White Mold
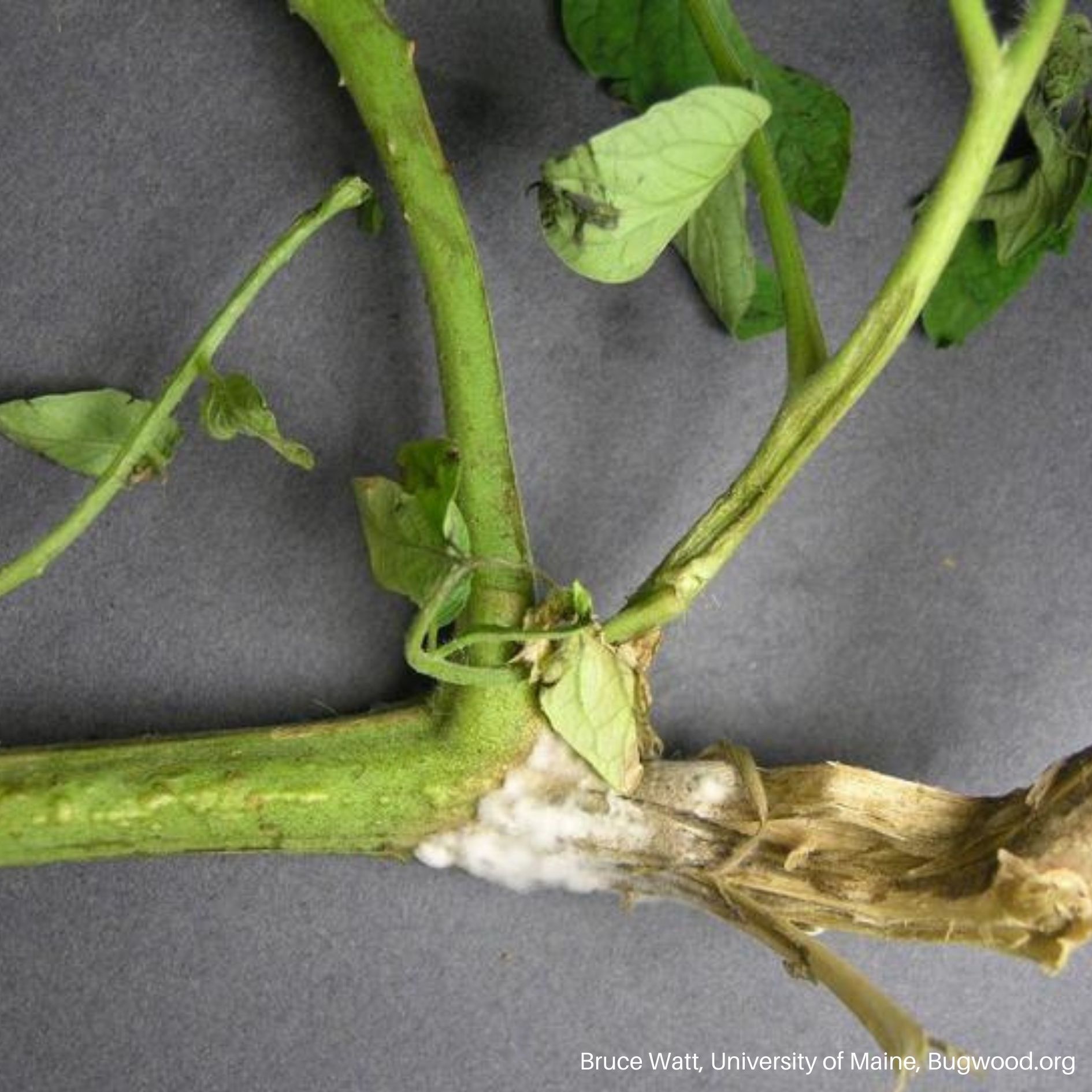 Tomato Plant with White Mold
Tomato Plant with White Mold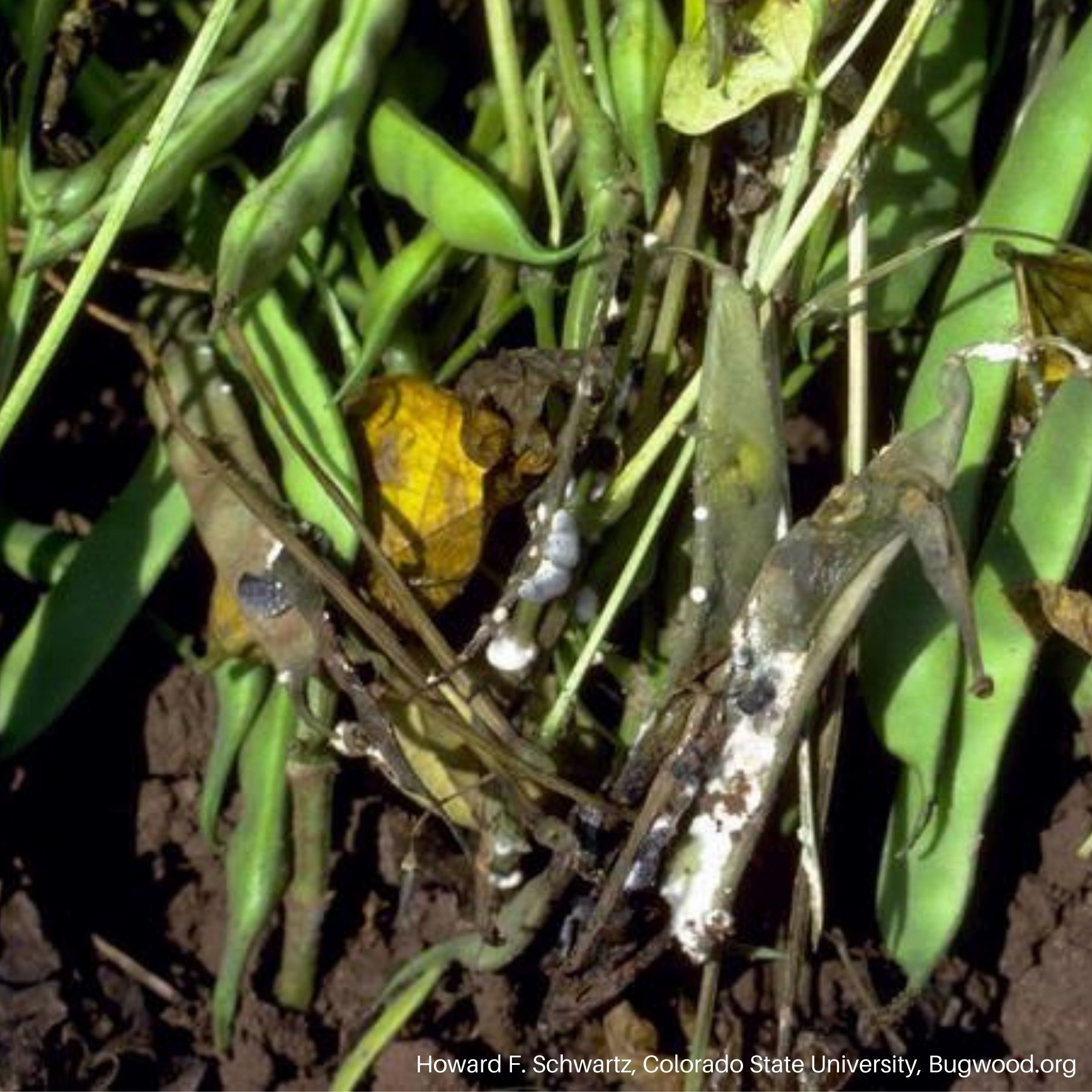 White Mold on Beans
White Mold on Beans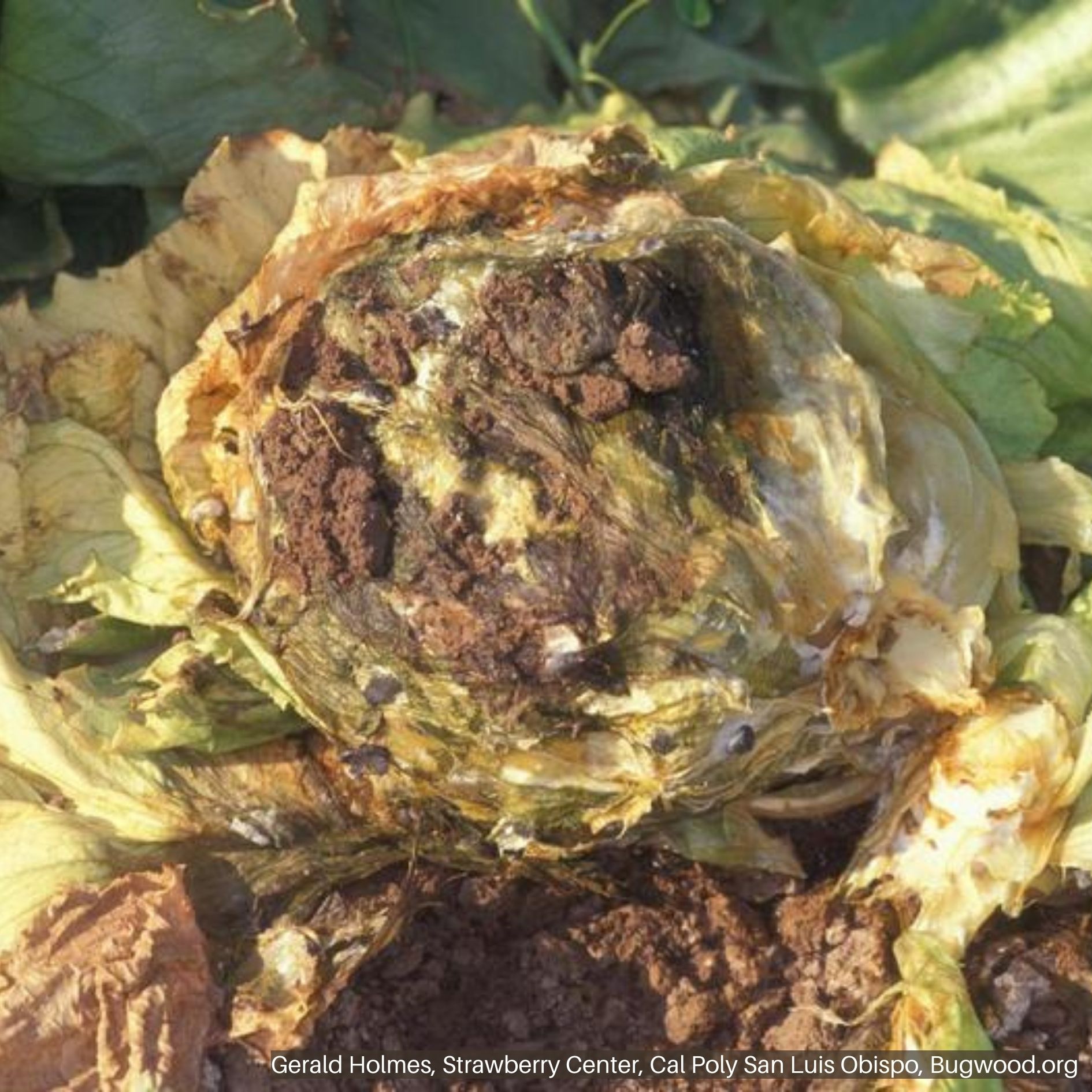 White Mold on Lettuce
White Mold on Lettuce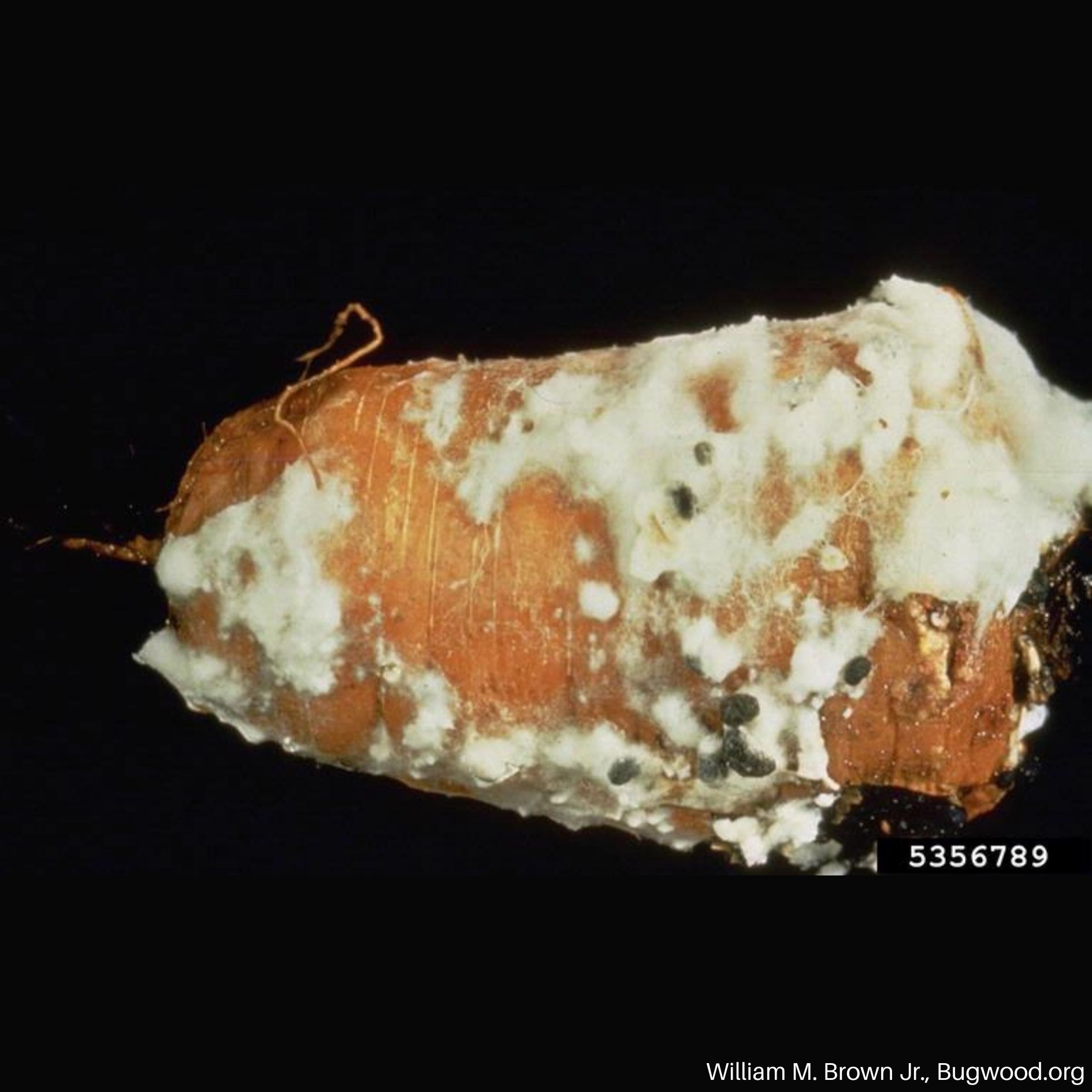 Cottony Soft Rot (White Mold) on Carrot
Cottony Soft Rot (White Mold) on CarrotHOSTS
- Brassicas
- Beans
- Brussel sprouts
- Leafy greens
- Potato
- Root crops
- Solanaceous crops
- Ornamental plants
- Weeds
DESCRIPTION
White mold is a fungal disease caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. The pathogen has a wide host range that includes fruit and vegetable crops and ornamentals. Depending on the affected host, the disease can be called different names such as cottony soft rot in carrots, drop in lettuce, and head rot in cabbage.
BIOLOGY
S. sclerotiorum produces hard, black structures called sclerotia during late summer and early fall. The sclerotia can survive dormant in the soil for extended periods. When conditions are wet and cool, optimally 60 °F to 70 °F, the sclerotia will produce fruiting bodies which release spores. The spores are spread by wind and water to new hosts.
SYMPTOMS
- White fungal growth that often starts around the soil line.
- Hard, dark structures that develop on and within infected plant tissue.
- Wilted stems and foliage
GENERAL MANAGEMENT
- Remove and dispose of infected plants.
- Manage weeds as they can serve as alternative hosts for the disease.
- Minimize moisture on plants by utilizing drip irrigation and providing space between crops for ventilation.
- Rotate with nonsusceptible crops such as grains or corn to reduce disease build-up.
Precautionary Statement: Utah State University and its employees are not responsible for the use, misuse, or damage caused by application or misapplication of products or information mentioned in this document. All pesticides are labeled with ingredients, instructions, and risks, and not all are registered for edible crops. “Restricted use” pesticides may only be applied by a licensed applicator. The pesticide applicator is legally responsible for proper use. USU makes no endorsement of the products listed in this publication.

