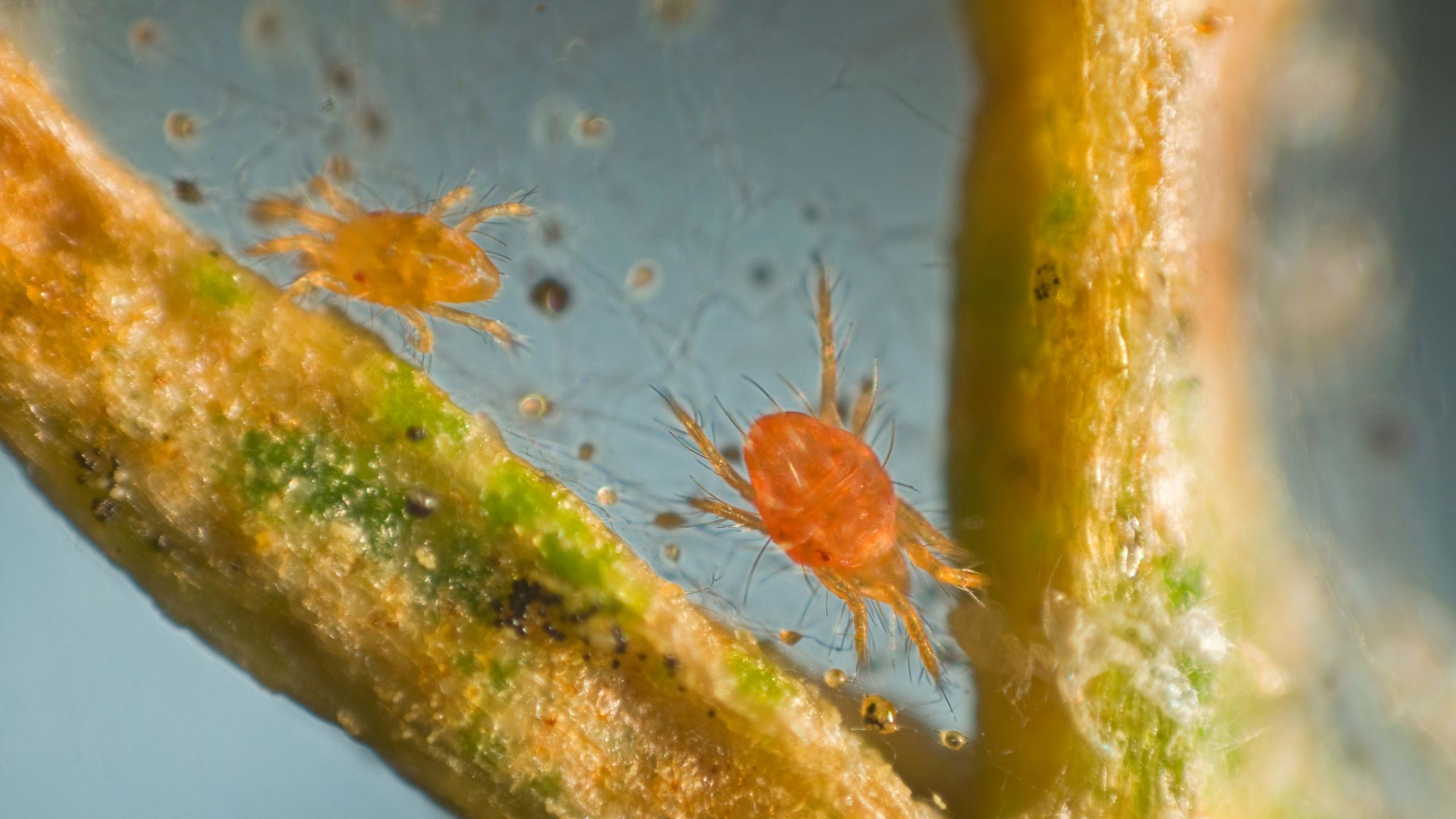

Mites are small arthropods that are more closely related to spiders and ticks than to insects. Mites in this group are web spinners, hence the name “spider” mites.
Western Cherry Fruit Fly
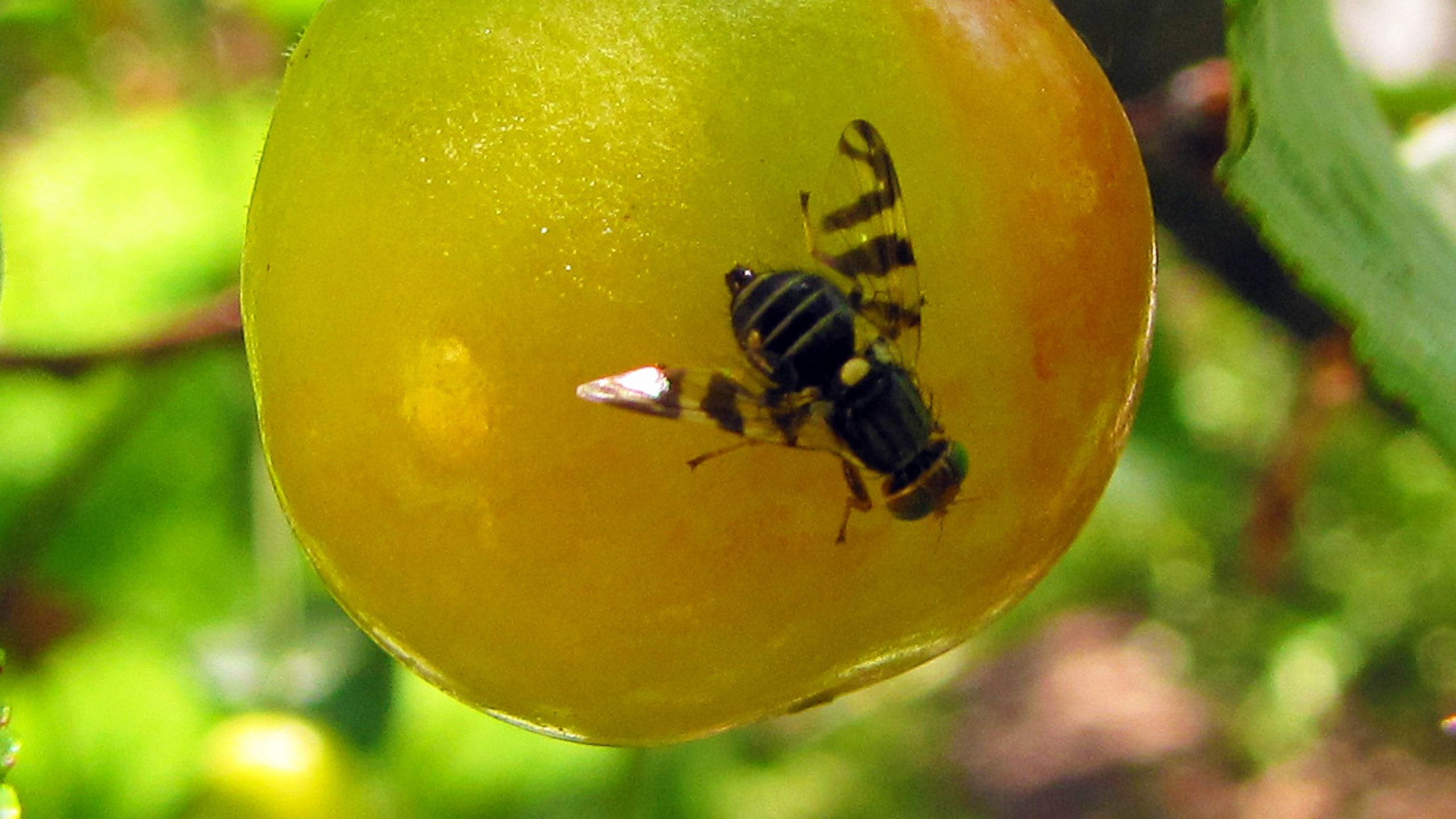

Western cherry fruit fly is the primary insect pest of sweet and tart cherries in Utah. Damage occurs from the larva developing inside fruit. Females lay eggs under the skin of fruit, so target adult flies for control.
Western Flower Thrips
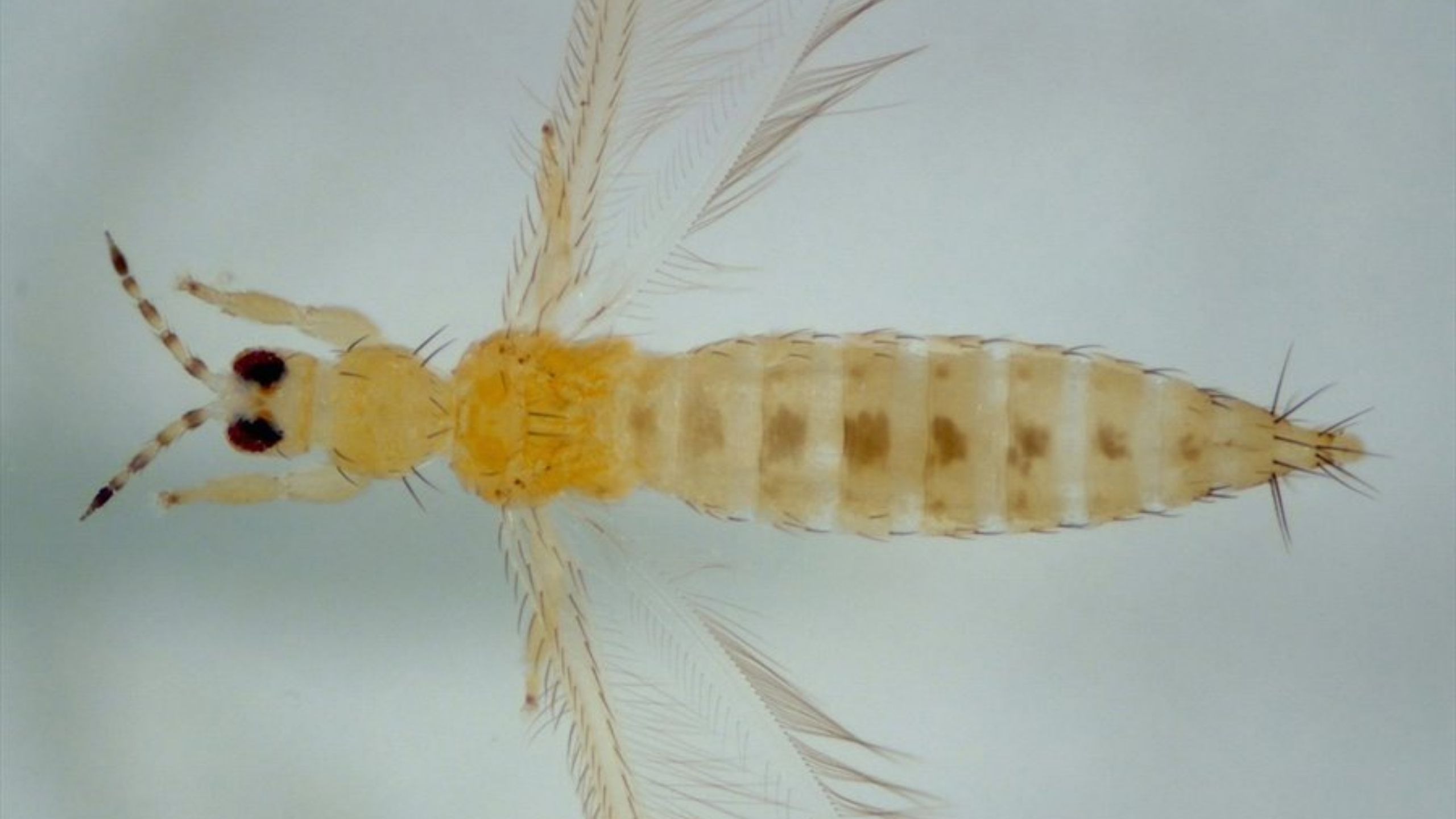

Western flower thrips (WFT) are a frequent pest of nectarine, and an occasional pest of apple and other fruits in Utah. WFT can be abundant on numerous weed and crop hosts.
Western Tentiform Leafminer
Western tentiform leafminer is an indirect pest that mines the leaves of apple and cherry. It can diminish the photosynthetic capability of trees and reduce fruit size and quality. Leafminer populations can fluctuate dramatically within and between years.
White Apple Leafhopper
White apple leafhopper is an indirect pest with two generations per year. Decision for control should be based on economic justifications as well as orchard and other pest considerations.























