Sale of Business Property
Guido van der Hoeven
Extension Specialist/Senior Lecturer Emeritus, North Carolina State University
Introduction
While operating a farm or ranch business, producers will dispose of property (e.g., livestock, equipment, real estate, etc.) used in the business. This can occur in a variety of ways, with two common methods being sales of assets and trading (like-kind exchange) of property. The purpose of this fact sheet is to discuss and illustrate correct income tax reporting when business assets are sold.
This discussion also addresses, for income tax purposes, different types of business assets and their tax treatment upon sale. One example is the sale of cull breeding animals that were raised by the operator of the farm or ranch. Though these animals may be regarded as “farm products” by business operators (and therefore receive ordinary income treatment), for income tax purposes these animals may receive capital gains treatment. Breeding animals’ purpose is to produce market calves. These market calves are “farm products”, where the breeding animals, are in a sense, “the factory”, and thus receive different income tax treatment (discussed below). Similarly, dairy animals’ purpose is to produce milk, and draft animals’ purpose is to provide power.
Sale of Tangible Personal Business Property
Business property that is tangible, such as tractors, machinery, and single purpose agricultural or horticultural structures is classified as Internal Revenue Code (IRC) Section 1245 property. Farm and ranch operators often purchase such property and place it into service in their farming or ranching business. The cost of this property is recovered (taken as a business expense) through depreciation. When these assets are sold, the owner must report the transaction on the tax return. The sale triggers a taxable event (gain or loss) that is reported on IRS Form 4797, Sale of Business Property, Part III. This form calculates recapture of depreciation as ordinary income, subject to income tax; however, it escapes self-employment tax, which is a tax benefit of sorts to the operator. Originally the depreciation deduction was allowed as a deduction against both ordinary income taxes and self-employment taxes. These assets are IRC section 1245 property, tangible business property, and depreciation is taken as a business deduction to recover the cost of this property.
Example 1:
Knight N. Gale operates a ranch which has a primary product of feeder calves. During the year Knight sold his used baler for $3,500 to a neighbor. Knight bought this baler 10 years ago for $15,000. His adjusted cost basis is zero (meaning he has had the tax benefit of $15,000 of depreciation). Since the baler is tangible personal property, it is IRC section 1245 property. He reports this sale (disposition) using IRS Form 4797, Part II and Part III. Finally, reporting the net result as calculated on Form 4797 on Line 4 of IRS Schedule 1 for Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return.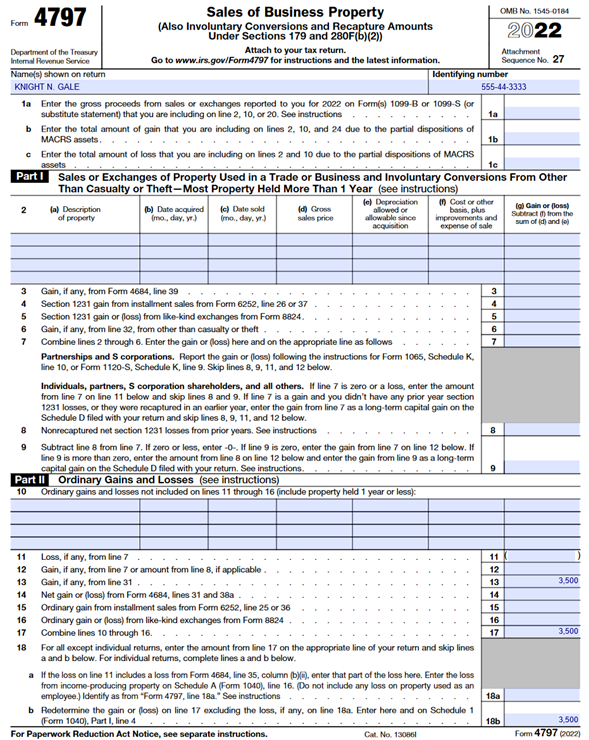
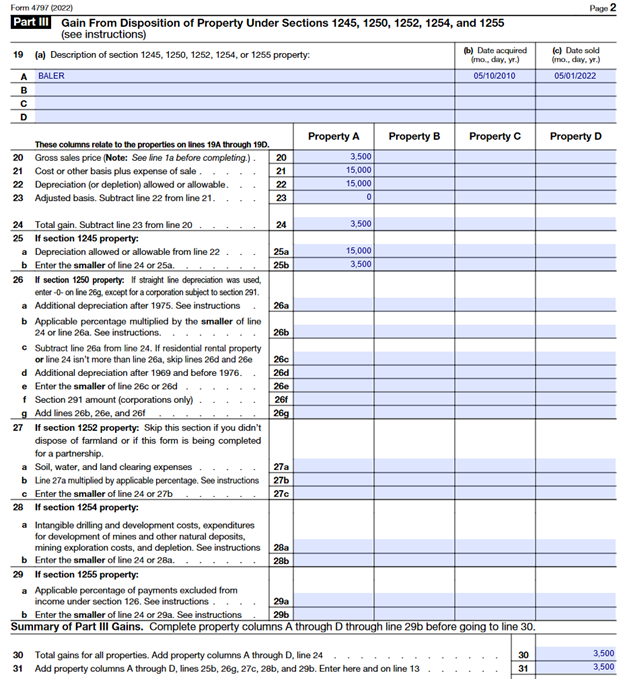
Knight begins the reporting of this sale on Line 19A of Part III by providing acquisition and sale dates.
Further Knight reports the original cost to him on Line 21 and the depreciation allowed on line 22. These two numbers are the same, $15,000 which represents the amount he paid for the baler 10 years ago and the depreciation taken over the baler’s depreciable life (7 years as an agricultural asset). Subtracting Line 22 from Line 21 yields $0 as seen on Line 23. Subtracting Line 23 from Line 20 calculates the net gain, which is depreciation recapture. Depreciation recapture is recognized as the lesser of the depreciation taken ($15,000) or the gain upon sale ($3,500). The $3,500 is now reported on Lines 30 and 31. The value reported on Line 31 is now reported on Page 1 of Form 4797 line 13 per the form instructions. Further, $3,500 is reported on Line 17 as the total from this example and on Line 18b because Knight is an individual. This example’s net number, $3,500, is now reported on Knight’s Schedule 1, Additional Income and Adjustments to Income, Line 4 as part of the calculation of other income, subject to income tax but not self-employment tax as shown below on Line 14.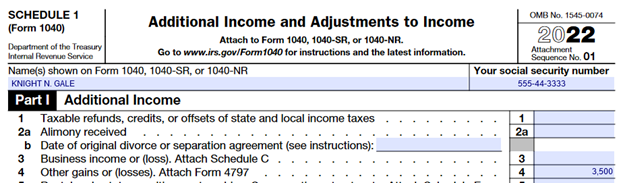
Sale of Business Property Triggering a Capital Gain
Sometimes a transaction involving personal tangible business property (or other business property) may trigger a capital gain when a sale or deemed sale occurs. A capital gain occurs when an individual receives, in a transaction, an amount greater than was paid originally for an item when sold. Long-term capital gain income receives preferential income tax treatment due to lower tax rates applied to capital gain income. Therefore, it is important for individuals to properly report the transaction on their tax return to benefit from the preferential tax rates that capital gains enjoy.
Long-term holding period is generally greater than one year. However, for breeding livestock, dairy, and draft animals the holding period is greater than 24 months.
Example 2:
Frazier Firr, a Christmas tree grower, suffered a theft when his 4-wheeler was stolen from his shop building. Frazier’s insurance company made a replacement payment of $4,750. Frazier had already purchased a new 4-wheeler when the insurance check arrived. Frazier’s adjusted cost basis in the stolen 4-wheeler was $3,612 ($4,250 originally paid less $638 allowable depreciation taken = $3,612). He bought the first machine fourteen months ago. Frazier must treat the insurance payment as a sale to the insurance company and report on IRS Form 4797 in a similar fashion as the previous example, however, an IRC 1231 gain of $500 is also calculated; this gain is treated as a capital gain and reported on line 11 of Schedule D. ($4,750 – $4,250 = $500 gain)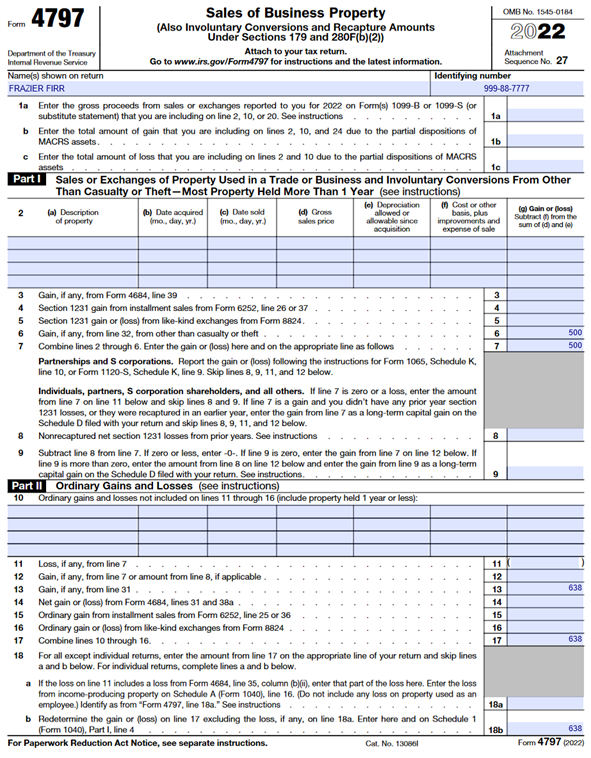
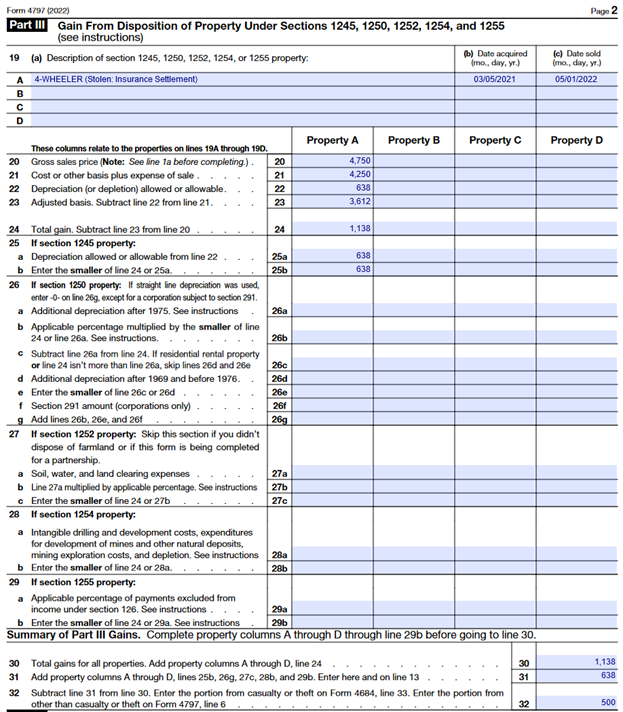

Frazier reports the insurance settlement payment as a sale on Form 4797, Part III in a similar manner as in Example 1; however, a $500 gain is recognized because the insurance settlement paid was greater than the original cost of the 4-wheeler. The $500, as calculated on Line 32 of Form 4797, is reported on Lines 6 and 7 of Form 4797 and further goes to Schedule D (illustrated below) to be treated as a capital gain. The net result of which is reported on Line 7 of Form 1040 as illustrated above.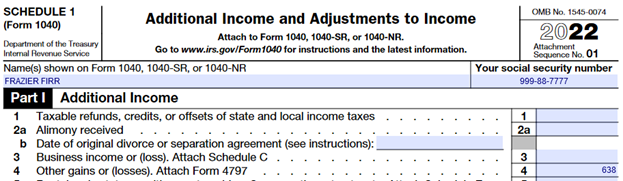

Sale of Raised Breeding, Dairy or Draft Animals
Farmers and ranchers often keep replacement heifers or draft animals from their own breeding herd to replace culled animals or to naturally increase the size of their operations. The farmer and rancher must report the sales of these animals for income tax purposes. Frequently, however, an easy and common error can be made on the individual’s tax return. That error is failing to recognize that these mature animals are treated as the “sale of business property” and qualify as IRC Section 1231 property. Being classified as Section 1231 property allows for favorable tax treatment. Property qualifying as Section 1231 is treated as being a “capital” good if the transaction triggers a gain. Further, if the taxable event triggers a loss, then the loss is treated as an ordinary loss not subject to any capital loss limitations. Simply said, Section 1231 property enjoys the best of both worlds from an income tax perspective. The required holding period is 24 months from the date of acquisition (birth for raised animals) for beef or dairy cattle and horses for Section 1231 treatment. Sales of these animals are not reported on Schedule F, Profit or Loss from Farming, which is where the mistake is made, resulting in a tax liability that is too high. Because these animals are not reported on Schedule F the gains escape self- employment tax and if a net gain is determined on all IRC Section 1231 transactions capital gains treatment results by reporting on Form 4797.
Cattle held for breeding or dairy purposes that do not meet the required holding period (24 months) still escape self-employment taxation, however, these sales are subject to ordinary income tax rates.
Other animals held for breeding, such as goats or swine, are treated in the same manner as the illustrated dairy cattle example; however, the holding period for IRC Section 1231 treatment is 12 months from the date of acquisition (birth in the case of raised animals).
Example 3:
Laque Toose, a dairy farmer, has a milking herd of 150 cows. Laque generally replaces 20 percent of his herd each year with his own raised heifers; he sells the replaced cull cows, which he raised, at the local livestock sales barn. During the course of the year, some of his replacement heifers develop conditions that require removal from the milking herd before they become productive. In 2022, Laque has sales of $20,000 of culled milk cows and $4,500 of culled replacement heifers. Laque reports his sales of these culled animals as illustrated below.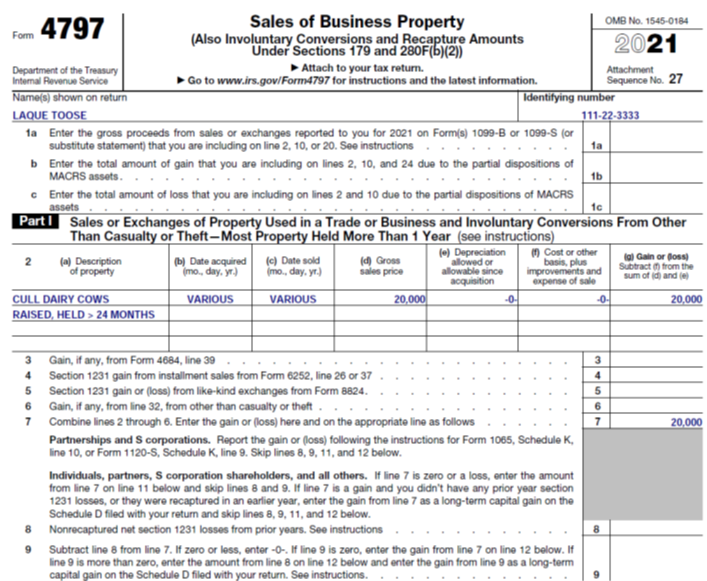
Laque begins reporting the culled milk cow sales on Line 2 by describing the property in Column a. Columns b and c are used to provide acquisition and sales dates, in this case “various” was used as a simplifying technique to report all raised cattle as one number. Column d is where Laque reports the gross sales price followed by Columns e and f with zeros since these cattle were raised on the farm. Column g is therefore the gain of $20,000, which is equal to the sales price. Line 7 is the total of Lines 2-6, in this example there is only one value on Line 2 that is summed. As can be seen in the line instructions for Line 9, Form 4797, the net gain, in this case $20,000 is reported on Schedule D, like Example 2 above, so that these cull cows will receive capital gains income tax treatment as well as escape self-employment tax.
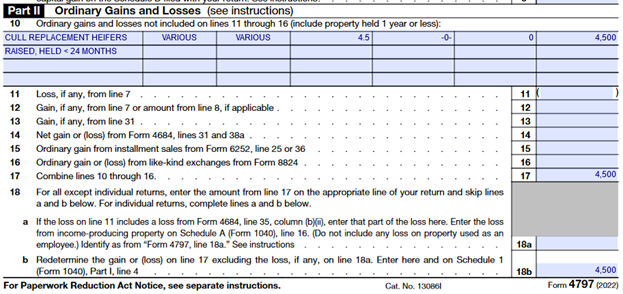
The reporting of the cull heifers- held less than 24 months is also reported on Form 4797, Sales of Business Property, however, on Part II instead of Part I as illustrated below.
Similarly, Laque uses Line 10 to describe and identify the culled heifers held less than 24 months; however, he uses Part II of Form 4797. His acquisition and sale dates varied throughout the ownership period; therefore, he uses the term “various” denoting these dates. The sale proceeds, $4,500, are reported in column d. Because these animals are raised on the farm there is no depreciation taken or basis to report. The entire sale is a gain and reported as such in column g. In this example, these cull heifers are the only reportable transaction, therefore the $4,500 is brought to Lines 17 and 18b as seen above on the partial Form 4797.
Laque reports the values: deemed capital gain of $20,000 and ordinary income of $4,500 on his IRS Form 1040 like Example 2 earlier in this discussion.
Deemed Sale Resulting from a Trade
With the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act in 2017, like-kind exchanges of personal property results in a “deemed sale”. The sale price is the trade allowance given by the equipment dealer for example. Therefore, there is an increased responsibility to report traded equipment correctly. Revisiting Example 1, Knight, instead of selling the baler to a neighbor he received a trade-in allowance of $3,500 however, the income tax reported would be exactly the same. However, Knight would be able to increase the basis of the newly acquired equipment by the trade allowance because he recognizes the gain on his income tax return for the year of the trade.
Conclusion
Obviously, Examples 1, 2 and 3 are simplified to illustrate the correct reporting of income that is generated by the sale of business property in the normal course of the operator’s farm or ranch management. A business, over the course of a year, may have several such transactions that will be combined on the tax return.
Operators are encouraged to properly record these transactions in their business records so that they or their tax professional can correctly and accurately report income on the individual’s income tax returns. Notations that reference these transactions, during the year, can provide invaluable information as income tax returns are being prepared and filed.
IRS Publications
To access the forms shown in this paper: Form 1040 and Form 4797, and other IRS forms and publications, go to www.irs.gov and click on “Forms and Publications”. Then click on “Publication number” under “Download forms and publications by:” Type the publication number in the find box to search for the publication. Publications may be viewed online or downloaded by double clicking on the publication.
IRS Publication 225, Farmer’s Tax Guide. Chapter 9 discusses dispositions of property used in farming and Chapter 12 discusses self-employment tax issues.
IRS Publication 547. This publication provides more detail relative to gains or losses from the destruction or theft of business property.
Additional Topics
This fact sheet was written as part of Rural Tax Education, a national effort including Cooperative Extension programs at participating land-grant universities to provide income tax education materials to farmers, ranchers, and other agricultural producers. For a list of universities involved, other fact sheets and additional information related to agricultural income tax please see RuralTax.org.
- Like-Kind Exchange (Trade) of Business Assets
- Involuntary Conversion of Business Assets
- Weather-Related Sales of Livestock
This information is intended for educational purposes only. You are encouraged to seek the advice of your tax or legal advisor, or other authoritative sources, regarding the application of these general tax principles to your individual circumstances. Pursuant to Treasury Department (IRS) Circular 230 Regulations, any federal tax advice contained here is not intended or written to be used, and may not be used, for the purpose of avoiding tax-related penalties or promoting, marketing or recommending to another party any tax-related matters addressed herein.
USDA is an equal opportunity provider, employer, and lender. Rural Tax Education is part of the National Farm Income Tax Extension Committee. The land-grant universities involved in Rural Tax Education are affirmative action/equal opportunity institutions.
This material is based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, under agreement number FSA21CPT0012032. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the U.S. Department of Agriculture. In addition, any reference to specific brands or types of products or services does not constitute or imply an endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture for those products or services.
Published February 2023