Utah Plant Pest Diagnostic Lab
Top 20 Identified Insects
Aphids (Aphididae)
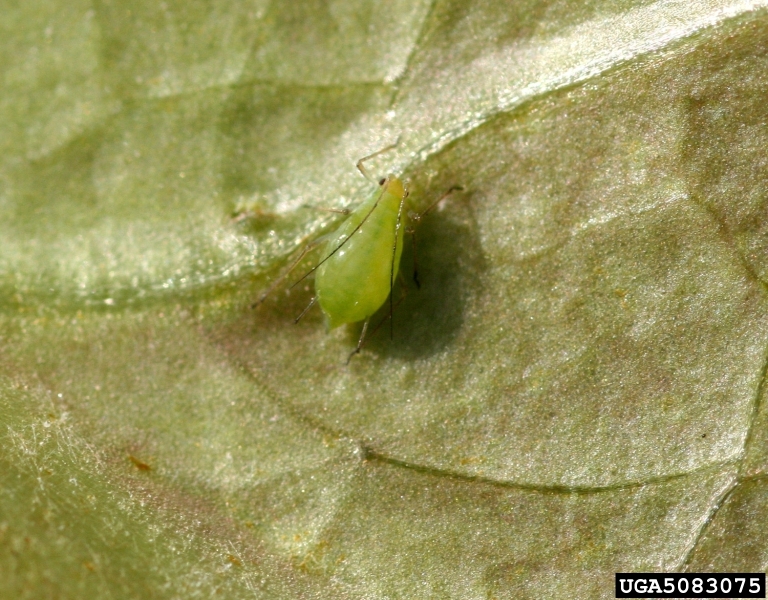 There are over 1300 aphids in North America that vary in color from green, brown, red, to black. These small (< 0.5 inches), sap-sucking insects can be identified by the tubes sticking out of their back side (cornicles), however not all aphids have well-developed cornicles. Healthy plants can tolerate substantial feeding, but excessive feeding can cause plant stress, excess honey dew production, and the growth of sooty mold on honeydew-covered leaves. Some aphids produce galls, while others produce white wax-like material on their bodies (woolly aphids)-some are vectors of plant pathogens.
There are over 1300 aphids in North America that vary in color from green, brown, red, to black. These small (< 0.5 inches), sap-sucking insects can be identified by the tubes sticking out of their back side (cornicles), however not all aphids have well-developed cornicles. Healthy plants can tolerate substantial feeding, but excessive feeding can cause plant stress, excess honey dew production, and the growth of sooty mold on honeydew-covered leaves. Some aphids produce galls, while others produce white wax-like material on their bodies (woolly aphids)-some are vectors of plant pathogens.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
|
Resources:
Carpet Beetle & Warehouse Beetle (Dermestidae)
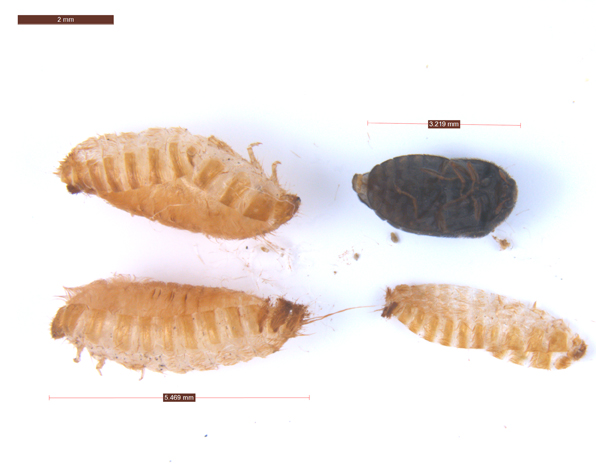

Dermestid beetles, also called carpet, hide, or warehouse beetles, are the second most frequently submitted insect group to the UPPDL. These household pests can infest everything from stored grains, powdered milk and protein mixes, etc., to leather furnishings, animal-based products, wool clothes, sweaters, human hair, and dead insects and animals. Given the variety of feeding habits, it is critical to have your beetle identified to help locate and eliminate the infestation source.
Larvae are small-1 to 10 mm in length-and usually have longer hairs at the end of the body. They are normally light to dark brown in color. When larvae grow, they shed their skin leaving behind a shell (exuviae), which can also be used to locate infestations. While not poisonous, some dermestid larvae are covered in arrow-shaped hairs which can cause throat and mouth irritation if consumed.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
|
Resources:
Armyworms, Cutworms, and Earworms (Noctuidae)
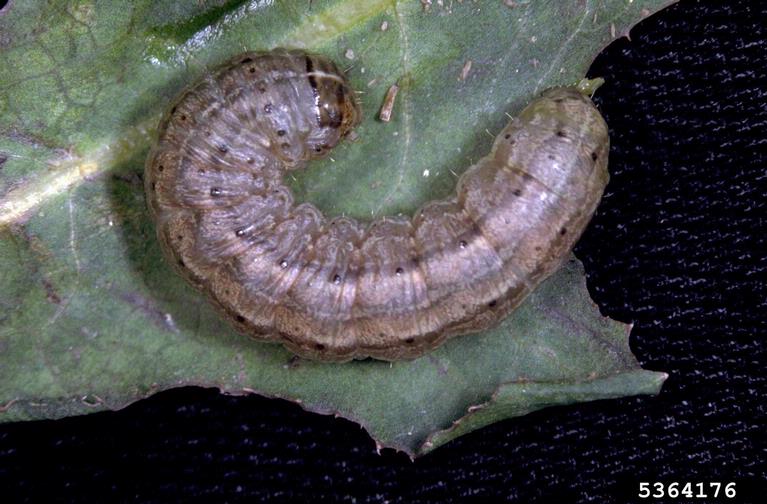 Noctuids are a large group of mostly night-flying moths that are major pests around the world. The plump, nearly hairless larvae are usually active at night or in hidden areas like in corn husks, just below the soil surface, or at the base of grass, plants, etc.
Noctuids are a large group of mostly night-flying moths that are major pests around the world. The plump, nearly hairless larvae are usually active at night or in hidden areas like in corn husks, just below the soil surface, or at the base of grass, plants, etc.
Most adult noctuid moths are difficult to distinguish from other related moths. In general, noctuids are mostly robust, brown, and have lighter-colored, kidney-shaped patches on their wings. Proper identification of related species requires dissection and examination of the genitalia.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
|
Resources:
Longhorned/Roundheaded Wood Boring Beetles (Cerambycidae)
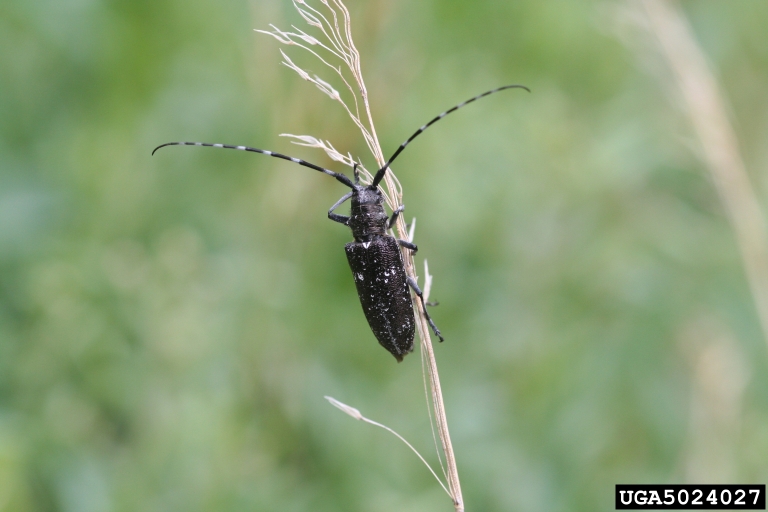 Immature borers (larvae) feed on wood tissues within the tree, moving from under the bark deeper into the tree with time. Eventually, larvae pupate and emerge from the tree as adults, leaving large circular holes in the bark. Adult beetles will seek a new host tree, mate, lay eggs, and continue the cycle. Insecticide applications should be timed to occur just before adult beetle emergence.
Immature borers (larvae) feed on wood tissues within the tree, moving from under the bark deeper into the tree with time. Eventually, larvae pupate and emerge from the tree as adults, leaving large circular holes in the bark. Adult beetles will seek a new host tree, mate, lay eggs, and continue the cycle. Insecticide applications should be timed to occur just before adult beetle emergence.
Longhorned borers are easily recognized by their long antennae, and a more rounded shape when compared to flatheaded borers. These borers lay their eggs on the bark of stressed trees. Upon egg hatch, the small larvae bore their way through the bark and into the wood causing damage. Control of larvae already under the bark is not feasible. Control of longhorned borers must be preventative.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Weevils, Billbugs & Bark Beetles (Curculionidae)
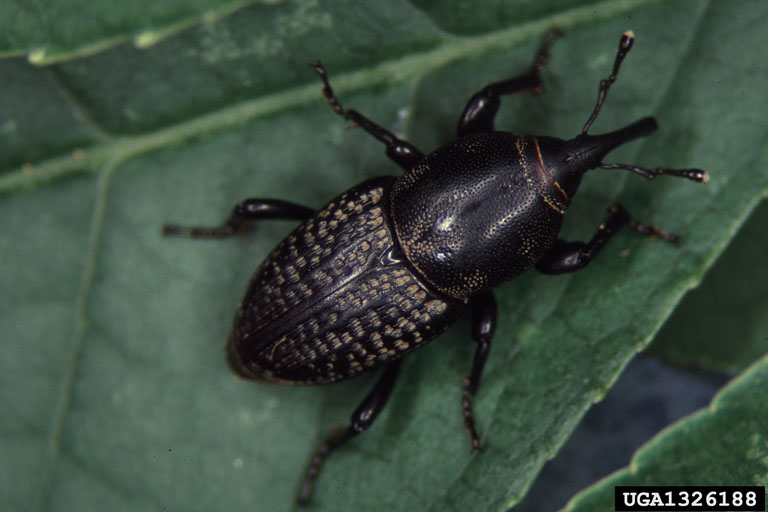 Weevils are beetles easily recognized by their long snouts. In Utah, root weevils are the most commonly encountered group. These beetles are responsible for the small notching patterns seen on leaf margins of lilac and other plants. The immatures, or larval stages, can be destructive to plant roots. Look for these beetles at night with a flashlight, as they are nocturnal.
Weevils are beetles easily recognized by their long snouts. In Utah, root weevils are the most commonly encountered group. These beetles are responsible for the small notching patterns seen on leaf margins of lilac and other plants. The immatures, or larval stages, can be destructive to plant roots. Look for these beetles at night with a flashlight, as they are nocturnal.
The next most frequently encountered weevils in Utah are the notorious turf pests-billbugs. These beetles are most frequently seen walking on sidewalks next to turf, and the larvae can cause major damage to turf roots/stems in the thatch layer.
Immature weevils, including bark beetles, are similar in appearance. The larvae are small, legless, white grubs with a brown head capsule. Look for these in turf thatch (billbugs), at the base of lilac or other plants (root weevils), or under the bark of trees (bark beetles).
Recently grouped into the weevil family, bark beetles are one of the most destructive forest pests in the world. Within the urban landscape bark beetles are major pests of spruce, pines, fruit and nut trees, and ornamental hardwoods. In Utah, species of Ips beetles are the most destructive to urban pines, while species of Scolytus are most detrimental to fruit and some ornamental trees.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
Root Weevils:
|
Bark Beetles:
|
Resources:
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Elm Bark Beetles and Dutch Elm Disease
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Billbugs in Turfgrass
- Fact Sheet Colorado State Univ.: Root Weevils
- Fact Sheet UC IPM: Root Beetles
- Fact Sheet Colorado State Univ.: Billbugs and White Grubs: Control in Home Lawns
- Fact Sheet UC IPM: Bark Beetles
- Fact Sheet Colorado State Univ.: Ips Beetles
Ants (Formicidae)
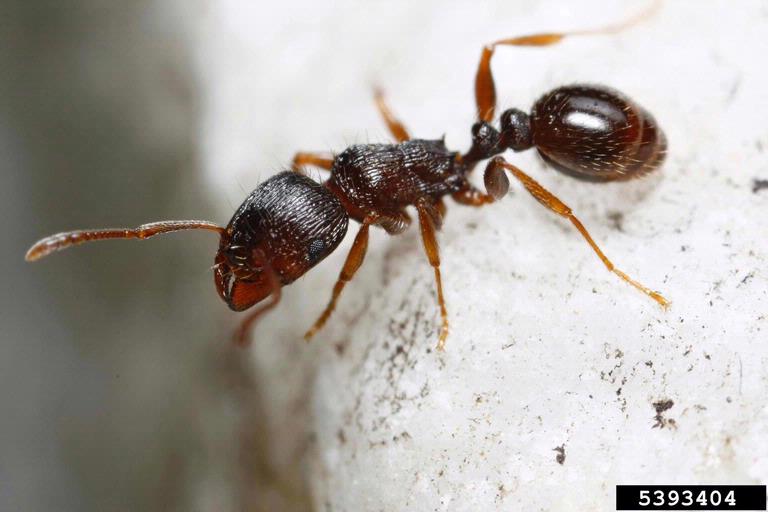

By far the most common household pest Utahn's experience during the spring months is the pavement ant (Tetramorium caespitum). These ants like to make their nests in cracks in the driveway, sidewalk, and foundation, and can often be seen forming large aggregations just outside of their nests. While they do not sting, they can become nuisance pests when the come inside to rummage through your garbage or cabinets.
The other major group of ants of concern in Utah are the carpenter ants. Certain species of these ants can cause major structural damage to homes and businesses if they are left uncontrolled. Identification of the exact ant is critical because different carpenter ant species are more destructive than others. The presence of some species may require extensive measures for eradication, while others may be handled by the average homeowner.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
Carpenter Ants:
|
Other Ants:
|
Resources:
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Carpenter Ants
- Fact Sheet Colorado State Univ.: Carpenter Ants
- Fact Sheet Colorado State Univ.: Ants in the Home
- Fact Sheet Univ. Nebraska-Lincoln: Ants around the Home and Landscape
- Fact Sheet Univ. Nebraska-Lincoln: Ant Identification Resources
- Fact Sheet UC IPM: Carpenter Ants
Leaf Beetles (Chrysomelidae)
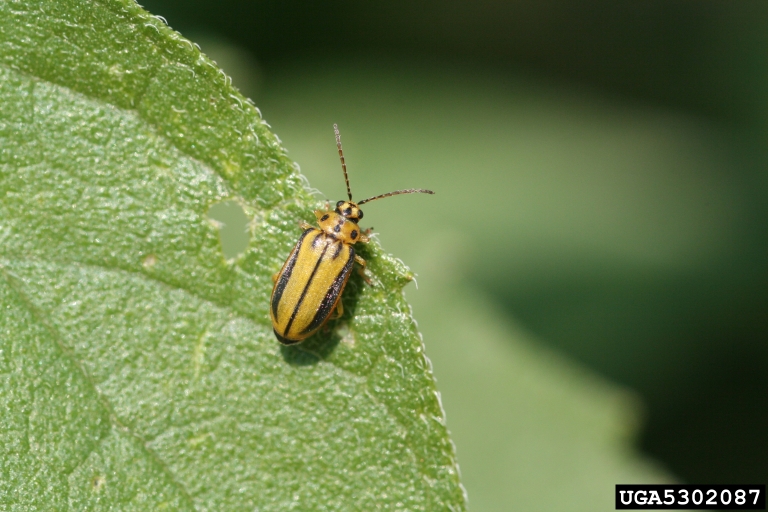

Commonly known as leaf beetles, many members of this large, diverse family are pests of vegetable and grain crops, as well as ornamental pests. Some species of this group could be mistaken for longhorned beetles, but their larval habits are very different. Chrysomelids are usually brightly colored, smaller beetles that give leaves a shothole or a tattered/skeletonized appearance under heavy infestations. Some leaf beetles are nuisance pests in the winter when they overwinter in peoples' homes in large numbers.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Asparagus Beetle and Spotted Asparagus Beetle
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Western Corn Rootworm
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Cereal Leaf Beetle
- Fact Sheet Colorado State Univ.: Flea Beetles
- Fact Sheet Colorado State Univ.: Elm Leaf Beetles
White Grubs/May/June/Beetles (Scarabaeidae)
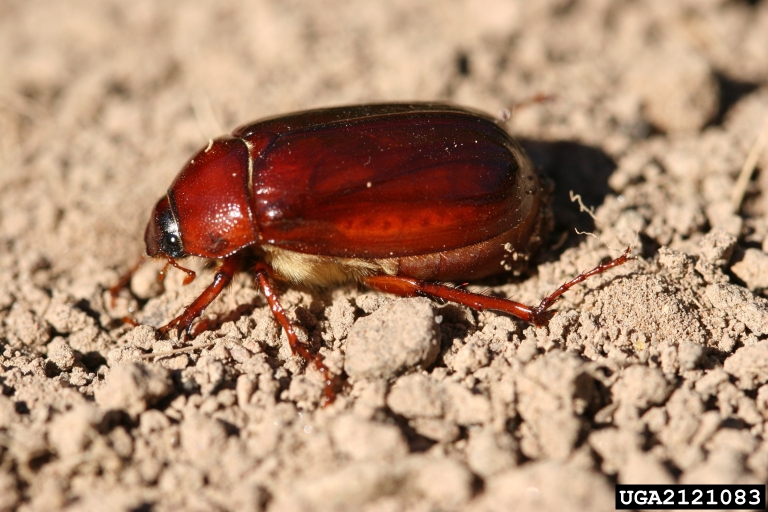

In Utah, white grubs are second to billbugs as turf pests. The adults of most May/June beetles are dull brown in color, with some notable exceptions such as the 10-lined June beetle. In some cases the adults can cause minor damage to crops and ornamental plants, however it is usually the larvae (grub) that causes most of the damage while feeding on host roots. White grubs are distinguished from billbug larvae by the presence of 6 legs near the front of the larval body, and the classic "C" shape in which white grubs are always found. Adults are often collected at porch lights at night because they are attracted to lights; larvae are normally found while digging in the garden or yard.
Japanese beetle, an invasive species of white grub, was detected in Orem, UT and a few other locations in Utah. Currently, an eradication program for this beetle is underway in Orem. If you think you've captured a Japanese beetle, please contact the UPPDL for an immediate identification.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Seed Bugs (Lygaeidae)
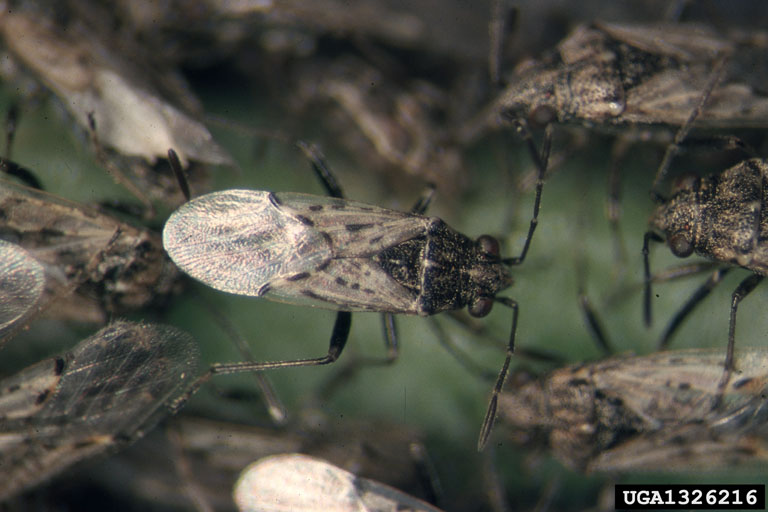

One of the most common seed bugs submitted to the UPPDL is the false chinch bug. It prefers to feed on plants from the Brassicaceae (mustard family) including broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, turnip, radish, etc. This insect can become very abundant during hot, dry conditions when their host plants begin to dry up. The habit of aggregating on, in, and around peoples' homes during drought periods is exacerbated by irrigation of turf, or nearby freshly cut alfalfa fields, etc., as the insects search for moisture. Aside for their aggregating habit, false chinch bugs rarely cause damage that warrants insecticidal control.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Clearwing Moth Borers (Sesiidae)
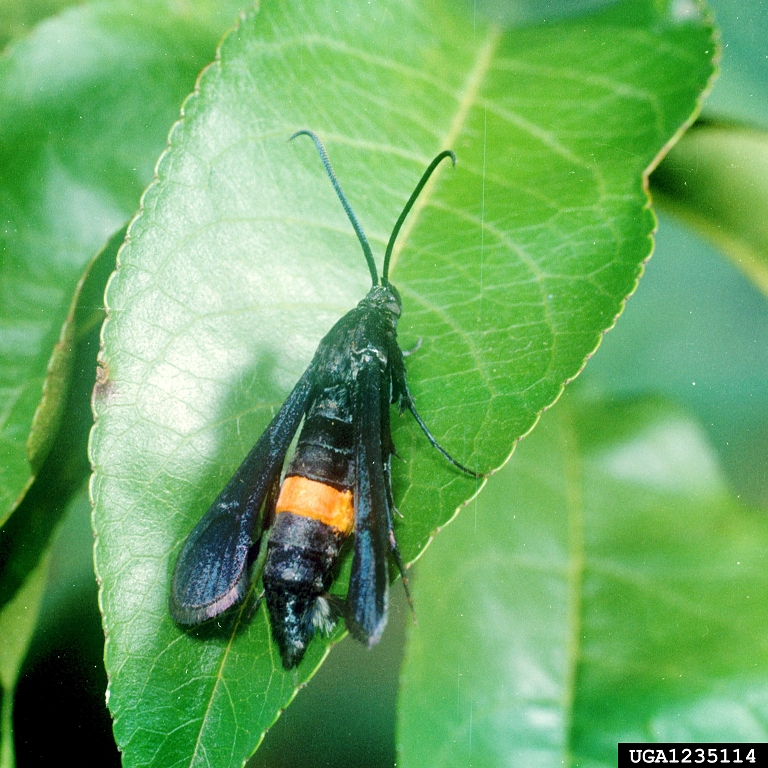

Clearwing moths are a little-known pest in Utah, however they cause major damage to fruit and ornamental plants every year. One diagnostic feature of clearwing moths is their shed pupal case, which can be found protruding from exit holes in the bark.
The lilac-ash borer closely resembles paper wasps and yellowjackets, but can cause major damage or death to ash and lilac trees. Young, stressed trees are particularly vulnerable.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Greater Peachtree Borer
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Lilac-Ash Borer
- Fact Sheet Colorado State Univ: Peachtree Borer
- Fact Sheet UC IPM: Clearwing Moths
Indian Meal Moth (Pyralidae)
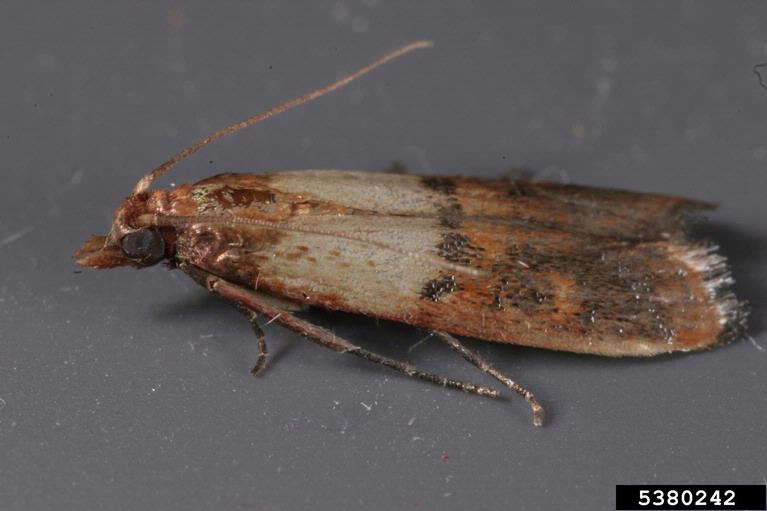

Indian meal moth is one of the most frequently submitted pests of stored food products in Utah. Infestations are often discovered by the presence of adult moths in the home, or by finding larvae and silk in stored food. Control measures for this pest are non-insecticidal. Identify and remove all infested food products. Thoroughly clean areas around the infestation. Store new products in air-tight containers to prevent reinfestation.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Codling Moth (Torticidae)
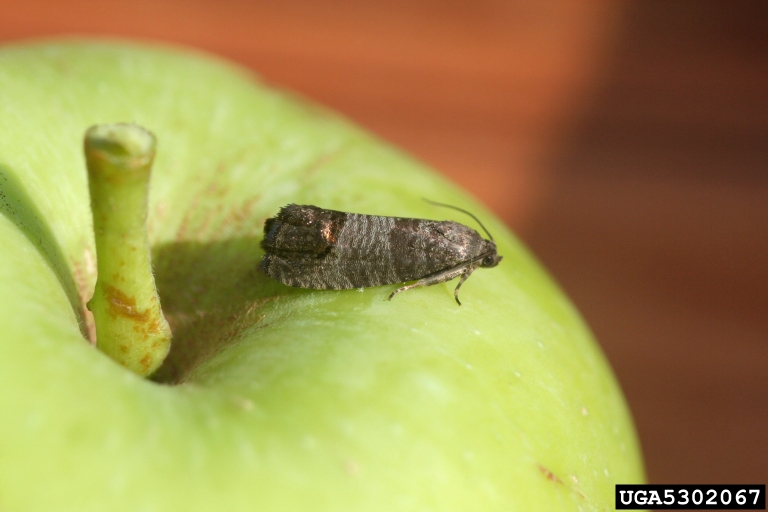

Codling moth is the major pest of apple and pear in Utah. The larvae are the damaging stage of this pest, boring into fruit and causing a loss of marketability of fruit. Control of this pest is best with an integrated approach. Pest monitoring and insecticide treatments should be strictly timed to minimize unnecessary sprays. Utah State's Integrated Pest Management Program reports weekly on codling moth, and other pests, advising when to apply sprays, and other control methods.
Please sign up for the pest advisories here: IPM Advisories
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Predaceous Ground Beetles (Carabidae)
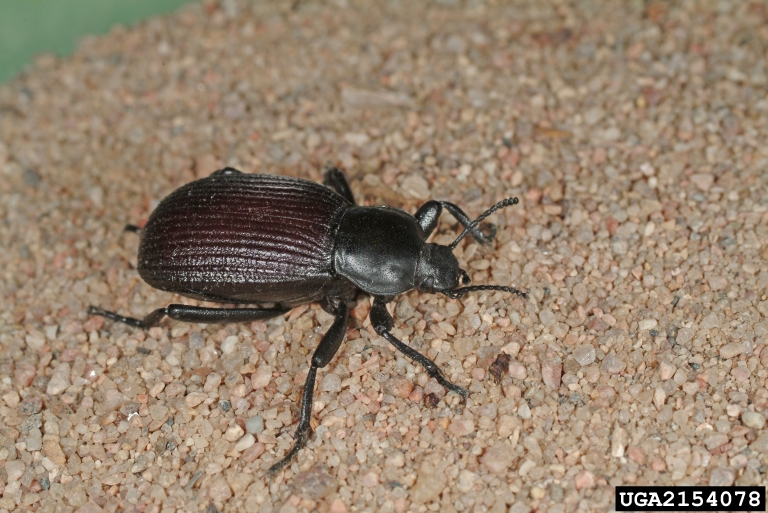 Most species of ground beetles are predaceous and should be considered beneficial. Identifying beetles can be difficult; if you have any doubt that the beetles around your home are predators or plant pests, please send them to the UPPDL for identification. Distinguishing between pest and beneficial insects is important so that natural pest controls are not unnecessarily killed.
Most species of ground beetles are predaceous and should be considered beneficial. Identifying beetles can be difficult; if you have any doubt that the beetles around your home are predators or plant pests, please send them to the UPPDL for identification. Distinguishing between pest and beneficial insects is important so that natural pest controls are not unnecessarily killed.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Millipedes (Diplopoda)
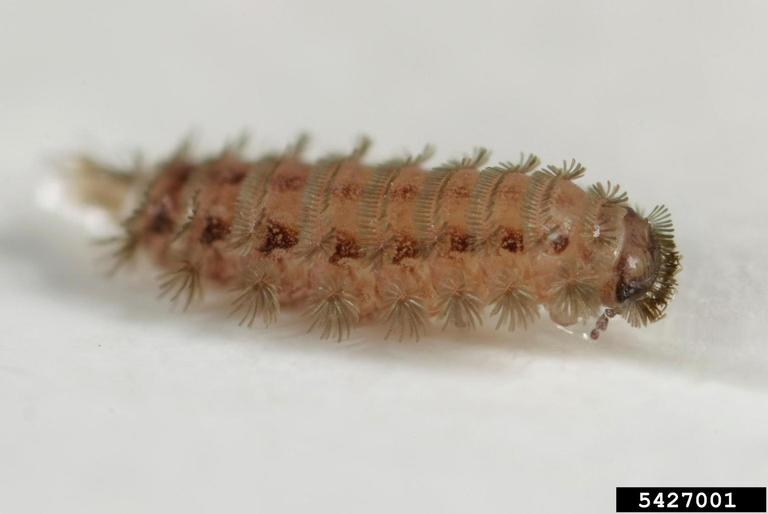

Millipedes are submitted to the UPPDL when they are found invading homes, or in the garden under rocks, duff, or logs. They pose no threat to humans, and rarely cause damage to plants. They are easily recognized as 1-1.5 inch brown "worms" that coil up when disturbed. They feed primarily on decaying plant material, not on healthy plants. Indoors, they are highly susceptible to drying out, so they usually die inside of a home unless there are moisture issues that need resolving.
Duff millipedes (Polyxenidae) can often be mistaken for carpet beetle larvae. Control methods for these two insects are very different. Have your suspect duff millipede identified to receive a targeted management plan.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Peach Twig Borer (Gelechiidae)

Peach twig borer is a major pest of peach, nectarine, and apricot in Utah. Spring and early generations can cause damage when larvae bore into new shoots, while summer and fall generations can cause damage to fruit. Control of this pest is best using an integrated approach. Pest monitoring and insecticide treatments should be strictly timed to minimize unnecessary sprays. Utah State's Integrated Pest Management Advisories report on peach twig borer, and other pests, advising when to apply sprays, giving examples of some available products.
Please sign up for the pest advisories here: IPM Advisories
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Thrips (Thysanoptera)
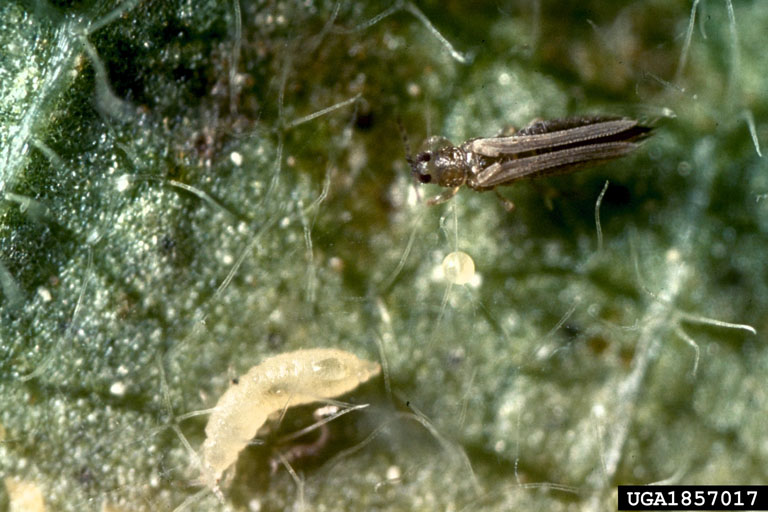 Thrips are small insects, barely visible to the unaided eye. Despite their small size, thrips can be very destructive to numerous plants. Typical damage appears as small yellowish specks on foliage (stippling), flowers, and fruit, wilting/stunting of plants or fruit, leaf drop, petal streaking, and fruit scarring. Their habit of feeding in sheltered places such as curled leaves, flower petals, or in buds makes control difficult. Their shiny silvery-black excrement can also be an indication of their presence.
Thrips are small insects, barely visible to the unaided eye. Despite their small size, thrips can be very destructive to numerous plants. Typical damage appears as small yellowish specks on foliage (stippling), flowers, and fruit, wilting/stunting of plants or fruit, leaf drop, petal streaking, and fruit scarring. Their habit of feeding in sheltered places such as curled leaves, flower petals, or in buds makes control difficult. Their shiny silvery-black excrement can also be an indication of their presence.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Onion Thrips
- Fact Sheet Utah State Univ.: Western Flower Thrips
- Fact Sheet UC IPM: Thrips
Assassin Bugs (Reduviidae)
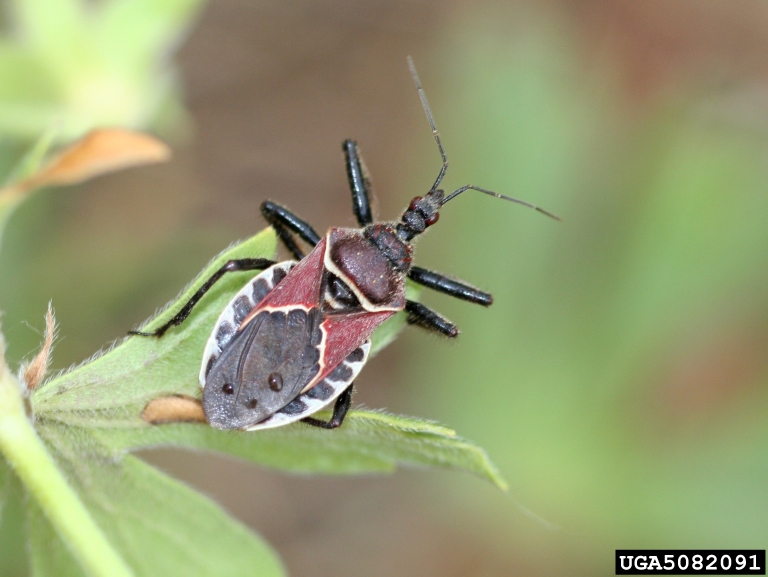 Assassin bugs are predatory true bugs that have piercing-sucking mouthparts. Their mouth parts (rostrum) are shorter than plant-feeding true bugs and only have 3 segments. The short, stocky rostrum allows easy penetration of their prey's hardened exoskeleton, through which they suck out their "juices." Assassin bugs can inflict a painful bite to humans if mishandled, however they should still be considered beneficial insects.
Assassin bugs are predatory true bugs that have piercing-sucking mouthparts. Their mouth parts (rostrum) are shorter than plant-feeding true bugs and only have 3 segments. The short, stocky rostrum allows easy penetration of their prey's hardened exoskeleton, through which they suck out their "juices." Assassin bugs can inflict a painful bite to humans if mishandled, however they should still be considered beneficial insects.
Immature assassin bugs sometimes resemble ants.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Hard Scales (Diasphididae)
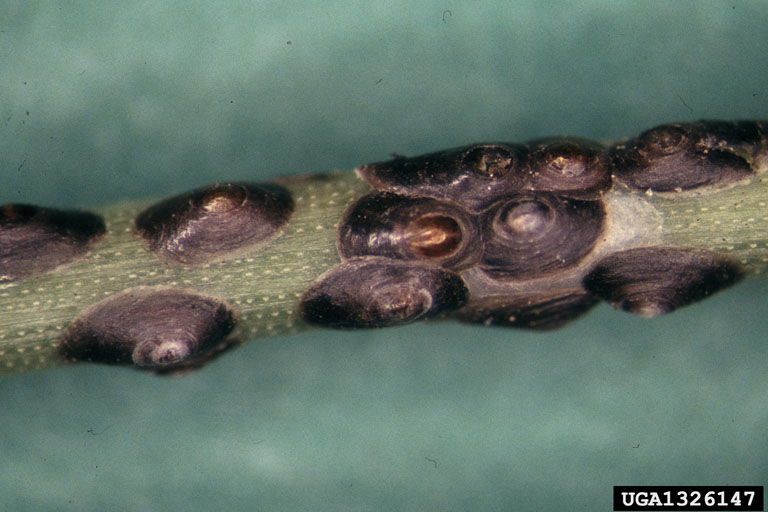 Scales are a common pest insect in Utah. Hard scales spend most of their life stuck in one spot, covered by a hard shell secreted by the insect under it. Immature scales, or crawlers, are very small and orange in color.
Scales are a common pest insect in Utah. Hard scales spend most of their life stuck in one spot, covered by a hard shell secreted by the insect under it. Immature scales, or crawlers, are very small and orange in color.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Darkwinged Fungus Gnats (Sciaridae)
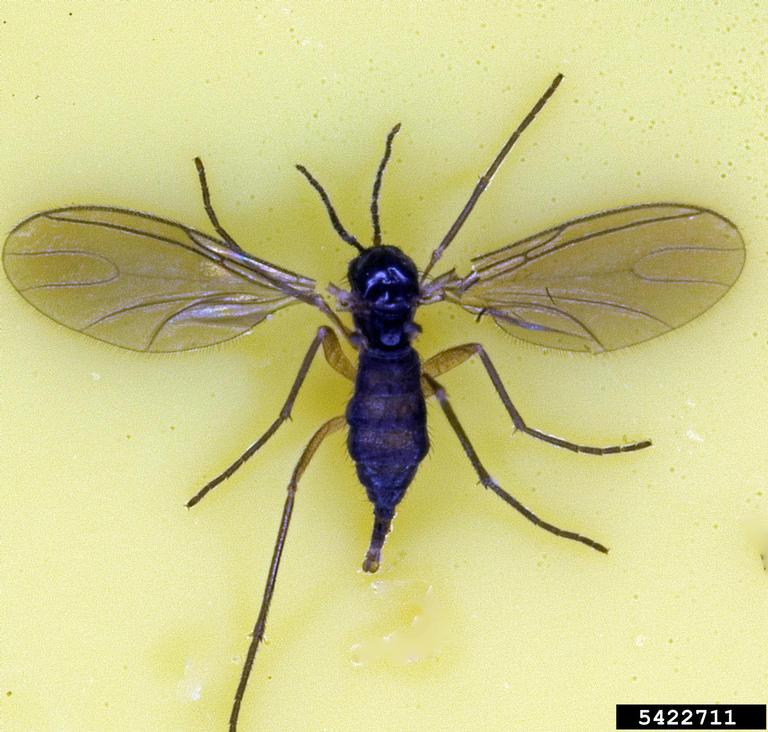 Darkwinged fungus gnats are small, long-legged flies that can become a nuisance indoors when they establish in potted plants, etc. While the adults are not harmful to plants, the larvae can damage roots and stem crowns. Indoor potted plants that are over watered and that have a high humus-content potting mix are at highest risk. If adult fungus gnats are noticed in the home, check all potted plants for signs of adults or larvae. Letting soil dry completely between waterings can help reduce their numbers by killing larvae. Other control methods can be found in the fact sheets listed here.
Darkwinged fungus gnats are small, long-legged flies that can become a nuisance indoors when they establish in potted plants, etc. While the adults are not harmful to plants, the larvae can damage roots and stem crowns. Indoor potted plants that are over watered and that have a high humus-content potting mix are at highest risk. If adult fungus gnats are noticed in the home, check all potted plants for signs of adults or larvae. Letting soil dry completely between waterings can help reduce their numbers by killing larvae. Other control methods can be found in the fact sheets listed here.
Darkwinged fungus gnat larvae have pale white to translucent bodies with black head capsules.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|
Resources:
Flatheaded/Metallic Wood Borer (Buprestidae)
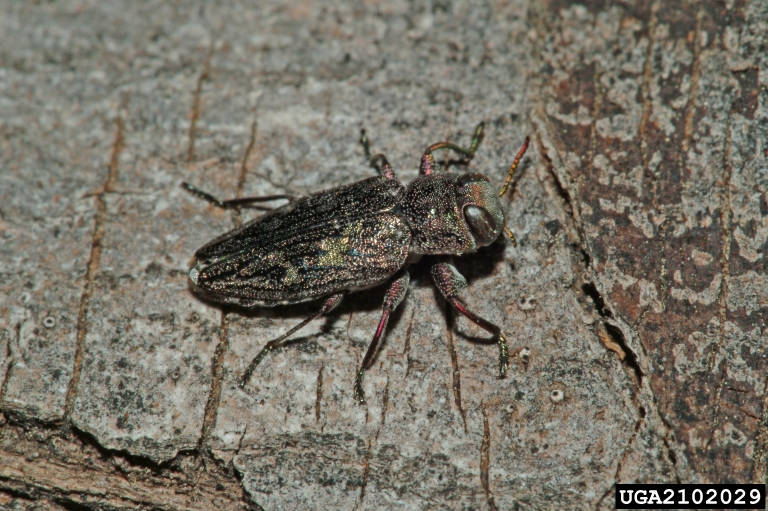 Flatheaded or metallic woodboring beetles can be major pests of fruit and ornamental trees in Utah. Similar to the longhorned beetles, flatheaded borers lay eggs on bark crevices. The eggs hatch and the larvae bore through the bark into the tree where they spend their immature life. Treatments include maintaining tree health, minimizing tree stress, and preventative insecticide sprays applied to the bark before beetle flight.
Flatheaded or metallic woodboring beetles can be major pests of fruit and ornamental trees in Utah. Similar to the longhorned beetles, flatheaded borers lay eggs on bark crevices. The eggs hatch and the larvae bore through the bark into the tree where they spend their immature life. Treatments include maintaining tree health, minimizing tree stress, and preventative insecticide sprays applied to the bark before beetle flight.
Flatheaded borer larvae are named so because of the flattened area just behind the mouthparts and first segment.
Commonly Identified by UPPDL:
|


