Integrated Pest Management
Sequoia Pitch Moth
 Sequoia pitch moth adult (Left) and larvae (Right)
Sequoia pitch moth adult (Left) and larvae (Right)
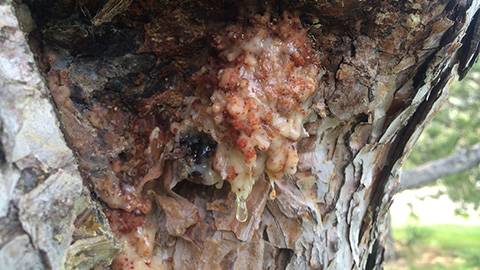 Sequoia pitch moth damage
Sequoia pitch moth damage
HOSTS
- Ornamental Pines
DESCRIPTION
Adult moths are daytime flying moths, but are seldom seen. Adults are black with yellow banding, and are about ¾” long. Sequoia pitch moth adults closely resemble paper wasps, yellowjackets, or other clearwing moth adults.
BIOLOGY
SPM takes 2 years to grow from an egg to an adult. SPM overwinters as larvae under the bark or in resin masses. Larvae will become active again in the late winter and early spring before pupating. SPM will spend about one month in the pupal stage prior to adult emergence.
SYMPTOMS
- Large resin masses on bark
GENERAL MANAGEMENT
Because SPM is mostly an aesthetic problem, control is usually unnecessary. When resin masses become numerous and unsightly, or if the moths are heavily attacking young trees (<20 feet), control may be warranted. The primary control methods for SPM are nonchemical.
INSECTICIDES
The primary control methods for SPM are nonchemical.
For Utah, the current recommendation is to target crawlers with a residual insecticide, horticultural oil, or soap in summer and/or fall. Specific timing of application to infested trees will depend on temperature, elevation, and location.

