Integrated Pest Management
Japanese Beetle
Popillia japonica
Pest Description
- adults: 1/2 inch long; metallic green head and thorax; bronze wing covers; five white hair tufts along each side of the abdomen with an additional pair on the last segment
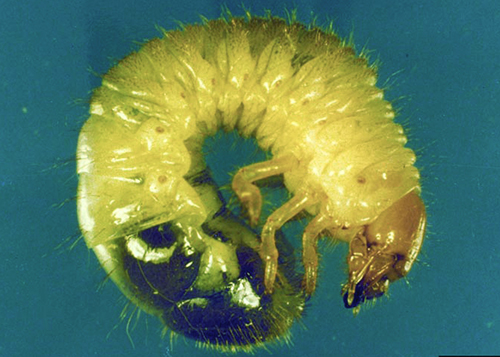
- larvae: 1/8 – 1 inch long; c-shaped; cream colored with a grayish rear end; yellow-brown head with three pairs of legs
Host Plants, Diet & Damage
- more than 300 plant species of ornamentals, trees, shrubs, turfgrass and vegetables
- adults prefer leaves, flowers, fruit, and sometimes stems of rose, maple, elm, birch, linden, apple and stone fruits
- larvae prefer feeding on roots of turfgrasses, young ornamental trees and shrubs
- adults have chewing mouthparts, leaving skeletonized leaves, and chew holes in flower buds, fruits and stems
- larvae chew on roots, leaving turf yellow and brown
Biology, Life Cycle & Damaging Life Stage
- overwinter as late-stage larvae in the soil
- pupate in the spring
- adults emerge late spring into summer
- females deposit eggs in soil around larval host plants
- one generation per year
- adult and larval stages are damaging
IPM Recommendations
- Japanese beetles are invasive pests and are not established in Utah. Report sightings of this insect the Utah Plant Pest Diagnostic Lab or the Utah Department of Agriculture and Food.
- Maintain healthy plants through proper cultural practices.
- Apply a preventive insecticide (anthranilic diamide; neonicotinoid) to suppress populations.