Wireworms (Click Beetles)
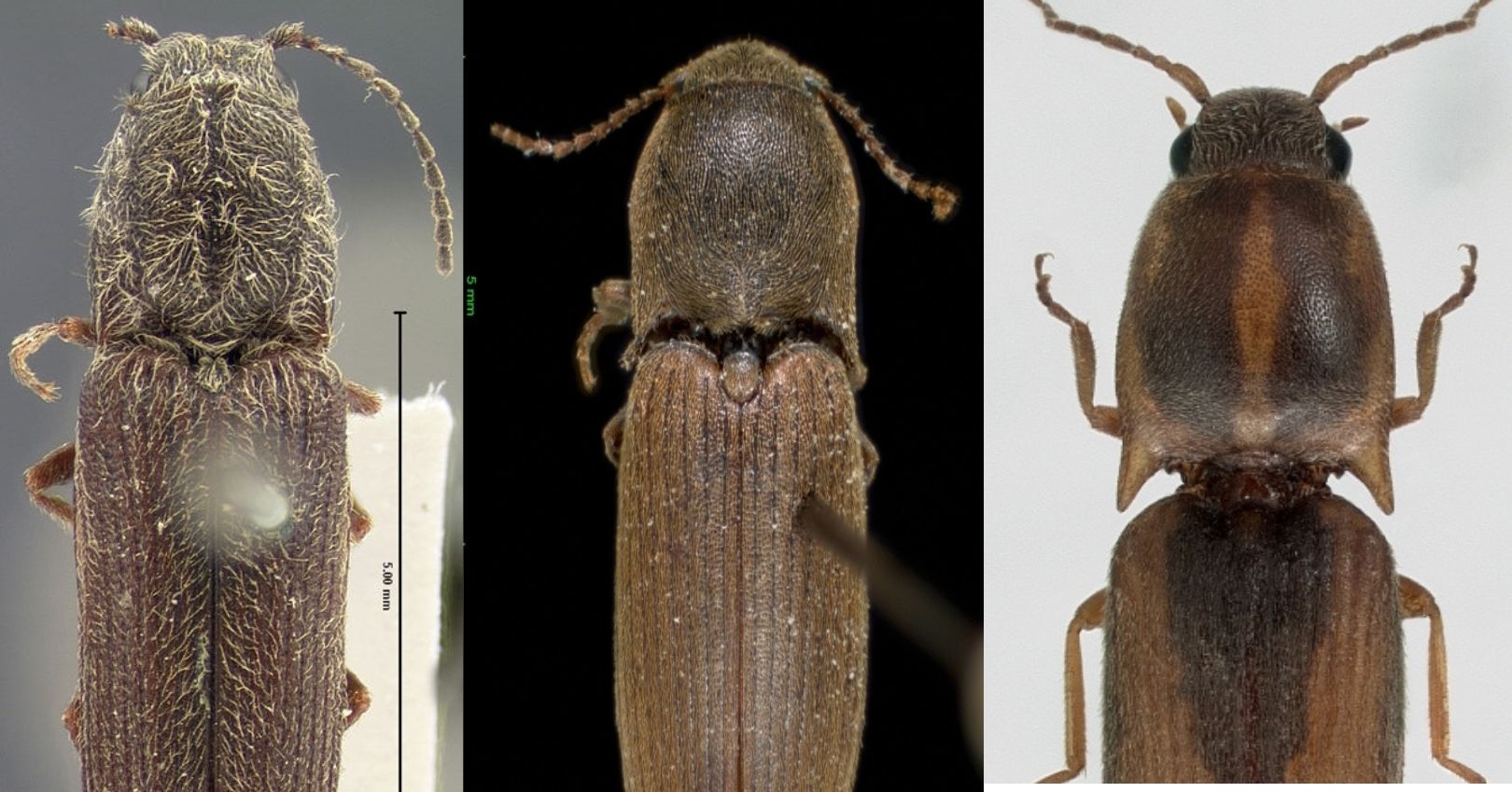


Description
Adult: About ¼ to ½ inch long. Known as click beetles with a hard-shelled body that is black to brown in color. Make distinctive clicking noises with a “hinge” between the thorax and abdomen. Use clicking mechanism to escape threats.
Egg: Small, round, and white; laid singly or in clusters in the moist soil of grassy areas.
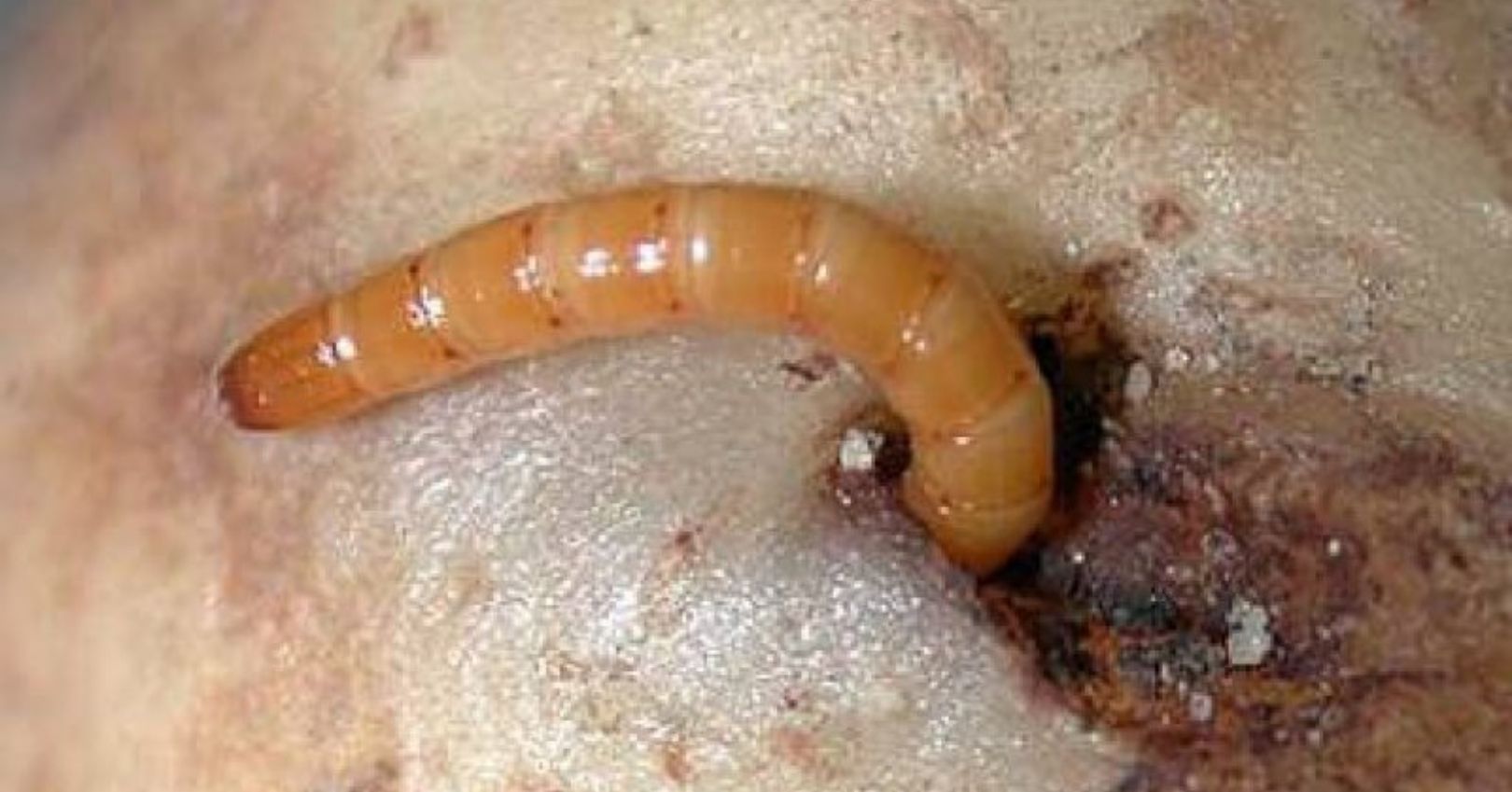
Larva: About ½ to 1 ½ inches long when mature with a wiry look. Shiny white at first, but become light brown or straw colored with age
Pupa: White-colored; contained in an earthen cell in the soil.
Life History
Adults overwinter in the soil and emerge in late April to early May in northern Utah. Between late May and early June, females lay 50 to 400 eggs in the soil about 6 inches deep. Larvae live in the soil for 1 to 6 years, and are closer to the soil surface in spring and fall. During hot summer periods, larvae move deeper into the soil. Some larvae can be found at depths of 1-5 feet or at the hard pan level.
Damage
Wireworms are uncommon, but there have been a few cases in Utah. Limonius species (Pacific Coast, Sugar Beet, Western Field, Columbia Basin wireworms) favor moist conditions while Ctenicera pruinina (Great Basin wireworm) prefers dry lands where annual rainfall is less than 15 inches. All crops are susceptible to wireworm attack; however, bean, grain, corn, potato, and other annual crops are preferred hosts.
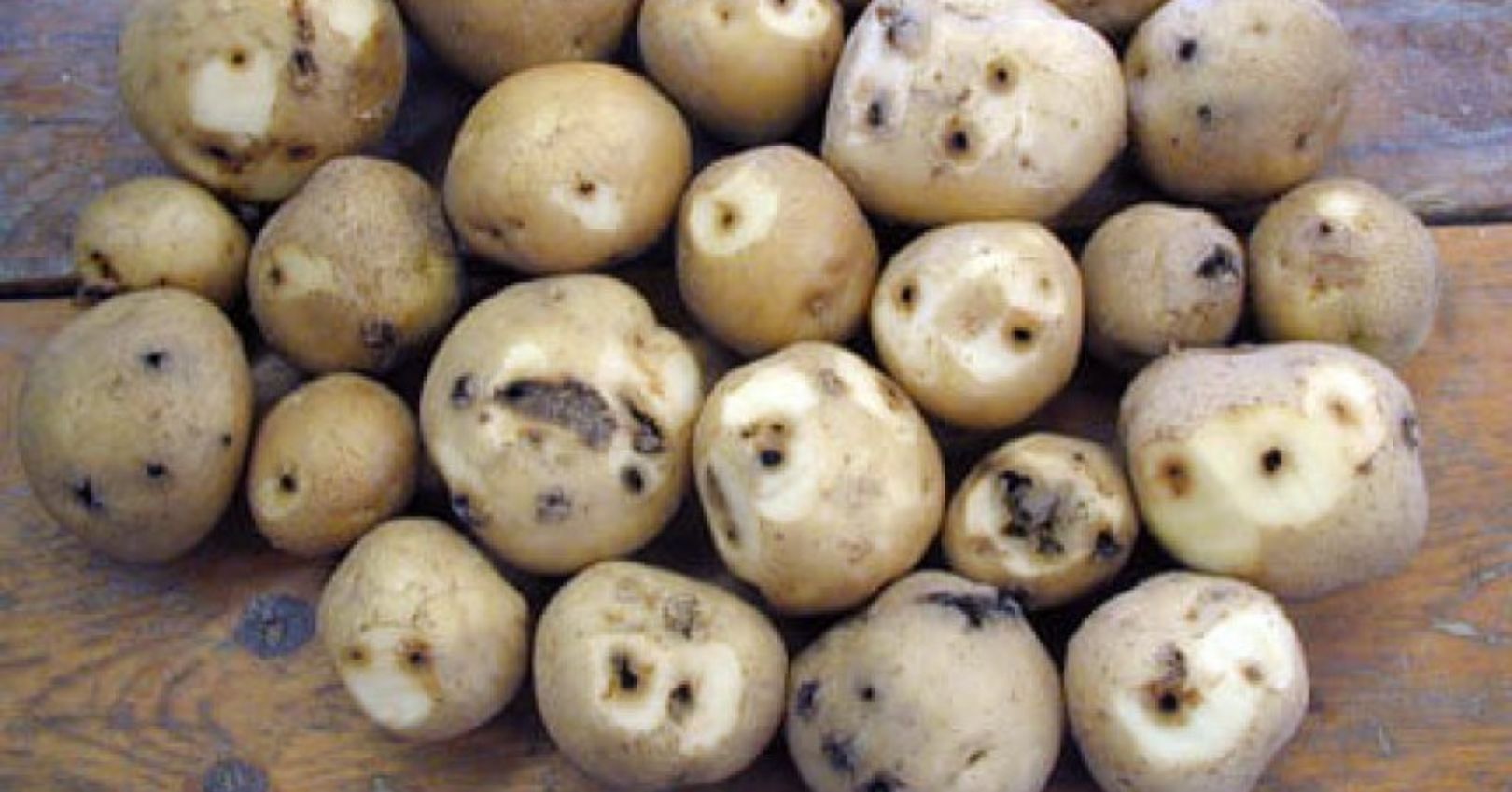
In potato, wireworms will feed on seeds and roots of young plants. Larvae can cause severe damage to potato by creating tunnels in tubers as they feed. Infestations do not spread rapidly from one field to another because female beetles are poor flyers.
Monitoring
Inspect the soil surface for wireworms after plowing or disking fields. Baits can also be used to detect wireworms. Baits include: carrots, untreated corn or wheat seed, or ground whole wheat flour. Place baits 4-6 inches deep in the soil when soil temperatures are at 50°F. If wireworms are detected, collect soil samples in spring with a 6 inch post hole digger and a shake/sifter to estimate the density of wireworms.
Wireworm Soil Sampling Guide
| Acres in field | Number of soil samples | Treatment threshold (# of wireworms) |
| 10 | 30 | 1 |
| 22 | 45 | 2 |
| 40 | 60 | 2 |
| 90 | 90 | 4 |
| 160 | 120 | 5 |
Godfrey, L. D., Entomology, UC Davis, D. R. Haviland, UC Cooperative Extension, Kern Co., UC IPM Pest Management Guidelines: Potato, UC ANR Publication 3463, Insects
Management
Although wireworms are generally uncommon in Utah, there have been a few cases reported. Once present in a field, wireworms can be difficult to eradicate.
Cultural
- Establish a dense plant stand to reduce the impact of wireworm damage.
- Crop rotation. Fields previously planted to grasses, including grass grains, or pasture are at a higher risk for high wireworm populations. Red and sweet clover and small grains, especially barley and wheat, can increase wireworm populations. Include alfalfa and mustards in crop rotations to reduce wireworm populations over time.
- Sanitation. Remove dead plants and tubers throughout the season and at harvest. Wireworm damage typically peaks at mid-season (showing up at harvest as scabbed-over holes in the tubers), and tubers of dead plants can be reinfested, resulting in an increase in wireworm population. Thus, it is important to avoid prolonged periods of time between vine death and harvest.
- Soil drying. Sugar beet and Pacific Coast wireworm (Limonius spp.) populations prefer moist soil and can be reduced by drying the top 15 inches of the soil for several weeks at midsummer. This will especially kill eggs and young larvae. Soil drying is more effective in light sandy to silt loam soils. Conversely, great basin wireworms (Ctenicera spp.) prefer dry soil and can be eradicated by converting dryland fields to continual irrigation.
- Soil flooding. Thoroughly saturating or flooding soils for at least 2 weeks when soil temperatures are above 68°F will significantly reduce wireworm populations. To increase wireworm mortality, alternate periods of flooding and drying.
- Intensive plowing. Wireworm populations can be reduced by plowing three or more times during late spring and early summer.
- Resistant varieties. There are some resistant varieties that may be worth testing if wireworms are a potential problem. A study in Oregon found a range of potato varietal susceptibility to wireworms.
Chemical
Chemical options for wireworm control are few. Organophosphate chemicals have shown to be the most effective and consistent when applied at preplant as a broadcast treatment, or planting-time as a furrow application.
Biological
Birds may feed on wireworms in recently plowed fields, but will not reduce populations below economic levels in seriously infested areas. There are no known biological insecticides.
Percentage of Wireworm Infected Tubers for Various Potato Varieties
| Variety | Percent Infected |
| AC9531 | 1% |
| VC1009 | 1% |
| Cherry Red | 3% |
| Ozette | 13% |
| Yukon Gold | 15% |
| Colorado Rose | 16% |
| Austrian Crescent | 17% |
| Red LaSoda | 17% |
| Satina | 20% |
| Mountain Rose | 20% |
| Nicola | 24% |
| POR01PG22 | 24% |
| Sangre | 27% |
| Huckleberry | 28% |
| Jacqueline Lee | 30% |

