Desert Parsley
Common Name(s):
Desert Parsley
Desert Biscuitroot
Carrotleaf Desertparsley
Carrotleaf Lomatium
Scientific Name:
Lomatium foeniculaceum (Nutt.) Coult. & Rose
Scientific Name Synonyms:
None Known
Symbol:
LOFO
Description:
Life Span: Perennial
Origin: Native
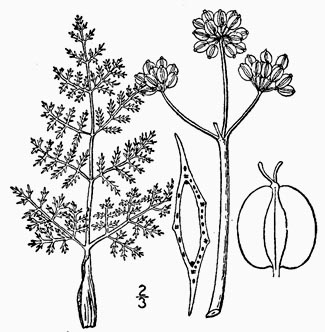
Growth Characteristics: Desert parsley is a prostrate plant with finely dissected leaves growing of to 8 cm high and 25 cm wide from a taproot. Flowers appear about the same time as the leaves. The stems and leaves are covered in hairs. Some plant’s foliage has a grayish look to them. Flowers April-May.
Flowers: This very early flowering plant has a yellow flower, in an umbel, on a long flowering stem. There is only one compound umbel per stem. . Each individual umbel (called umbellets) is subtended by a small hairy bract. There are up to 15 flowers per umbellet. For each individual flower in the umbels, the rays are up to 2 cm long, with dense, long, soft hairs. Each flower has 5 petals which are yellow, and glabrous. There are 5 stamens, and the filaments are yellowish, up to 2 mm long, and glabrous. Anthers are yellow, .6 mm long. There are 2 styles which are erect, 2.5 mm long, curled, yellowish, glabrous, and surround by an inflated nectary at base. The ovary is inferior, green, glabrous, 1.5 mm long, with 2 chambers.
Fruits/Seeds: Fruits up to 4 mm long, 2.5 mm wide, football shaped, pubescent, and 2-seeded. The seeds are very similar to those of dill, and have papery “wings.”
Leaves: The leaves are similar to parsley leaves, only lead-gray in color because of an insulation of silky hairs. They are alternate, with petioles, 3-4 times pinnately divided. The petioles are sheathing, and often purplish, at the base. The entire leaf can be up to 20 cm long, 10-15 cm wide, and hairy. The first divisions on the leaf are opposite, all other divisions are alternate.
Stems: No real “stem”; the leaves and flower stalks instead arise directly from the crown of an exceptionally thick taproot. Flowering stems are up to 25 inches tall, branching or simple, single or multiple. Stems are fragrant, with ridges running the length of them, soft-hairy to course-hairy, herbaceous, and erect.
Ecological Adaptions:
Habitat is prairie grasslands, eroded slopes, glades, and rocky open ground. It cannot grow in shade.
Soils: Prefers light (sandy), medium (loamy), and heavy (clay) soils and requires well-drained soil. The plant prefers acid, neutral and basic (alkaline) soils. It requires dry or moist soil.
Associated Species: Black sagebrush, pinyon pine, Utah juniper.
Uses and Management:
Desert parsley seems to be avoided by livestock and has no known economic uses. This plant is a member of the parsley family (Apiaceae).
The family includes the useful carrot, parsnip, caraway and dill, but also deadly species such as the water hemlock, which probably is the most poisonous plant in the North Temperate Zone. The generic name Lomatium stems from the Greek lomation, "a little border," in reference to the winged fruit. The specific epithet foeniculaceum means "resembling fennel" in botanical Latin.
The cooked root can be dried and ground into a powder and then be mixed with cereal flours or added to soups etc. The leaves are edible and said to taste like parsley.

