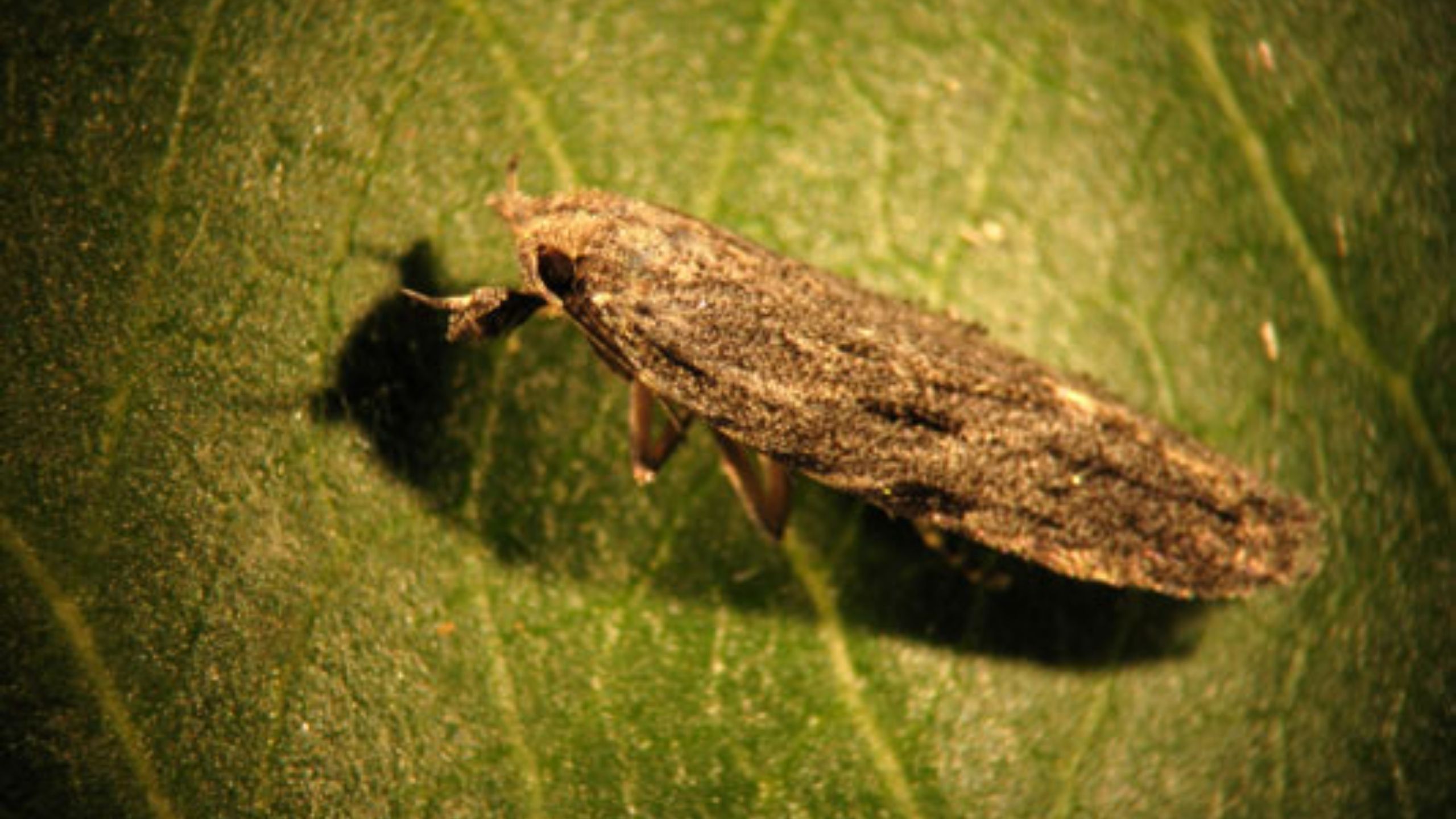
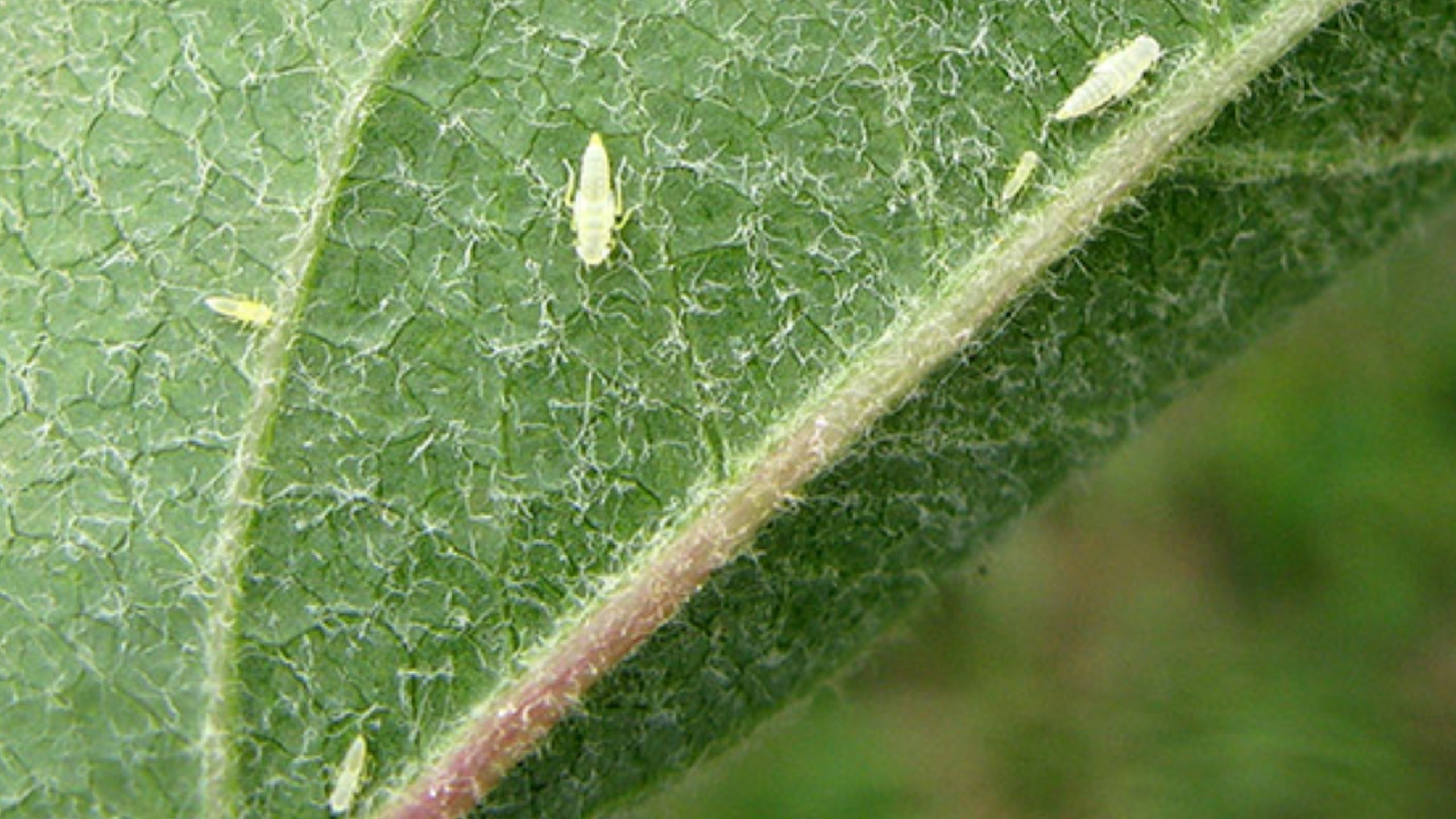
An Alternate Method for Setting Codling Moth Biofix
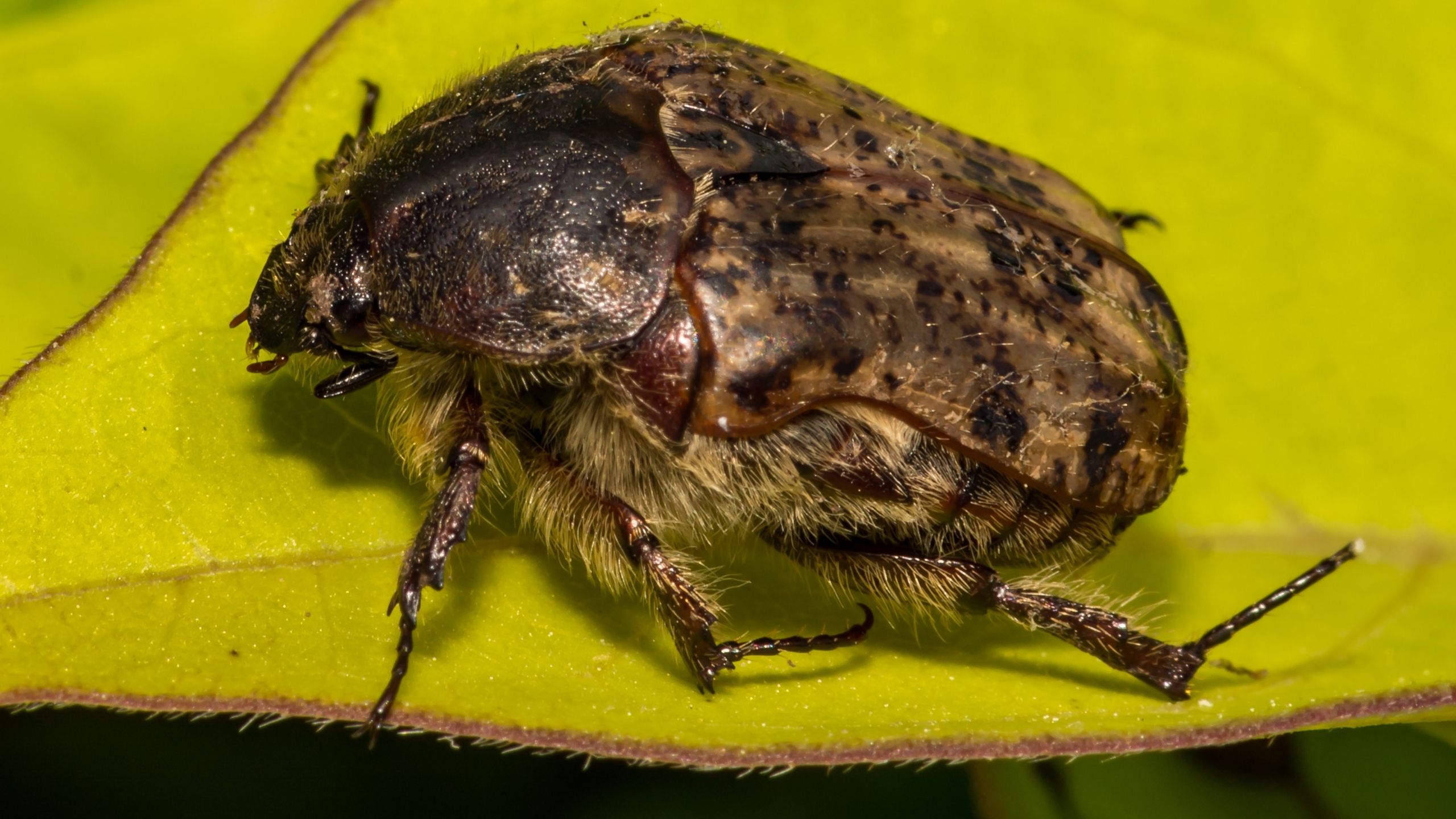
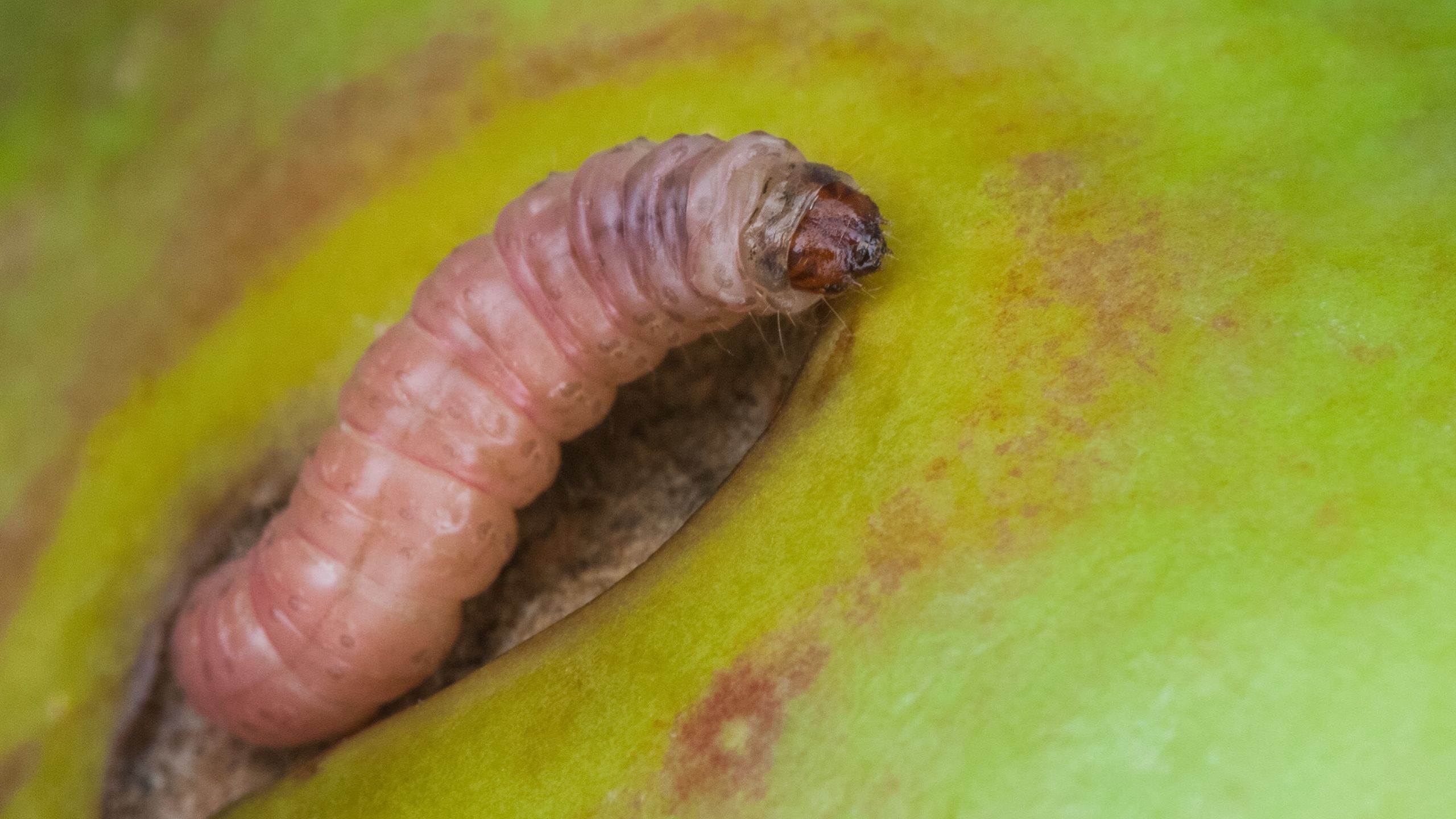
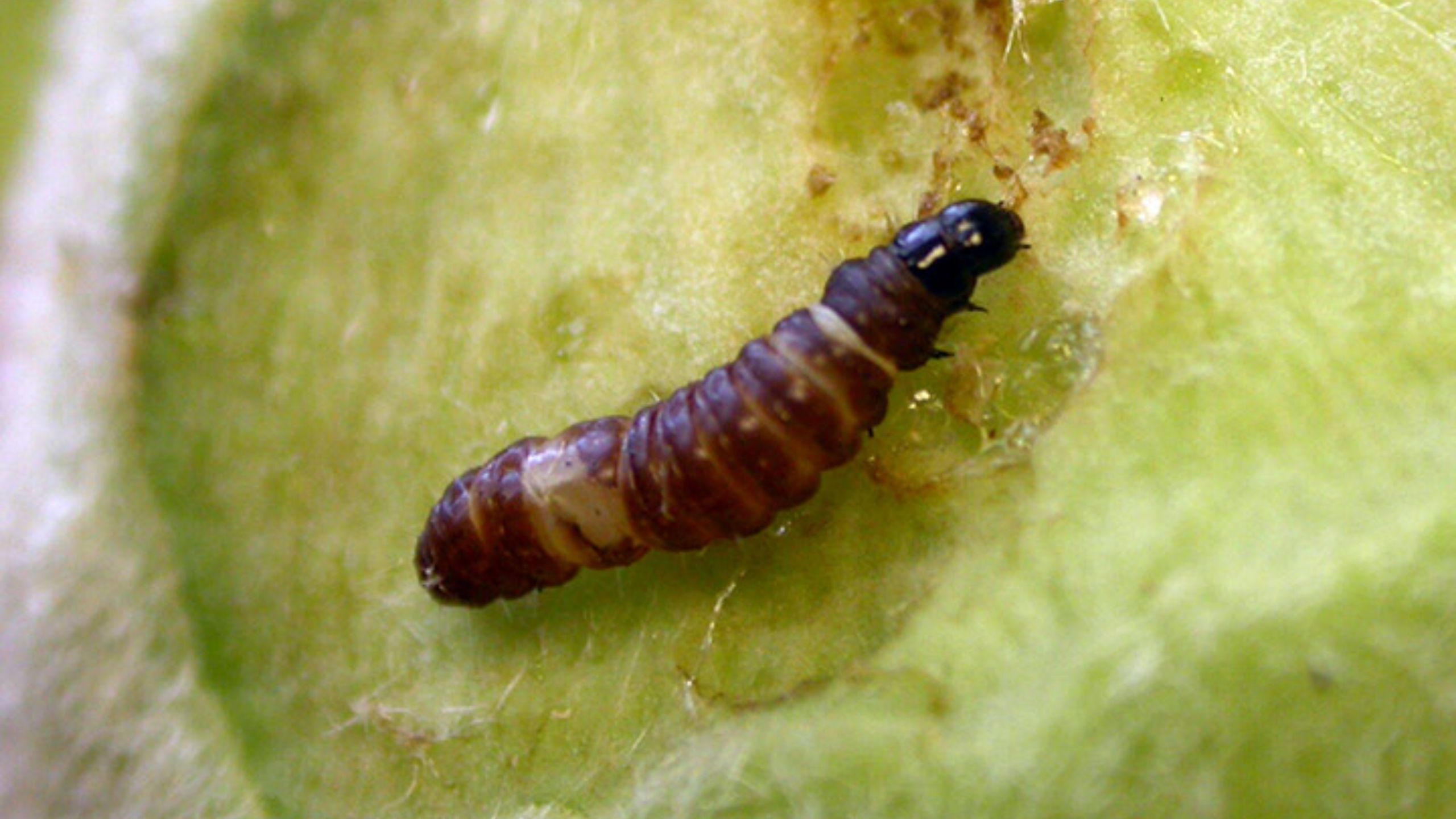
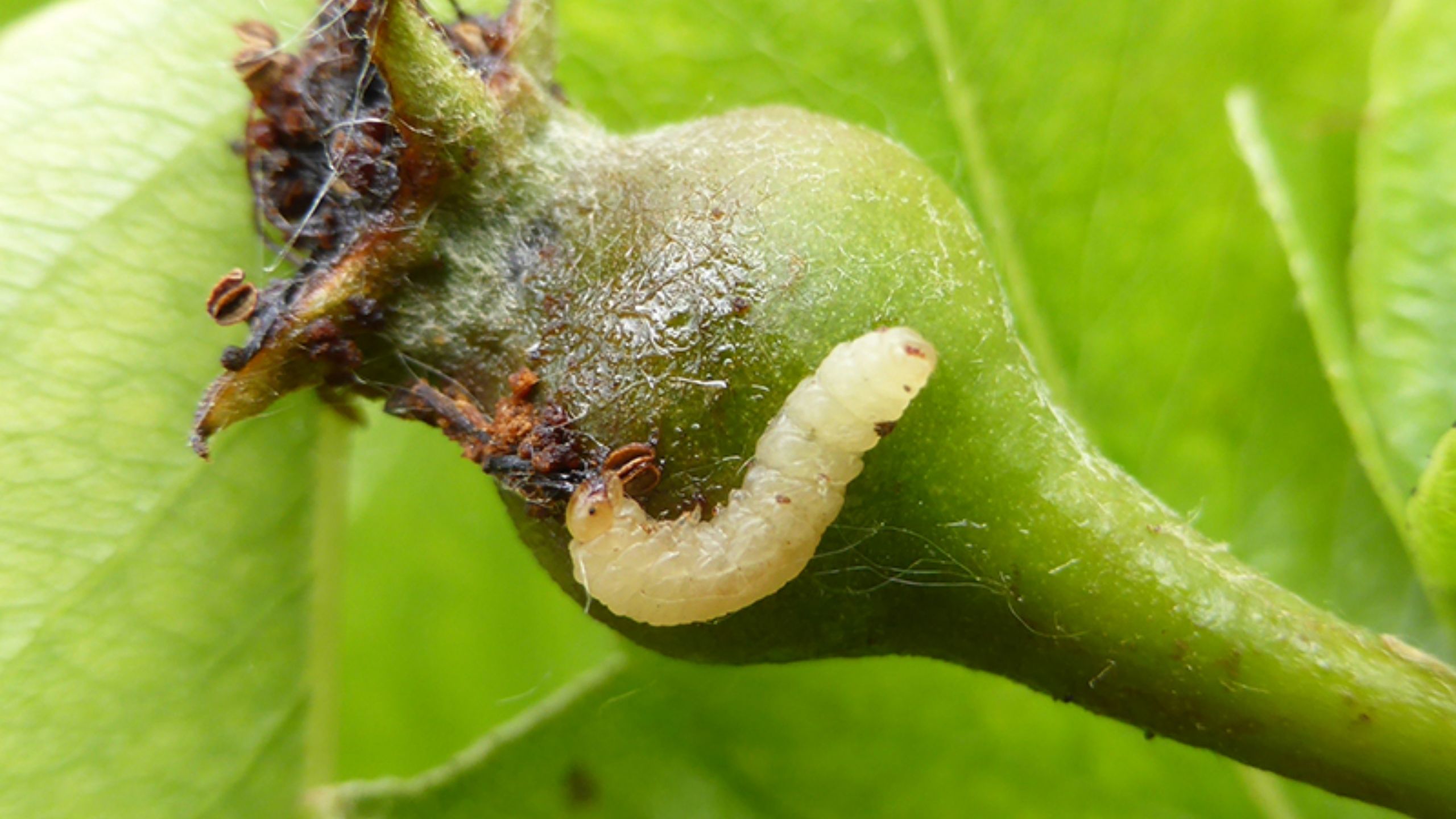
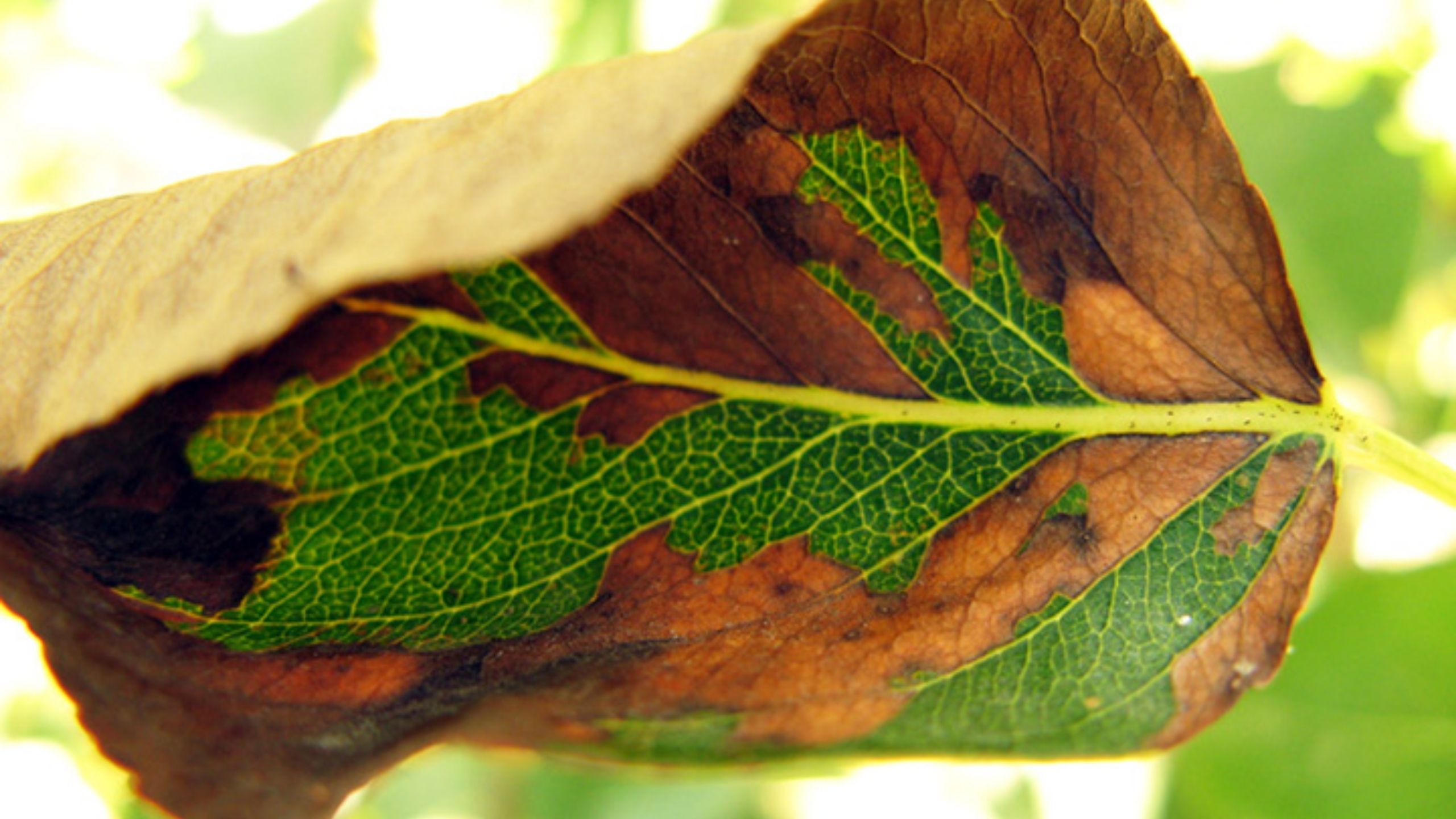
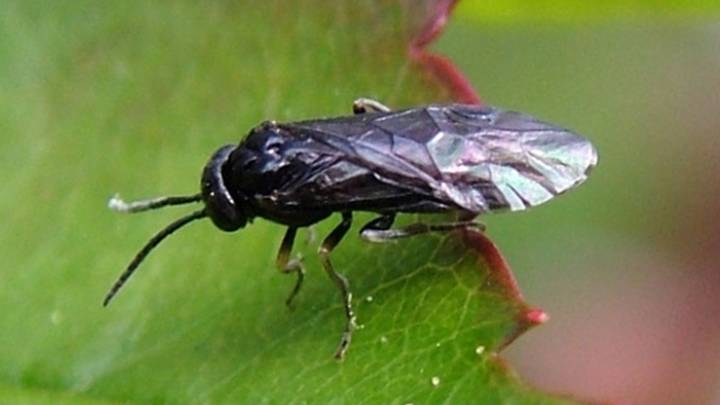
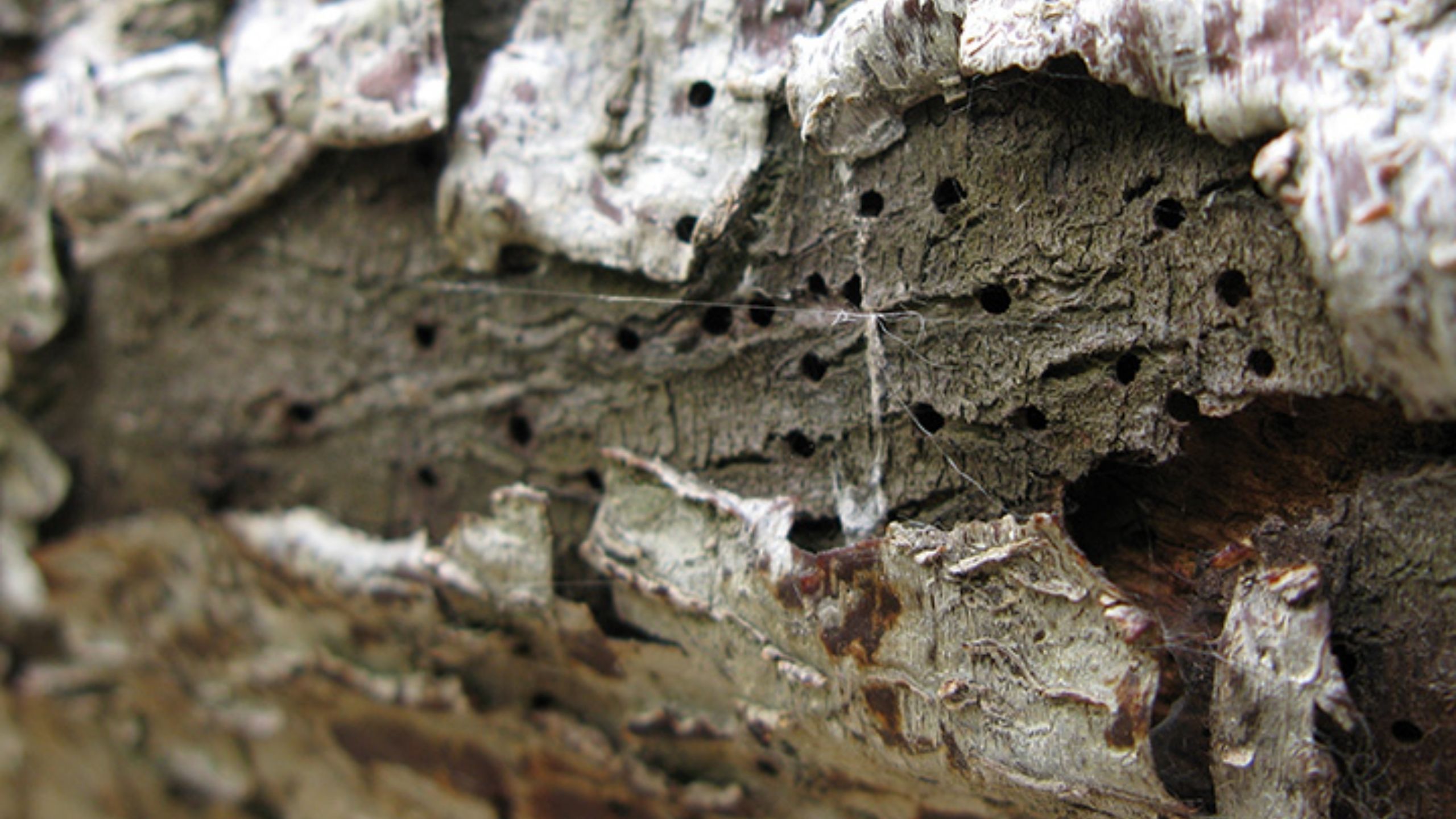
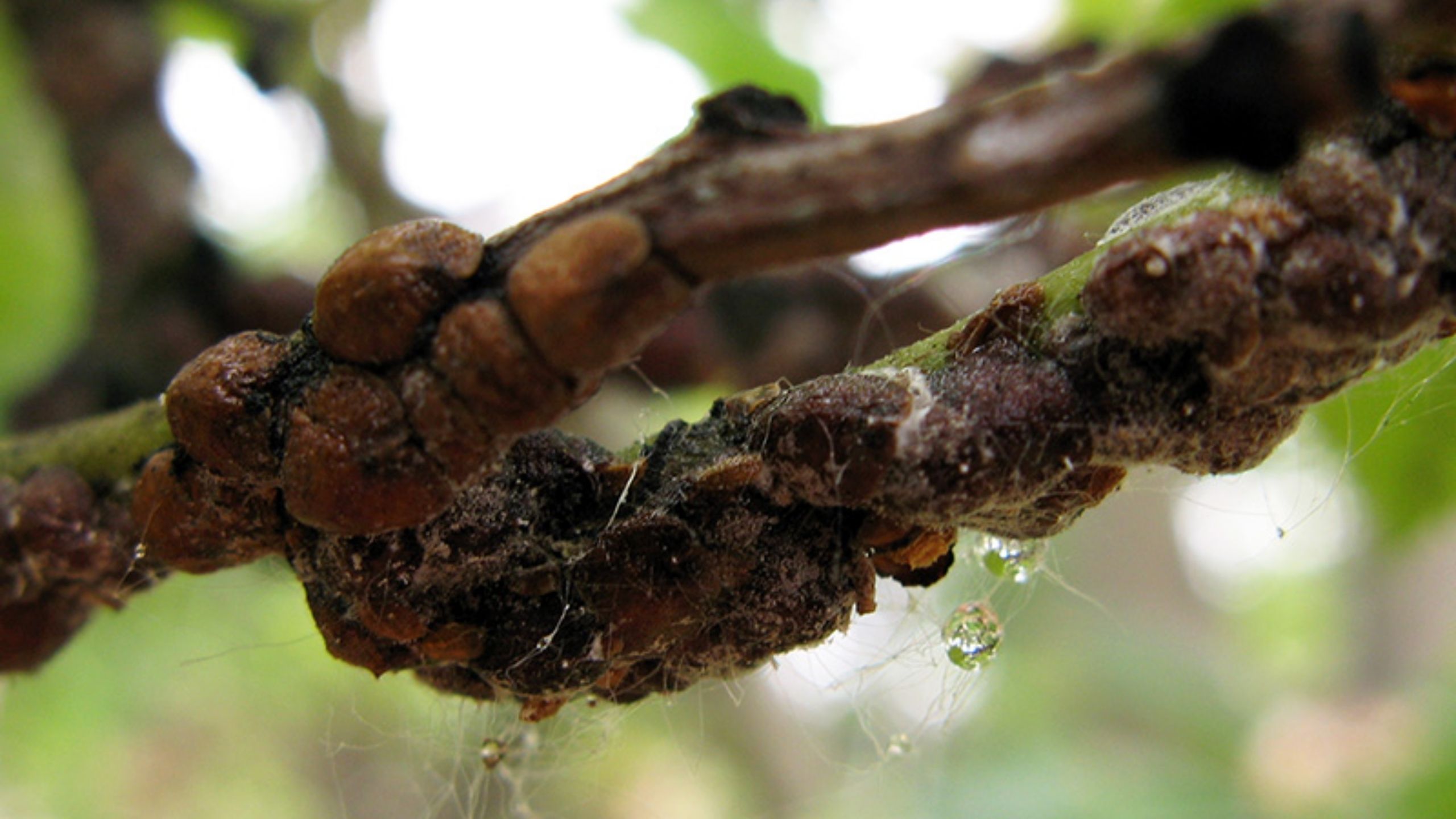
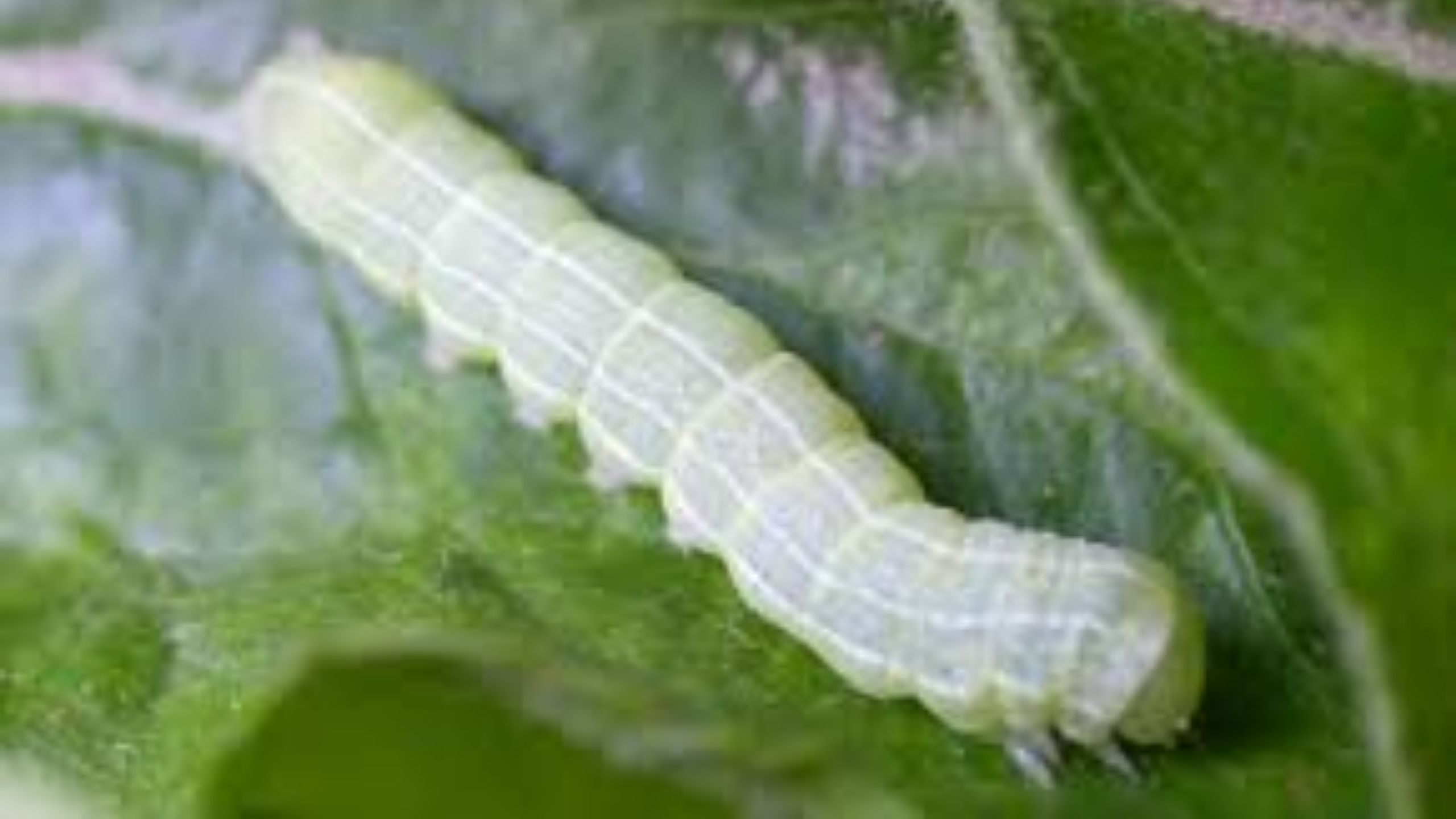
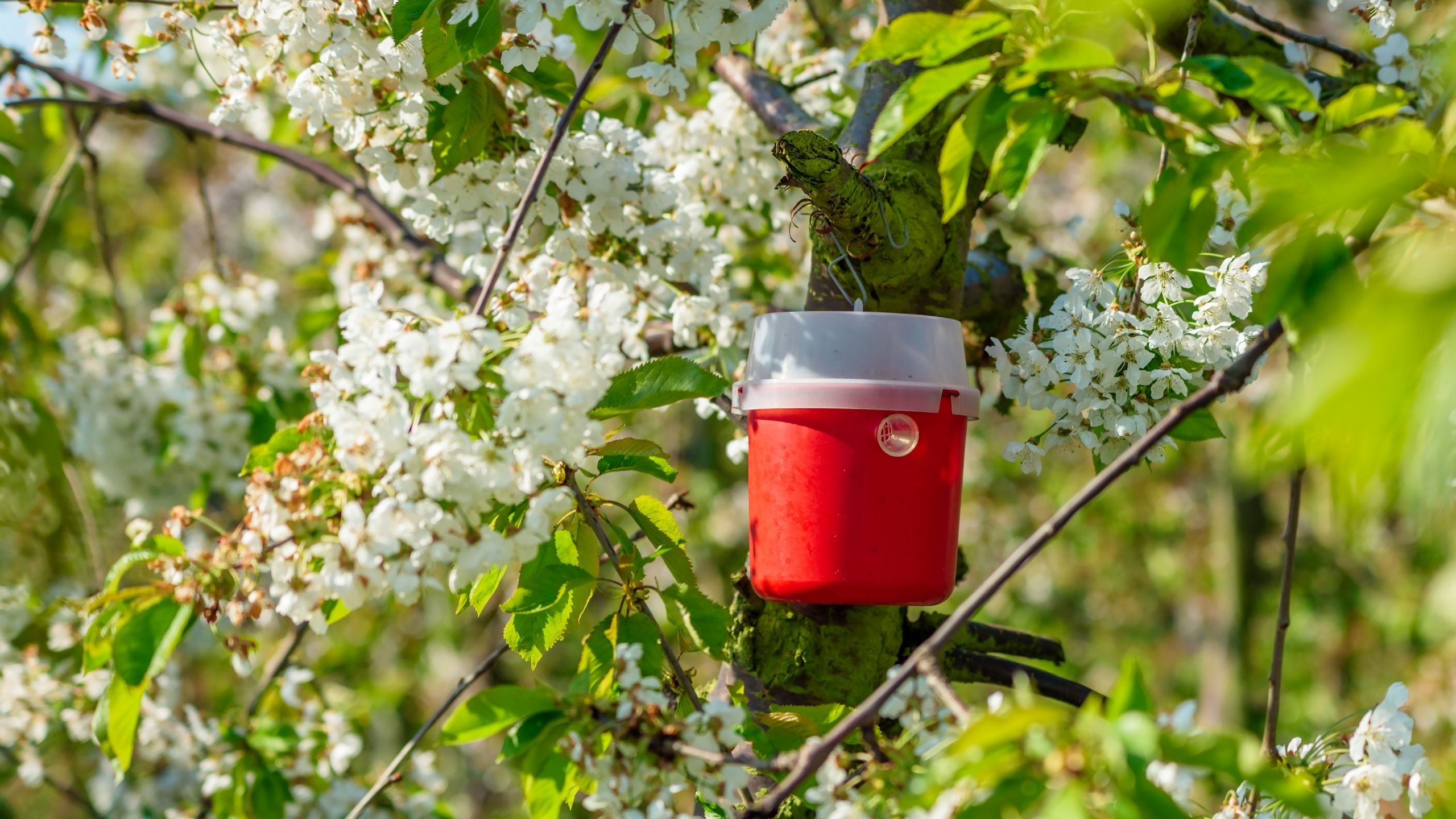
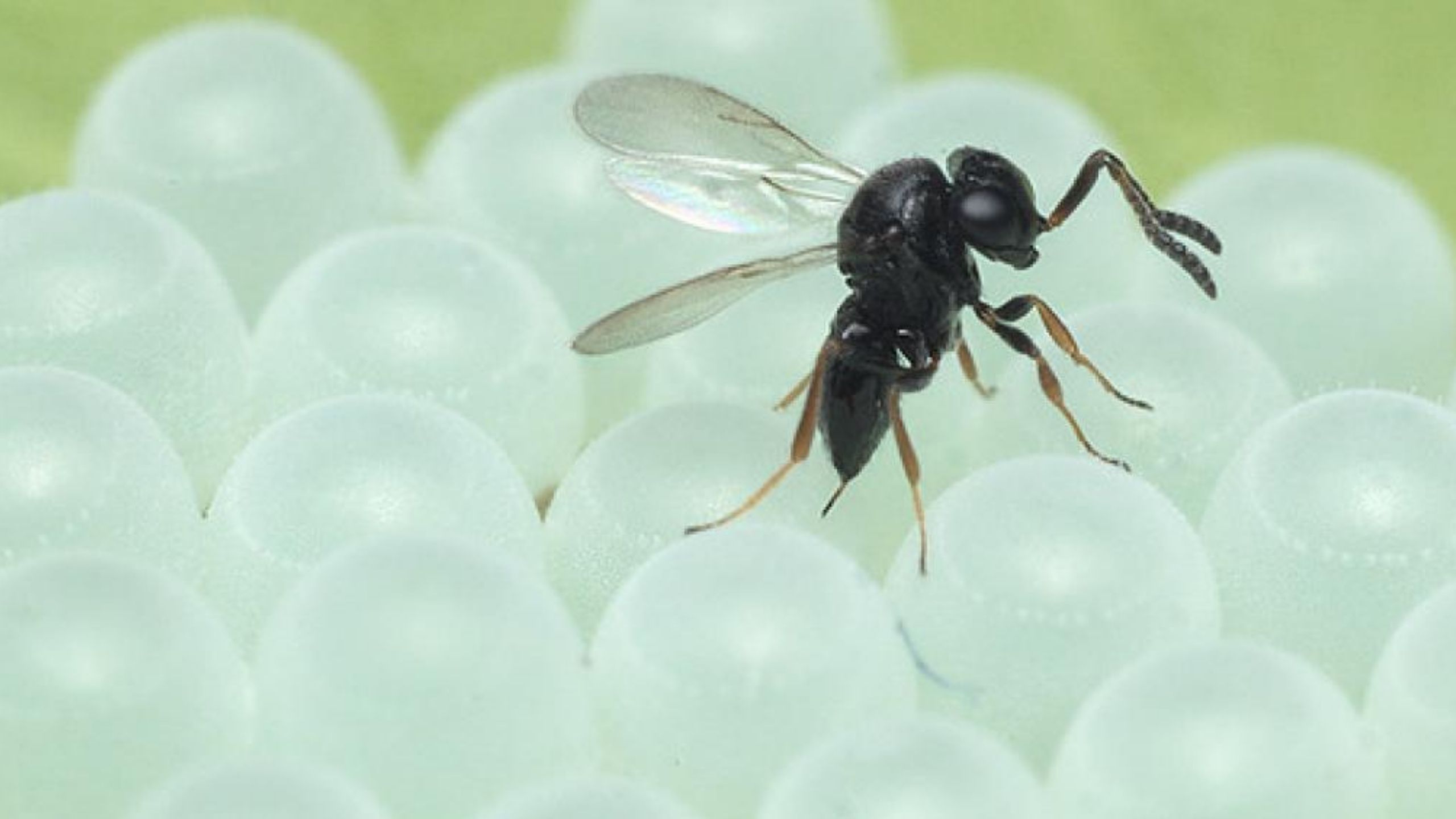
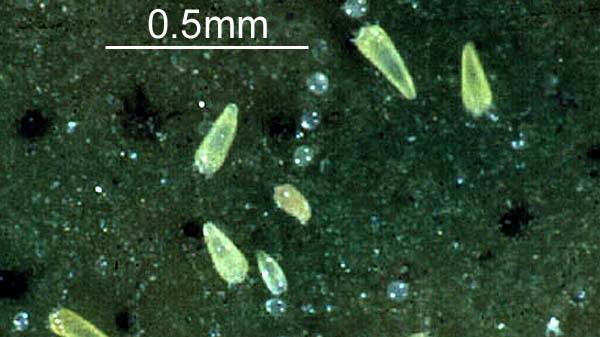
Codling moth, Cydia pomonella, is the key insect pest of apple, pear, and walnut throughout the world, including Utah (apple and pear). Effective management practices are based on accurate determination of the first flight of codling moths in the spring, ...