Fact Sheets - Forage and Field Insects
For more forage and field insect information reference the Beneficial Insects & Pests of Utah Alfalfa Guide
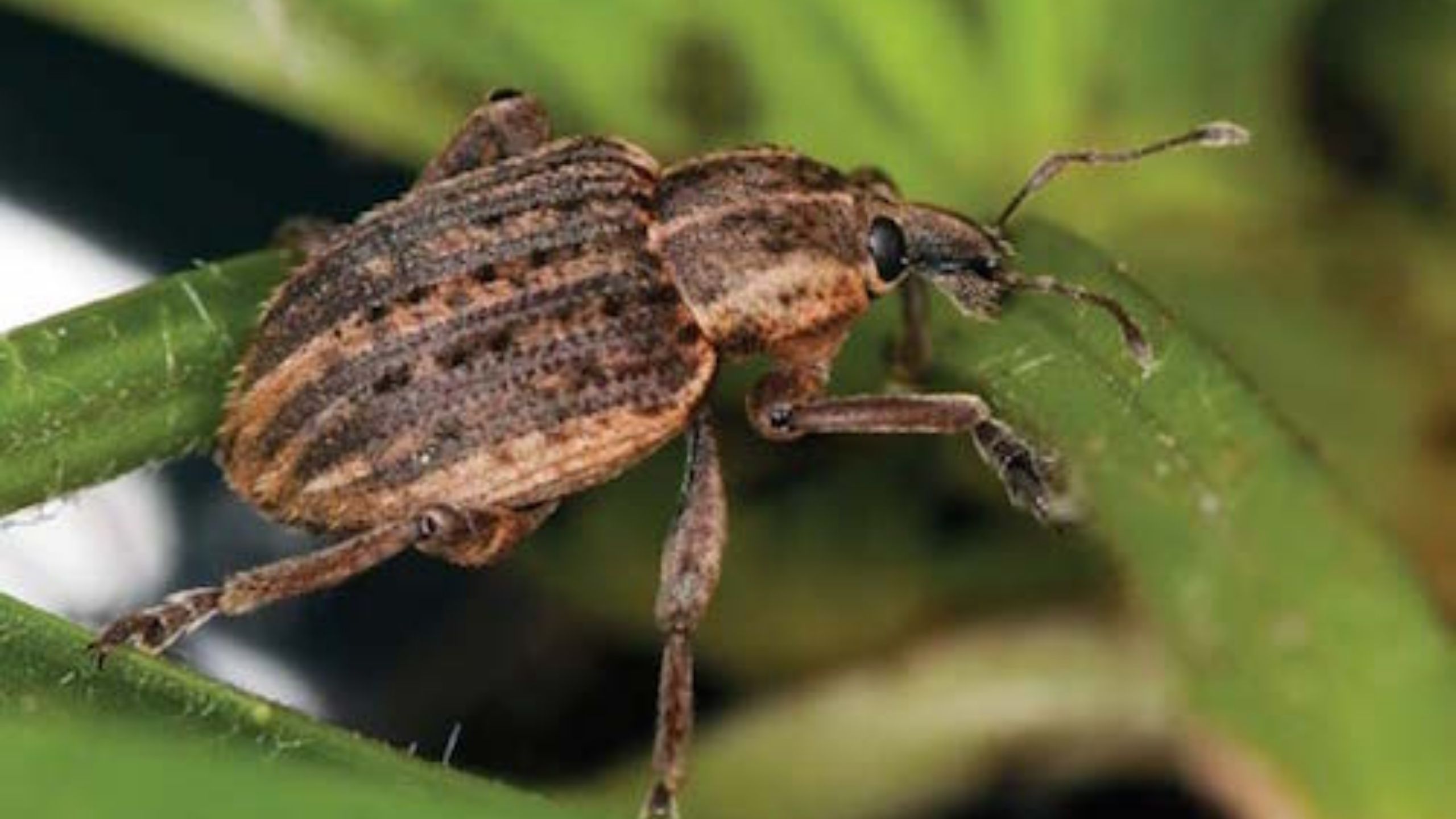
Alfalfa Weevil
The alfalfa weevil is a major pest throughout Utah. It is a beetle with one generation per year. Eggs hatch in the spring, and the grub-like immature weevils (larvae) feed by chewing on the alfalfa foliage.
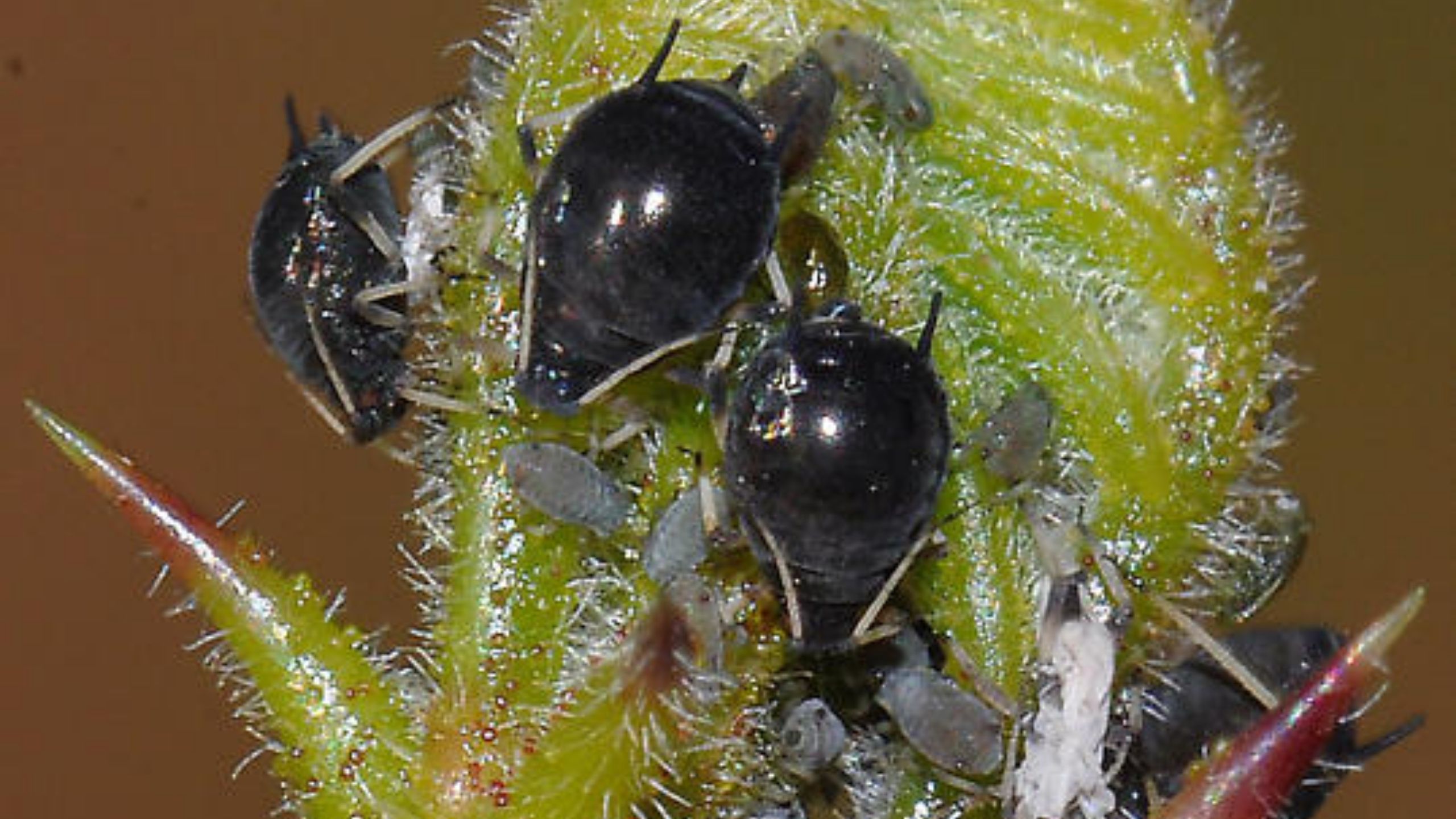
Aphids in Alfalfa
Aphids are soft-bodied insects that remove plant sap from stems and leaves. Heavy infestations can reduce plant vigor, and cause leaves to wilt, curl or become mottled. Some aphids can vector disease or plant toxins while feeding, and cause plants to decrease in productivity.
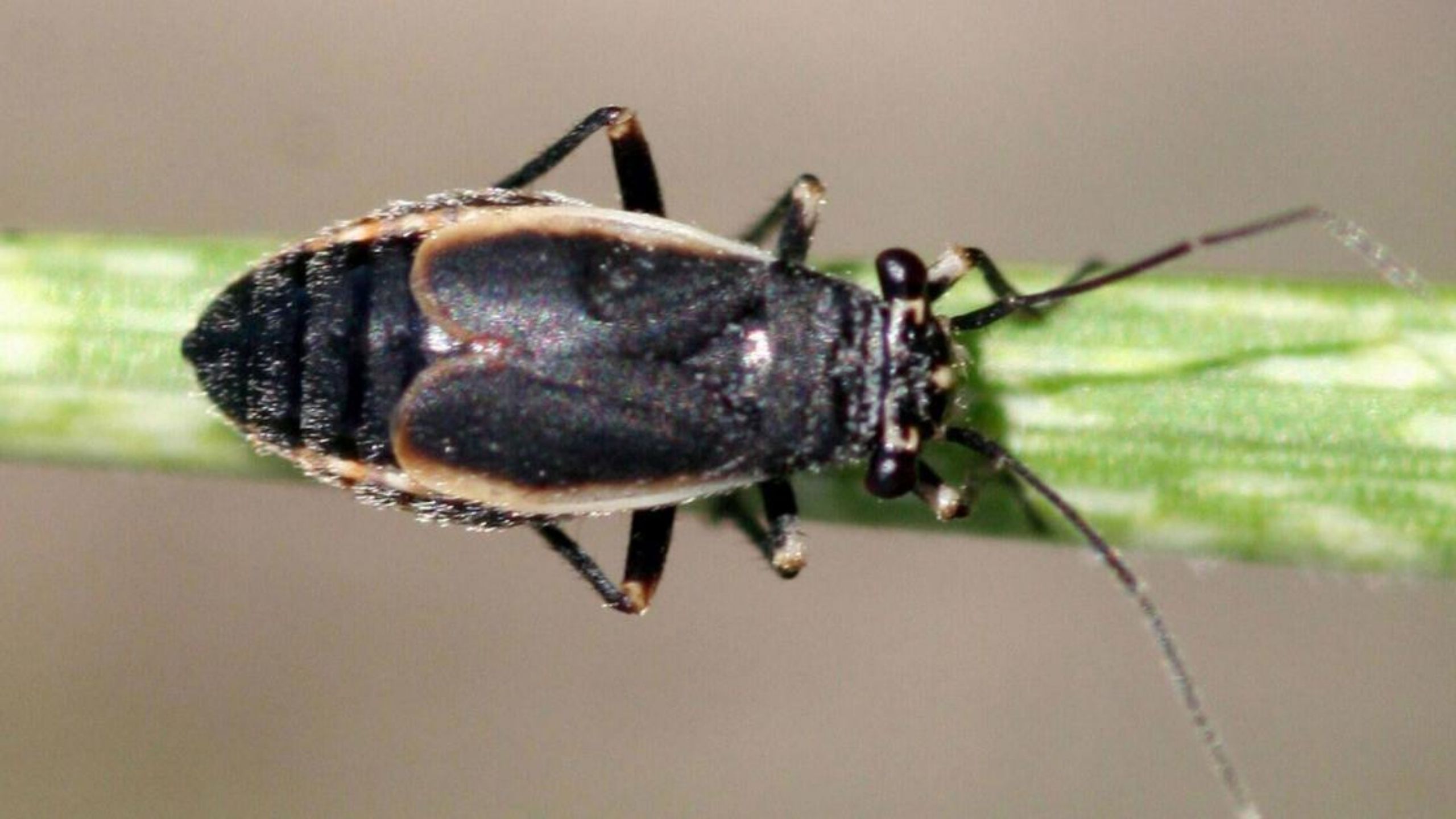
Black Grass Bugs
Black grass bugs are native to western North America. Monoculture reseeding of rangelands may contribute to outbreaks and severe plant damage. Black grass bug control with insecticides is often not practical to apply or economically feasible.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bug
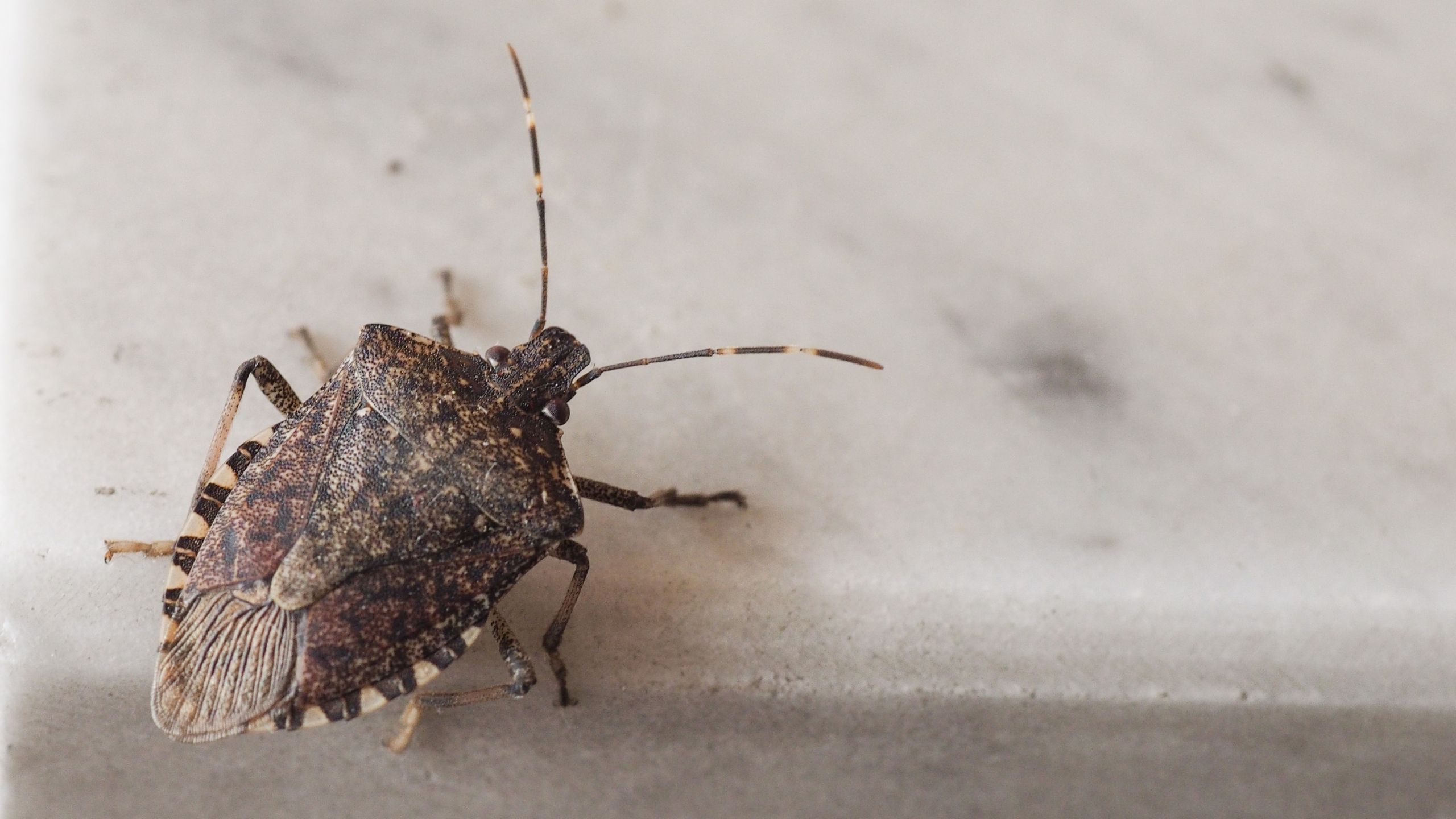

The brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) was accidentally introduced into the eastern U.S. from Asia in the late 1990s and was first detected in Utah in 2012. BMSB can now be found in several northern Utah counties. BMSB can be a nuisance pest as it aggregates in large numbers, and it has a broad host range that includes fruit, vegetable, ornamental, and field crop plants.
Cereal Leaf Beetle
Cereal leaf beetle is a serious insect pest of small grains throughout much of the United States. This insect is of regulatory concern to Utah; the presence of cereal leaf beetle in grain can restrict exporting to other counties and states.
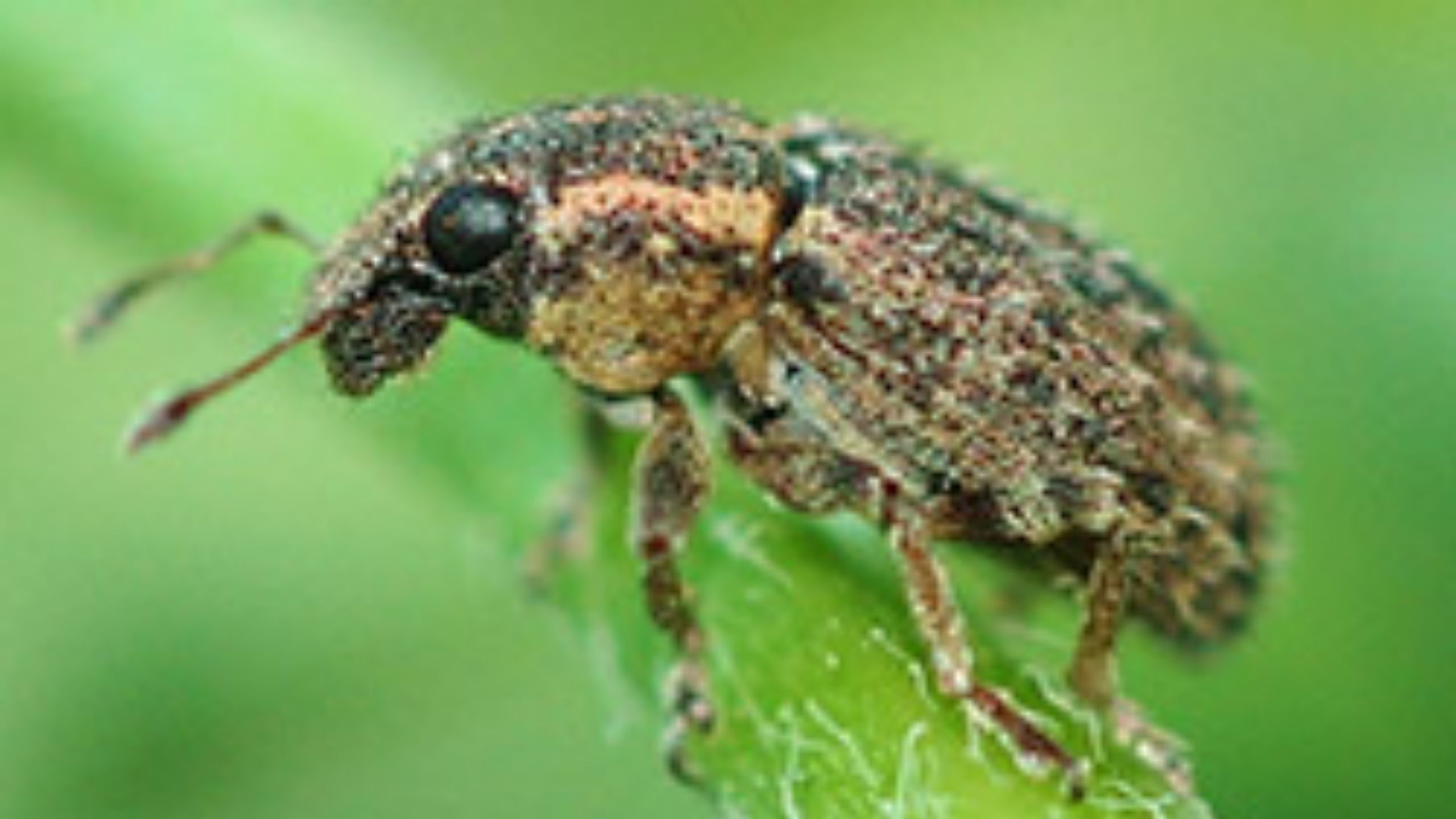
Clover Root Curculio
The clover root curculio is an important agricultural pest in forage crops. Adult beetles feed on foliage while the more damaging larval stage feeds on roots. Heavy larval feeding has been associated with reduced stand establishment, disruption of nutrient and water uptake, and reductions in forage quality and yield.
Community-Wide Grasshopper Control

Springtime, while grasshoppers are still nymphs, is the best time for communities or neighborhoods to work together to suppress grasshopper populations. Treating as wide an area as possible is the key to success.
Grasshopper
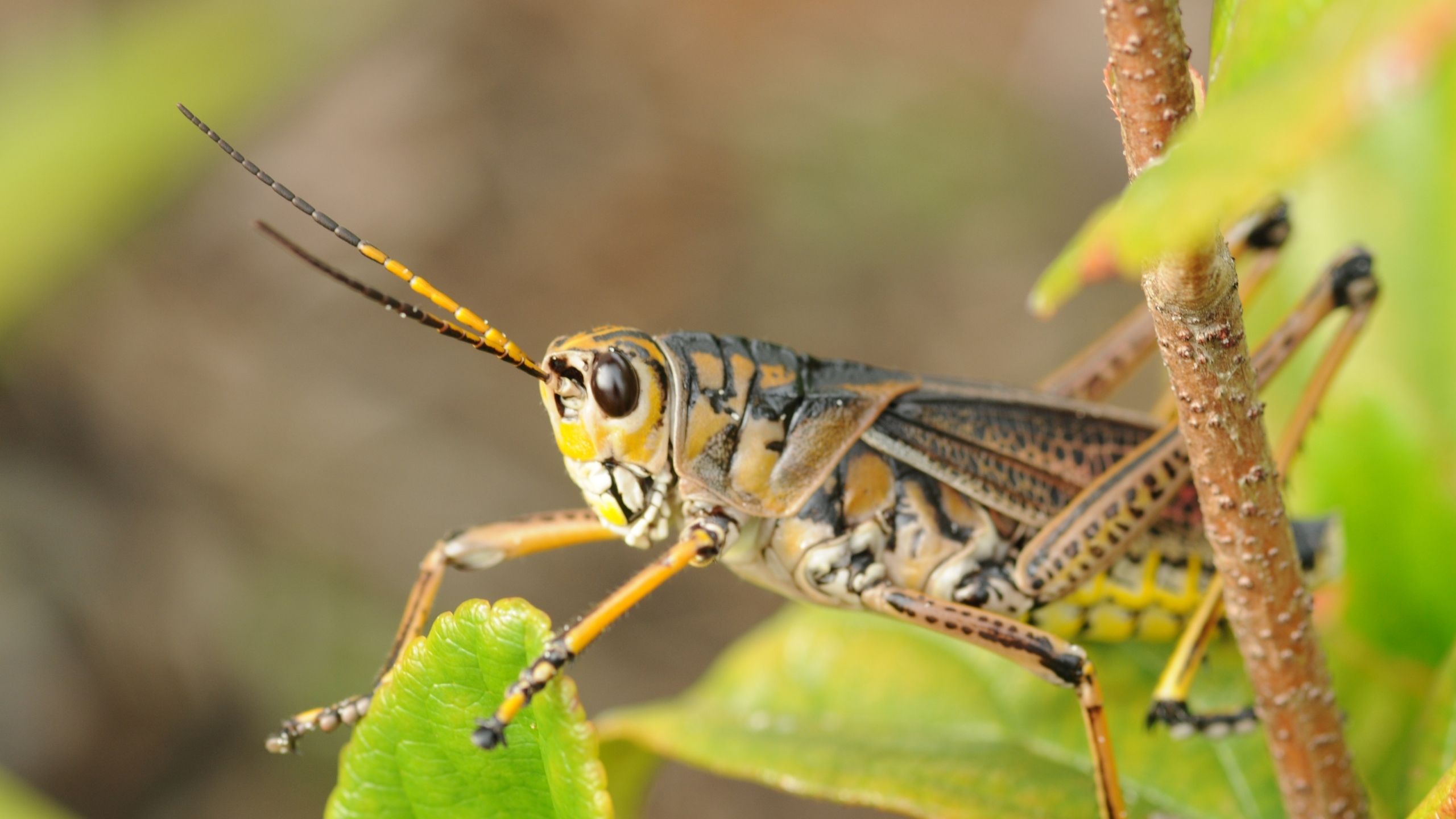

About 400 different grasshopper species are native to North America, and most are well-adapted to forage and grasslands in Utah. Area-wide treatments are generally more effective than spot treatments because grasshoppers are highly mobile insects.
Imported Fire Ants
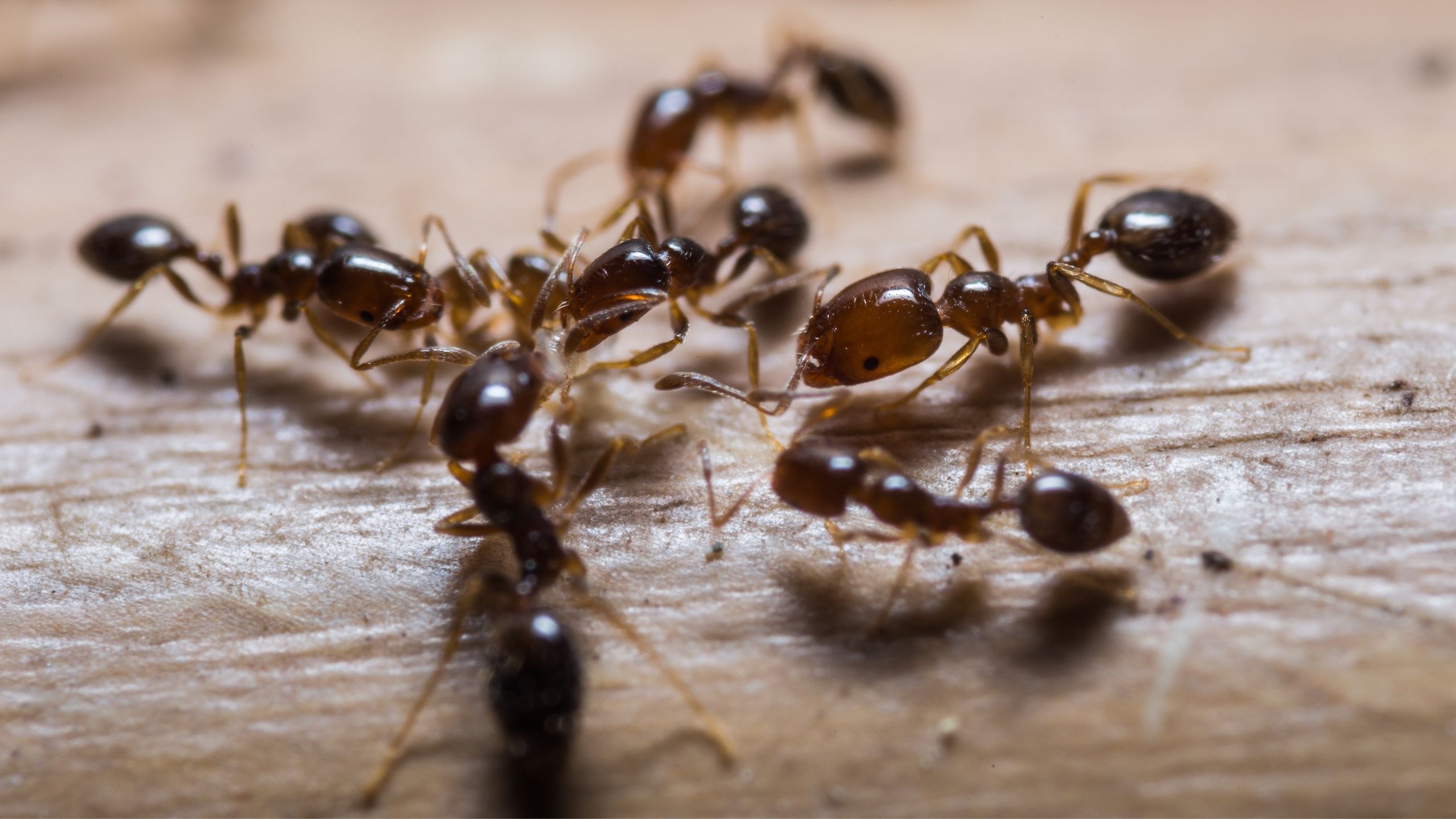

The red and black imported fire ants (IFA) are an invasive and aggressive pest not known to occur in Utah, but parts of southern Utah may be suitable for colony establishment, particularly in areas that have accessible water from irrigation or natural sources. IFA cause agricultural, ecological, economical, nuisance, and public health issues.
Japanese Beetle
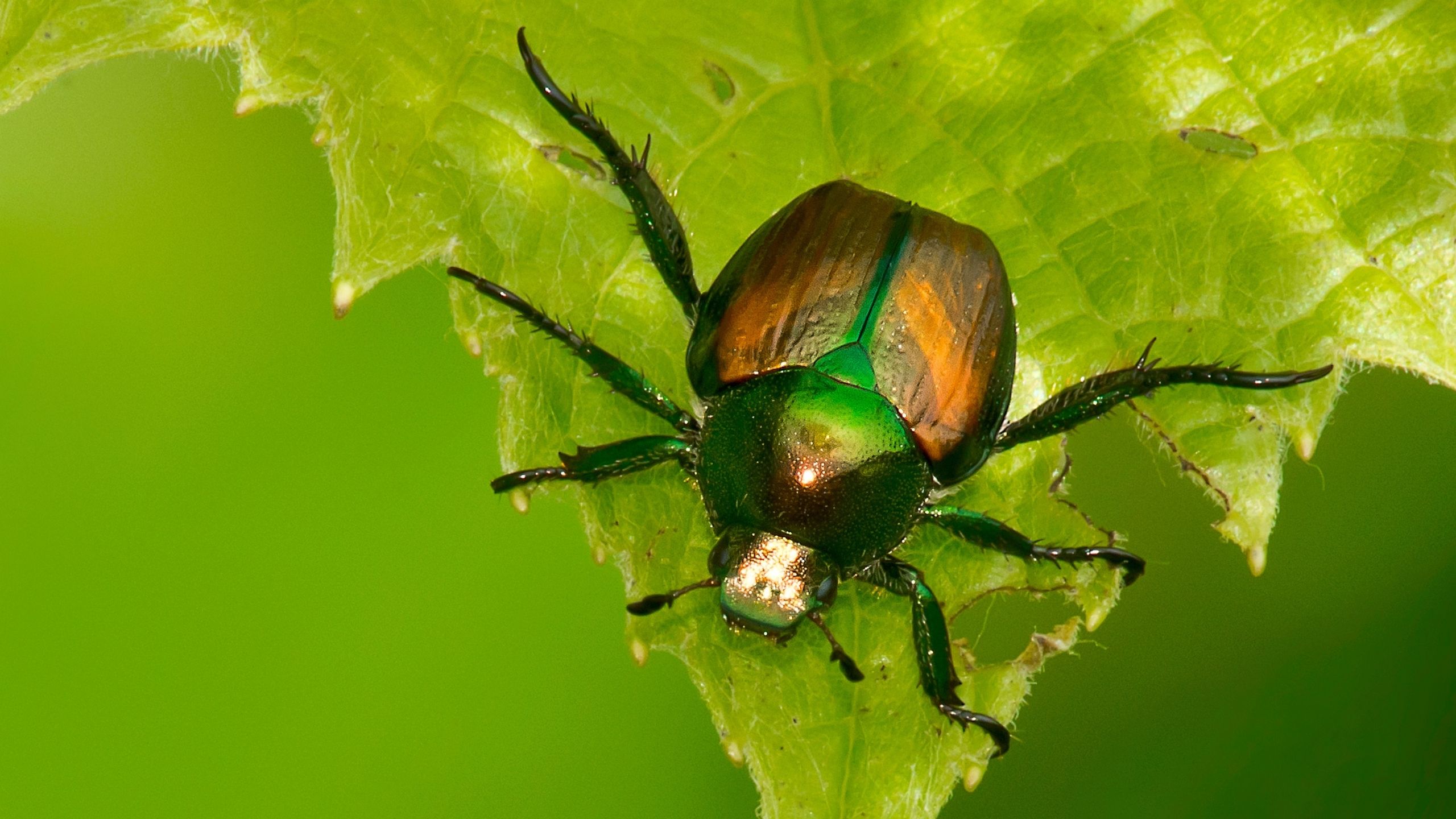

Japanese beetle was initially detected in Orem, Utah, in July 2006. Past eradication efforts were highly successful. However, constant pressure from travel and trade has resulted in a few additional captures in monitoring traps in recent years. Adults have a broad host range of more than 300 plant species and can cause significant damage.
Lygus Bug in Alfalfa Seed
Lygus bug is the primary pest of alfalfa grown for seed in Utah. When in high numbers, lygus bug can prevent seed production or severely reduce yield potential. Early scouting can help make management decisions.
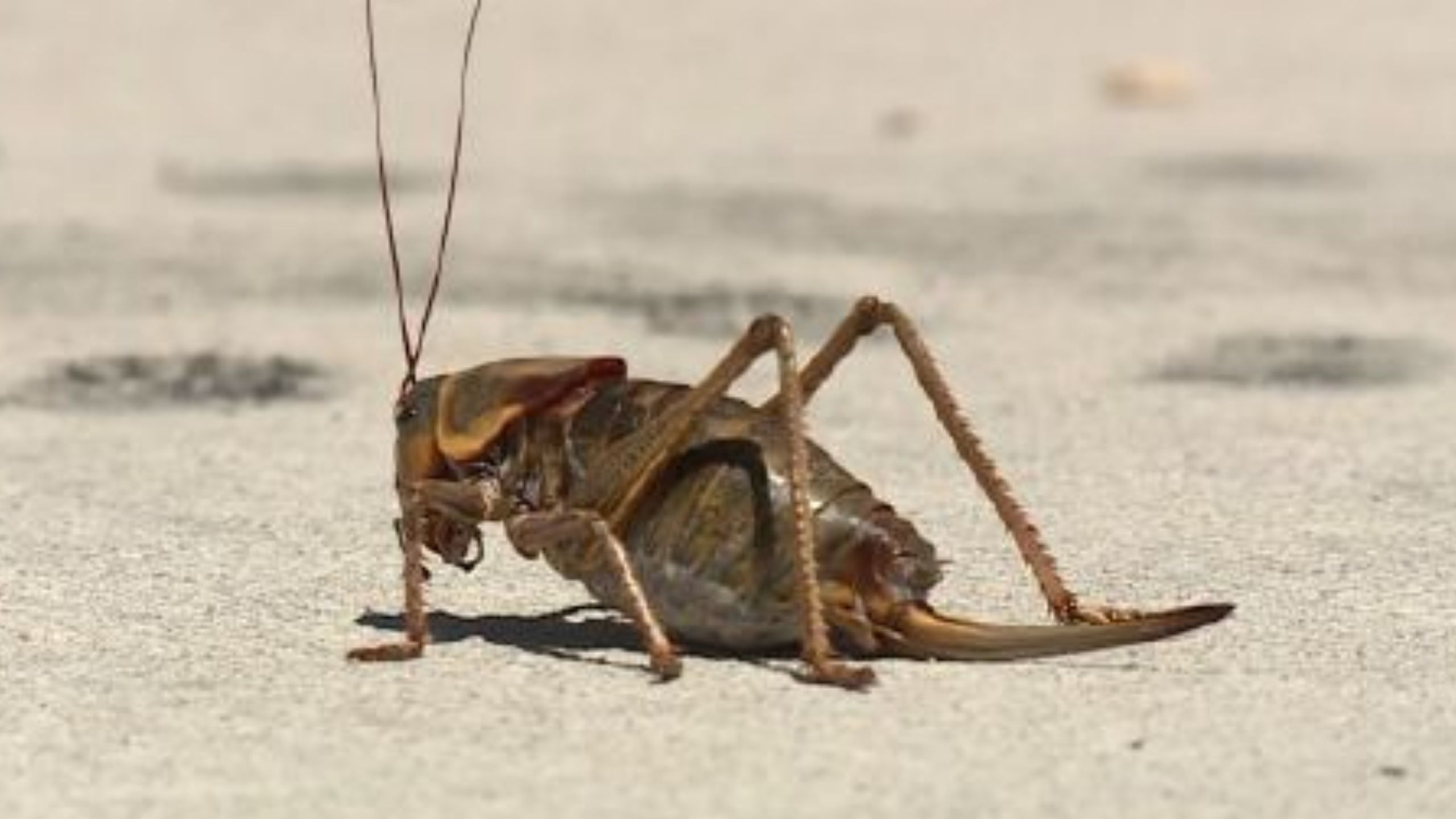
Mormon Crickets
In a recent appraisal of Mormon crickets (Anabrus simplex Haldeman), Raffelson (1989) reminds us that these insects are a subject of great concern and dislike among Western ranchers and farmers.
Russian Wheat Aphid
Russian wheat aphid is a common pest of small grains. Controlling volunteer plants and adjusting planting dates can help reduce aphid outbreaks. Weekly scouting and timely insecticide applications can protect grain yields.
Spider Mites in Corn
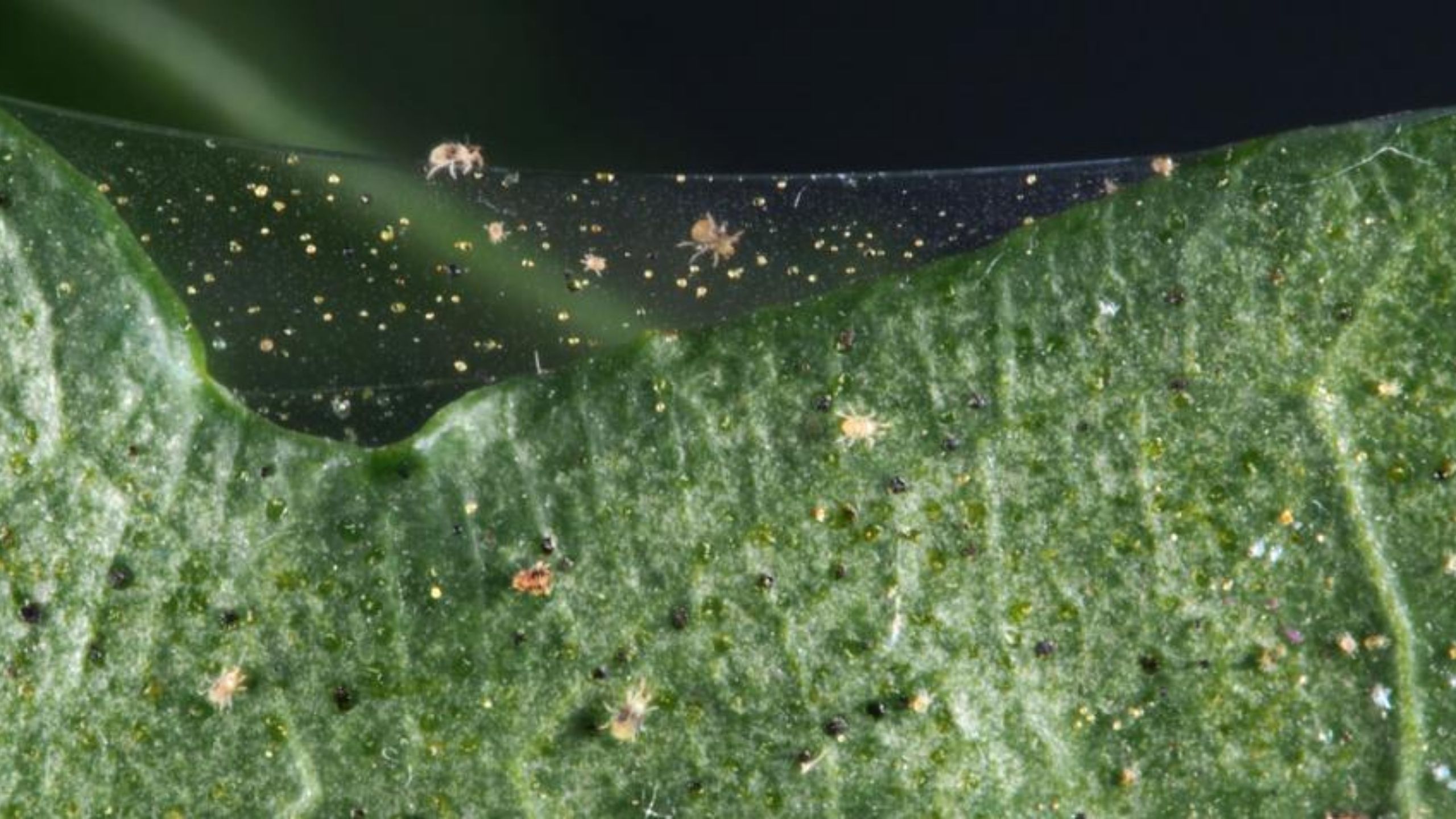
Banks grass mites and two-spotted spider mites are common pests of field and sweet corn and a wide variety of other plants. Prolonged hot and dry conditions promote spider mite development.
Western Corn Rootworm

Western corn rootworm can be a serious economic pest in corn because larvae feed on corn roots, making plants unstable or severely reducing water uptake. Scouting for western corn rootworm adults can help make treatment decisions for the following year, and is critical to keeping production costs down.
Wireworms
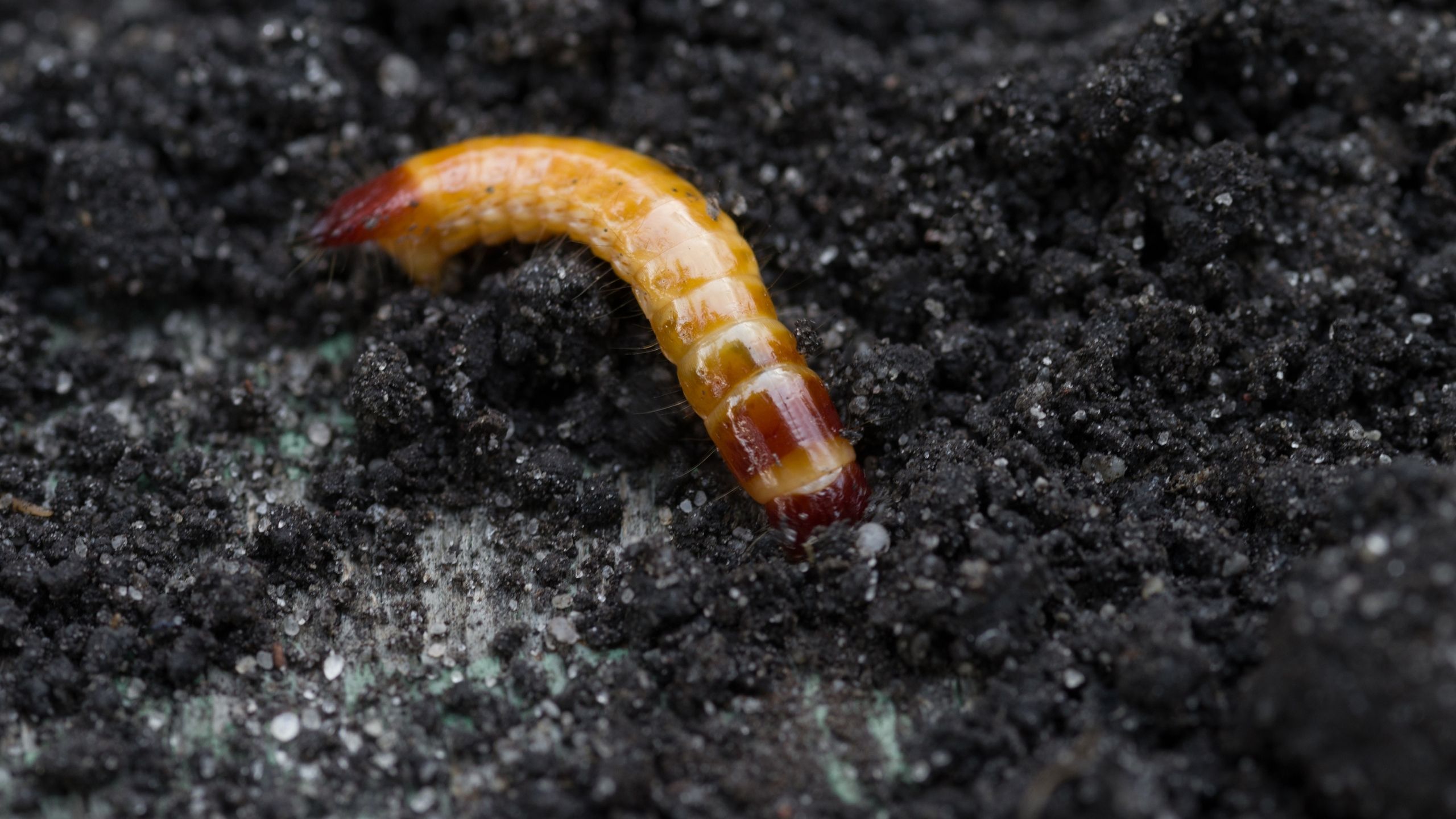

Wireworms are the larvae (immatures) of click beetles. Adults are elongate, slender, hardshelled beetles that take their name from their habit of flipping into the air (sometimes with an audible clicking sound) when they are placed on their backs.









