Integrated Pest Management
Ash Flower Gall and Cottonwood Catkingall Mites
Eriophyes fraxiniflora; Eriophyes neoessigi
Pest Description
- minute; four-legged, cigar-shaped mite; white to yellow
- microscope or hand lens required to see mites; use symptoms for identification
Host Plants, Diet & Damage
Ash Flower Gall Mite
- found on the flowers of male ash trees
- swollen masses of fused male flowers remain green throughout the growing
- season
- brown, lumpy galls are noticed after leaf drop and are present from year to year
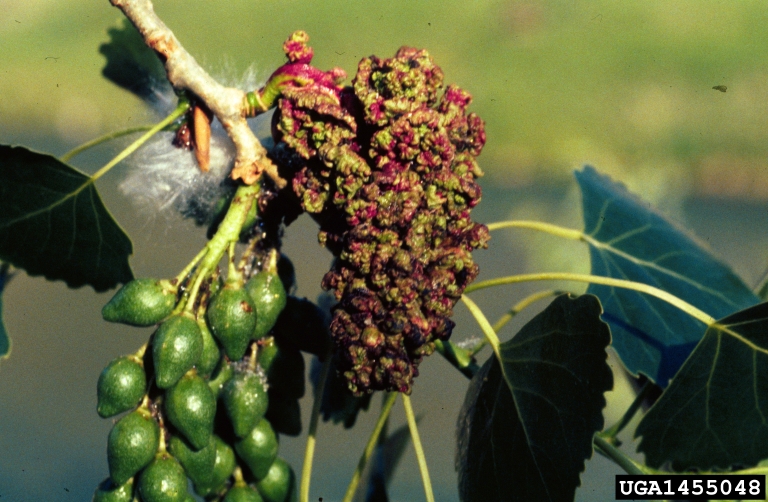
Cottonwood Catkingall Mite
- colonize catkin flowers on Freemont cottonwood and other cottonwoods
- produce wrinkled/curled catkins that hang grapelike
- galls present until mid-summer (healthy catkins fall in spring)
- new galls are green but eventually turn brown
Biology, Life Cycle & Damaging Life Stage
- overwinter in budscales
- emerge from budscales in spring just prior to budbreak
- migrate from buds to feeding sites in spring
- migrate back to buds in the fall
- immatures and adults are damaging
IPM Recommendations
- Damage is aesthetic; tolerate pest.
- Apply horticultural oils at budbreak to target migrating mites.
- Apply an insecticide (avermectin; carbamate; METI acaracide; insecticidal soap; lime sulfur; tetronic and tetramic acid derivatives) at or just prior to budbreak.
- Do not use horticultural oils in combination with, or within 30 days of applying sulfur or a sulfur-containing product.
For more information, see our Eriophyid Mites fact sheet.