Bacterial Speck

Casual Agent
Bacterial speck is caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato and only affects tomato. Infected tomato fruit is unacceptable for fresh market production, but fruit can be used for canning where tomatoes are peeled.
Symptoms
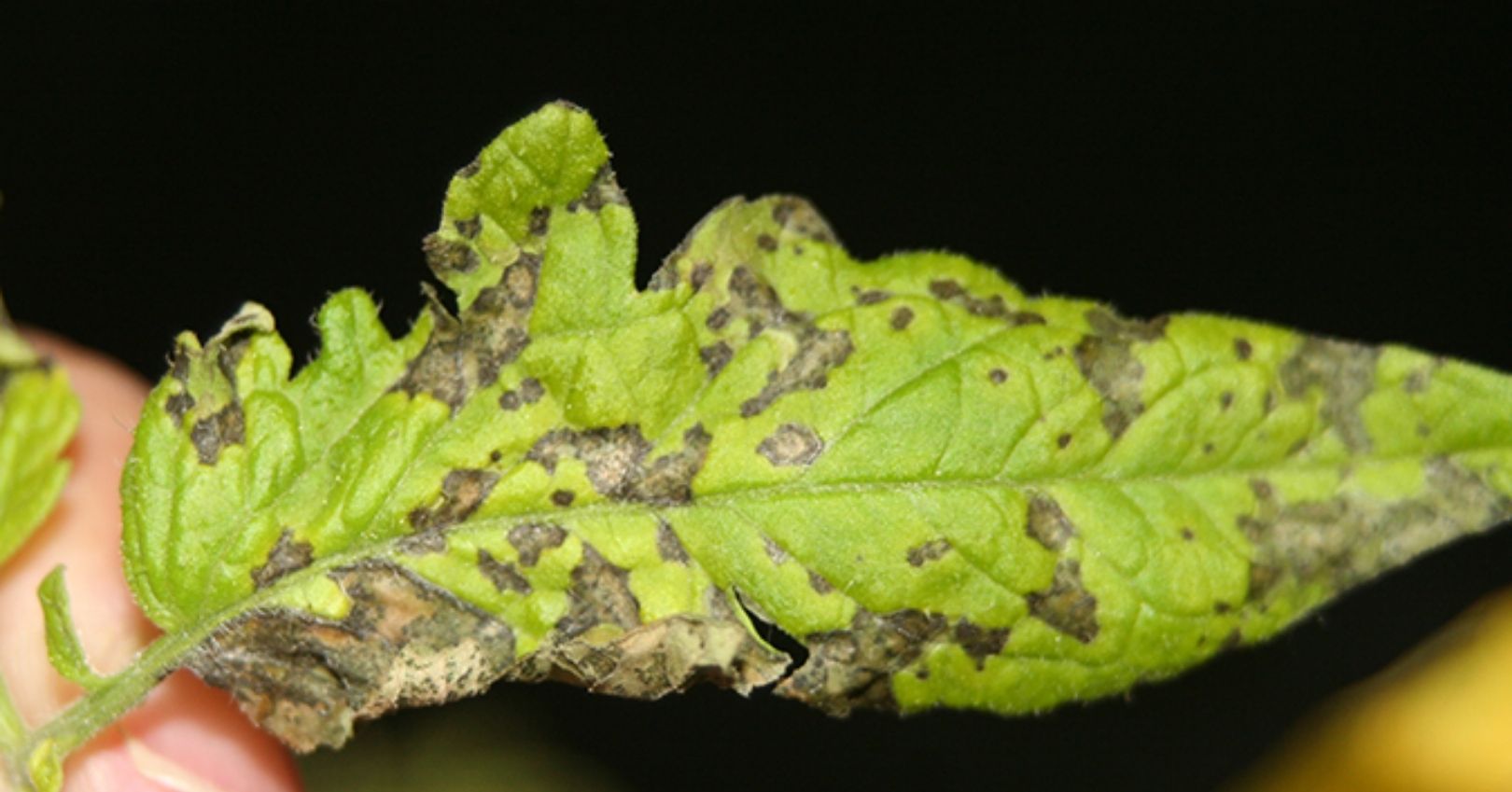
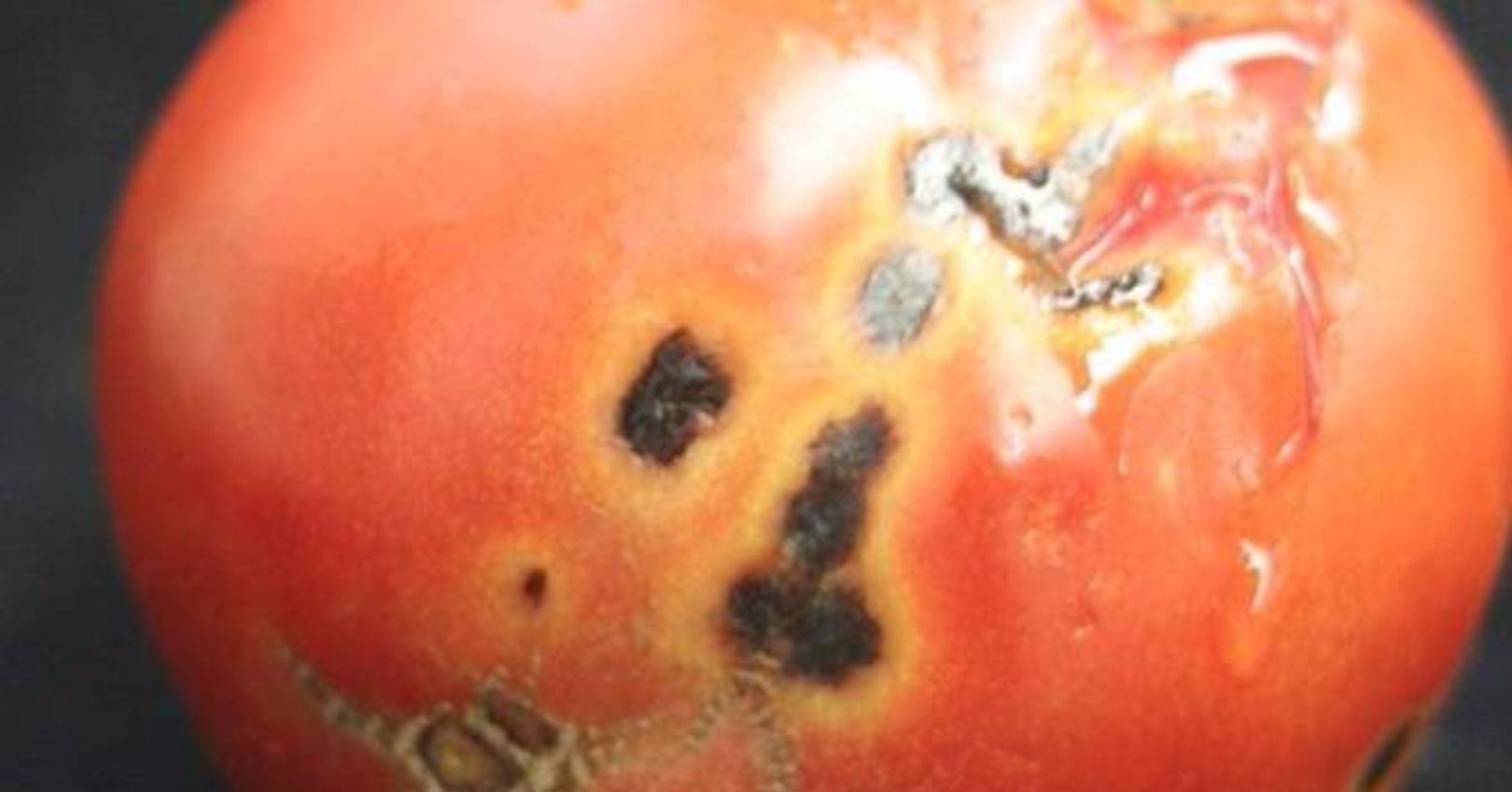
Tomato leaves develop small irregular shaped brown, necrotic lesions, often surrounded by a yellow halo. On small fruit (about 1 mm in size), round, black, superficial skin lesions develop.
Disease Cycle
The bacteria can be seedborne and can survive for at least a year in plant debris. There have been reports that the bacteria can also survive on weeds. Spread between plants occurs by splashing water from overhead irrigation or rain, by using contaminated tools, and by workers brushing along plants. Transplants in greenhouses may carry the bacteria on the surface without disease development. However, once the plants are in the field and environmental conditions are conducive to infection, the disease can develop. Generally, bacterial speck is considered to start under cool, moist conditions but it has been observed in Utah during hot temperatures as well.
Management
- Only use disease-free seed. When saving seed from plants, do not use seed from infected plants.
- Use resistant tomato varieties when available.
- Avoid overhead irrigation.
- Apply preventive copper-based bactericides. Once infection occurs, bactericides will no longer be effective.
- Remove plant debris and weeds.
- Rotate out of tomato for two years to non-host crops.

