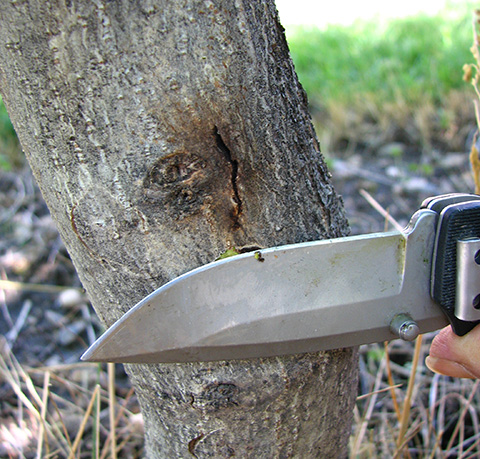
Carpenterworm
The larval stage of the carpenterworm, Prionoxystus robiniae is a wood-boring insect that affects various ornamental trees. Unlike most other wood-boring pests of ornamentals, which are mostly beetle larvae, the carpenterworm is a caterpillar belonging to
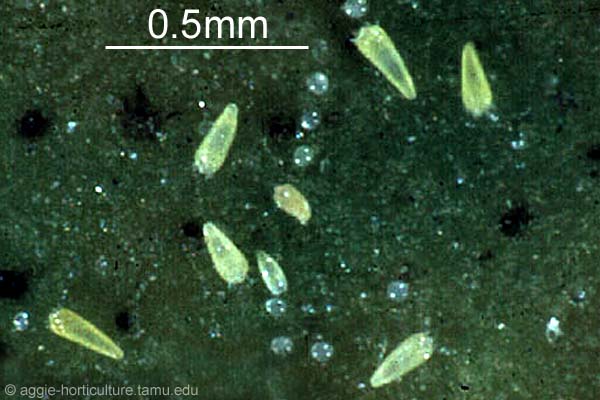
Eriophyid Mites
Eriophyid mites are translucent, cigar-shaped microscopic mites that cause deformities on many plants species. These mites are noticed when their feeding causes abnormalities of plant tissues such as erineum, galls, brooms, leaf curling, blisters, rusts,
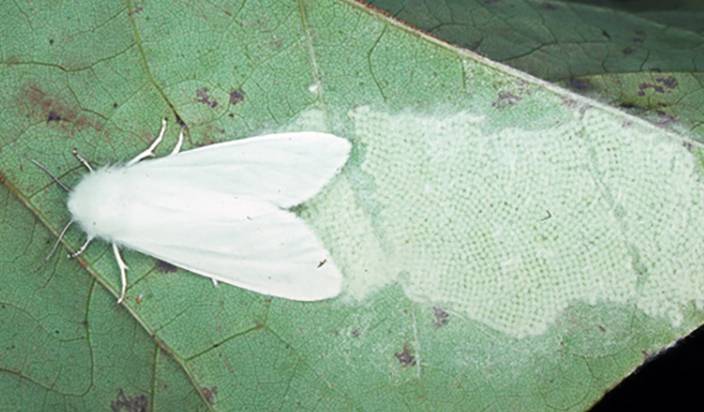

Fall Webworm
The fall webworm is a common defoliator of ornamental and fruit trees in Utah. Starting around late July, the caterpillars, webbing, and damage become noticeable, particularly in some of the canyons adjacent to populated areas.

Important Pests of Ornamental Aspen
Aspens are one of the more popular forest trees in the Intermountain West. They add a brilliant yellow glow to the collage of fall colors. In an attempt to enjoy these beautiful trees around the home environment, many well-intentioned homeowners purchase

Locust Borer
The locust borer, Megacyllene robiniae, belongs to the longhorned beetle family (Cerambycidae), referring to the long antennae of most of the species in this group. This insect occurs in Eastern Canada and in most of the U.S., wherever its host, black

Oystershell Scale
The oystershell scale (Diaspididae Lepidosaphes ulmi) belongs to a group of insects called the armored, or hard scales. The adult insect is enclosed in a shell made up of its own shed skins and waxy secretions and resembles an oyster’s shell. Under th
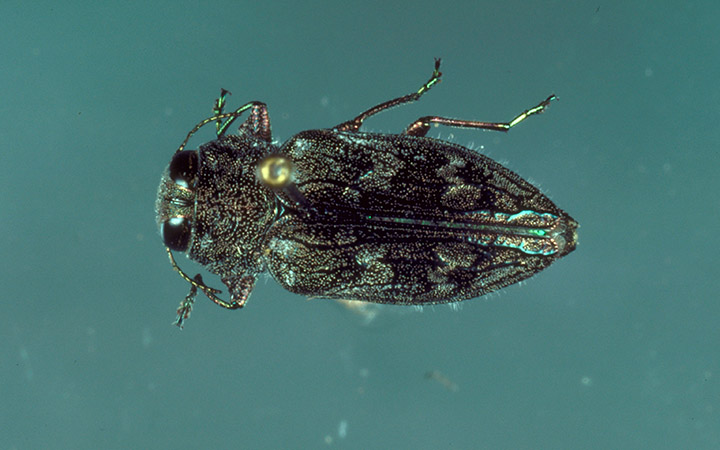

Pacific and Appletree Flatheaded Borers
Trees that are under stress or that have bark wounds are most susceptible to attack by Pacific flatheaded or flatheaded appletree borers Mature trees are not usually killed, but borer activity can weaken trees or contribute to eventual death. Newly plant
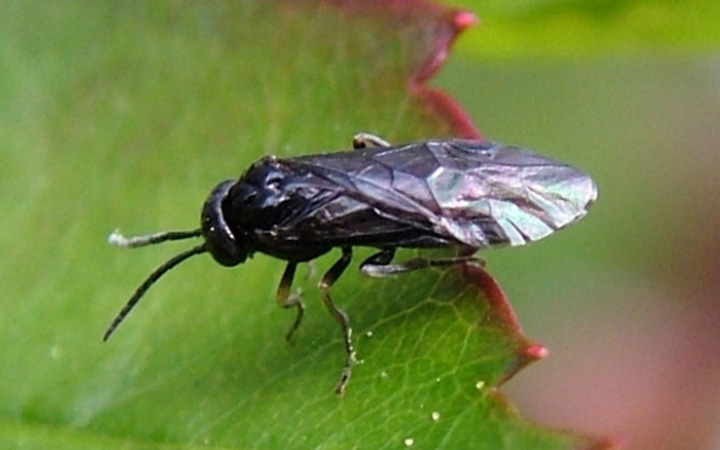

Pear Sawfly
The pear sawfly, which is actually a wasp, is a common pest on pear, cherry, and hawthorn in Utah. The slug-like appearance of the larval stage has prompted this insect to also be referred to as the pear or cherry slug in various parts of the country. Alt

Poplar Borer
The poplar borer, Saperda calcarata, is a member of the longhorned beetle family (Cermabycidae), so-named because of the adults’ long antennae. The larvae are known as roundheaded wood borers.

Poplar Bud Gall Mite
The poplar bud gall mite (Eriophyes parapopuli) is an eriophyid mite. It is microscopic and about one-fourth the size of a spider mite. Adults are reddish and spindle-shaped. Poplar bud gall mite hosts include species of poplars, cottonwoods, and aspe
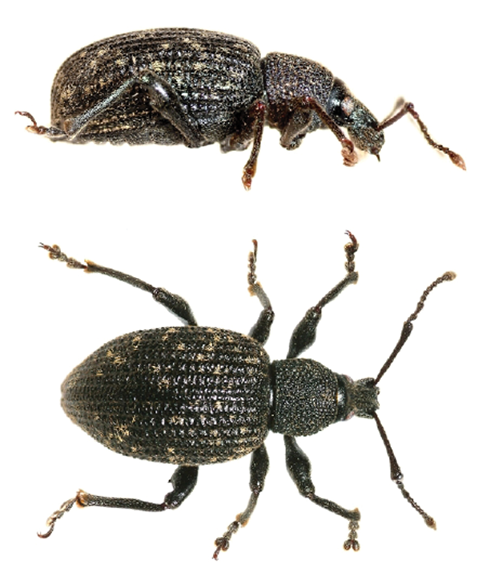

Root Weevils
The black vine weevil (Otiorhynchus sulcatus), lilac root weevil (O. meridionalis) strawberry weevil (O. ovatus) and rough strawberry root weevil (O. rugosostriatus) are a complex of non-native, snoutnosed beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) that cau
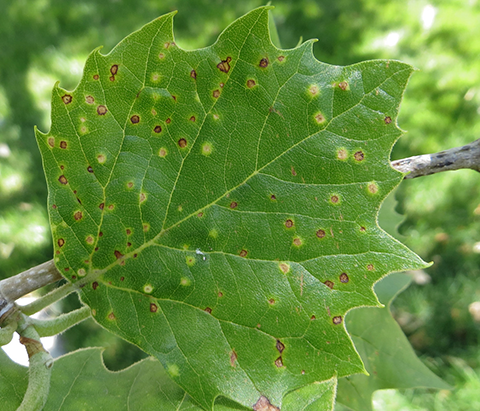

Sycamore Scale
Sycamore scale (Hemiptera: Coccoidea Stomacoccus platani) is a pest of increasing importance on London planetree (Platanus x acerifolia) and California sycamore (P. racemosa) in urbanized areas throughout Utah. It is unknown how susceptible American s

Thousand Cankers Disease of Walnut
Thousand cankers is a newly recognized disease of walnuts, caused by a fungus (Geosmithia morbida) that is spread by the walnut twig beetle (Pityophthorus juglandis). The beetle is endemic to the native range of Arizona walnut (Arizona, New Mexico, an
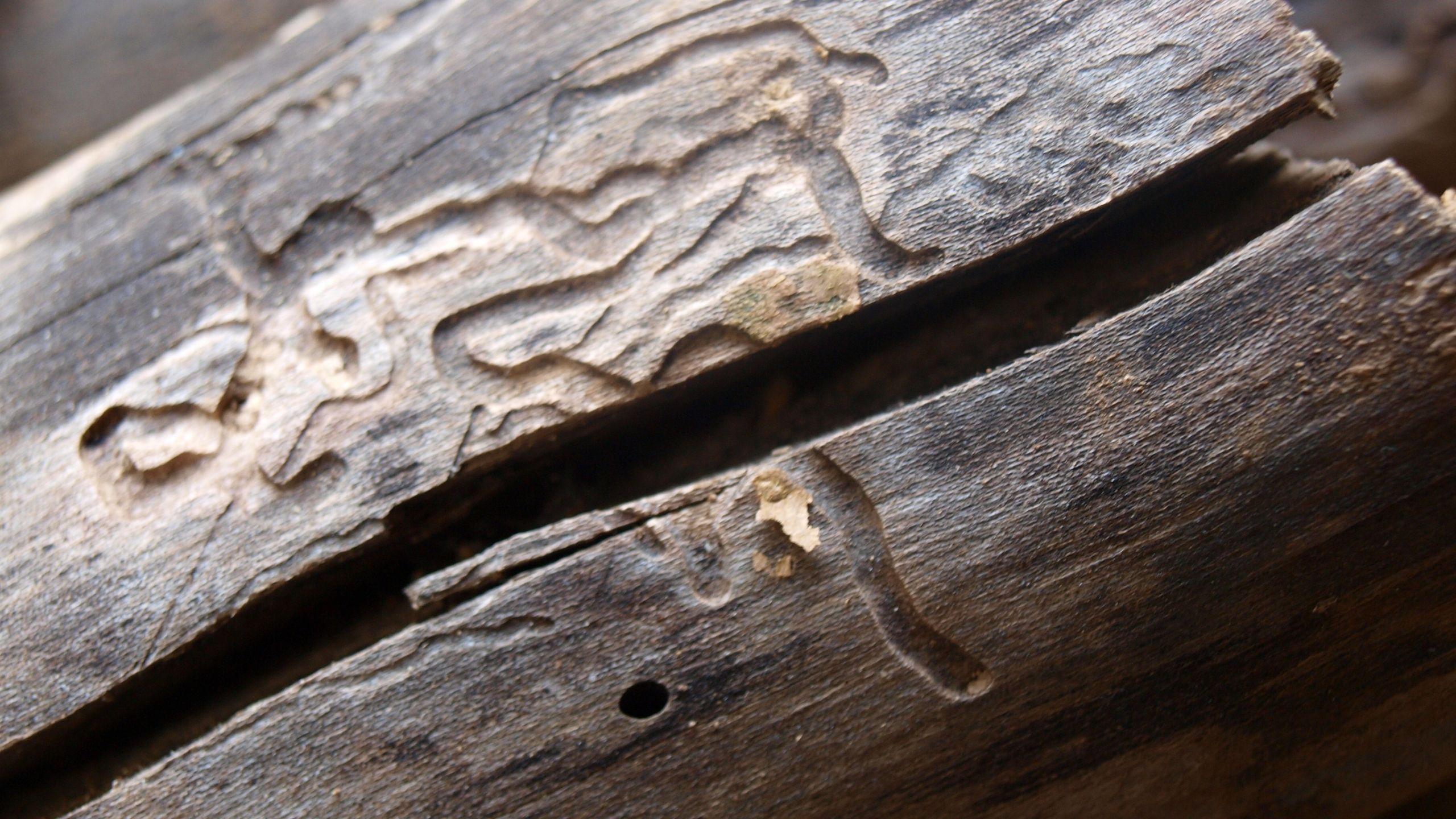

Bark Beetles
Bark beetles are one of the most destructive forest pests in the world. They are different than the larger longhorned and roundheaded/metallic woodboring beetles commonly infesting the inner wood of trees.
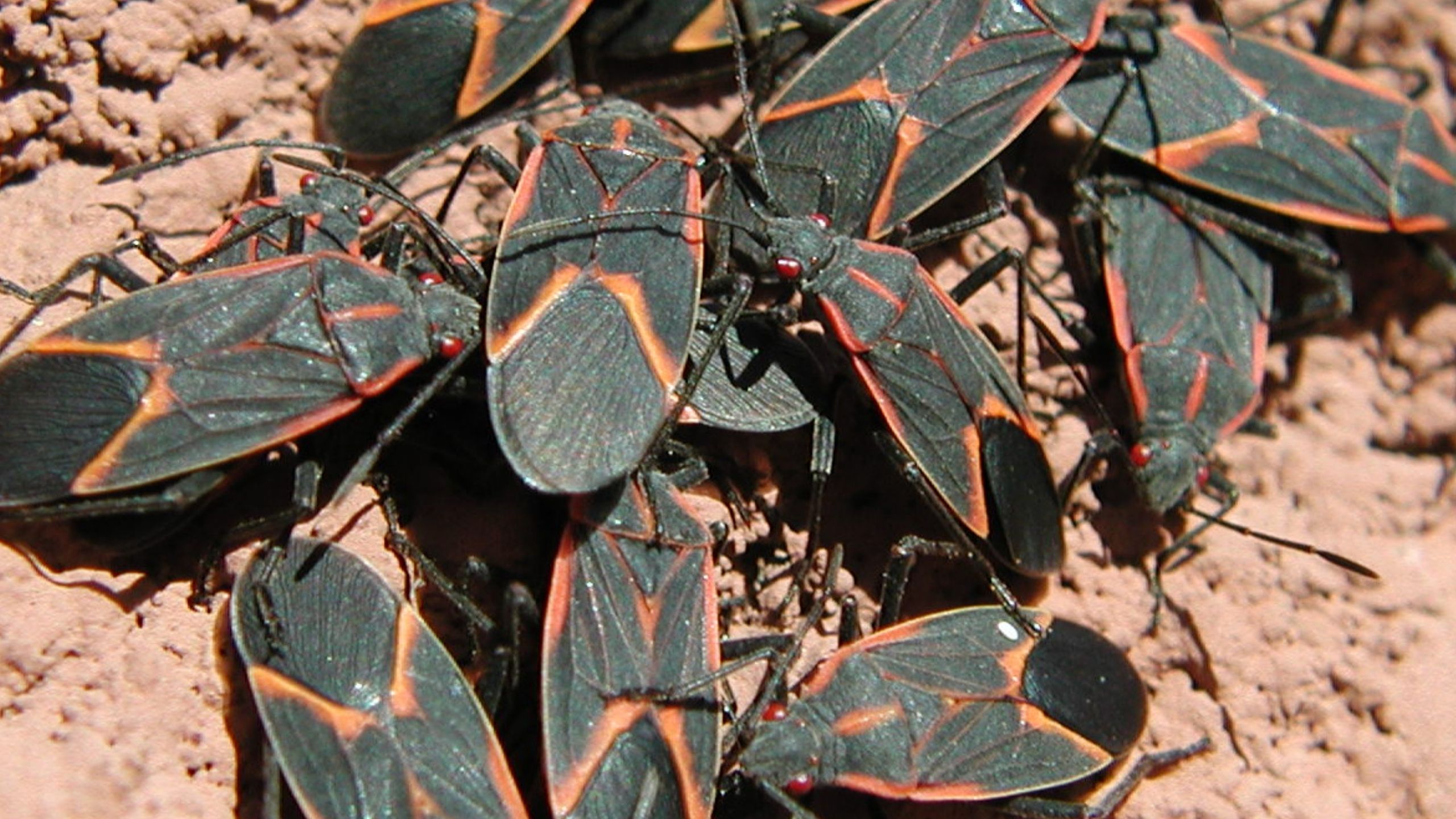

Boxelder Bug
Boxelder bugs are a common nuisance insect to many homeowners. Although boxelder bugs are active throughout the summer, many people don’t notice them until they start “sunning” themselves on structures, particularly the southern-facing walls.
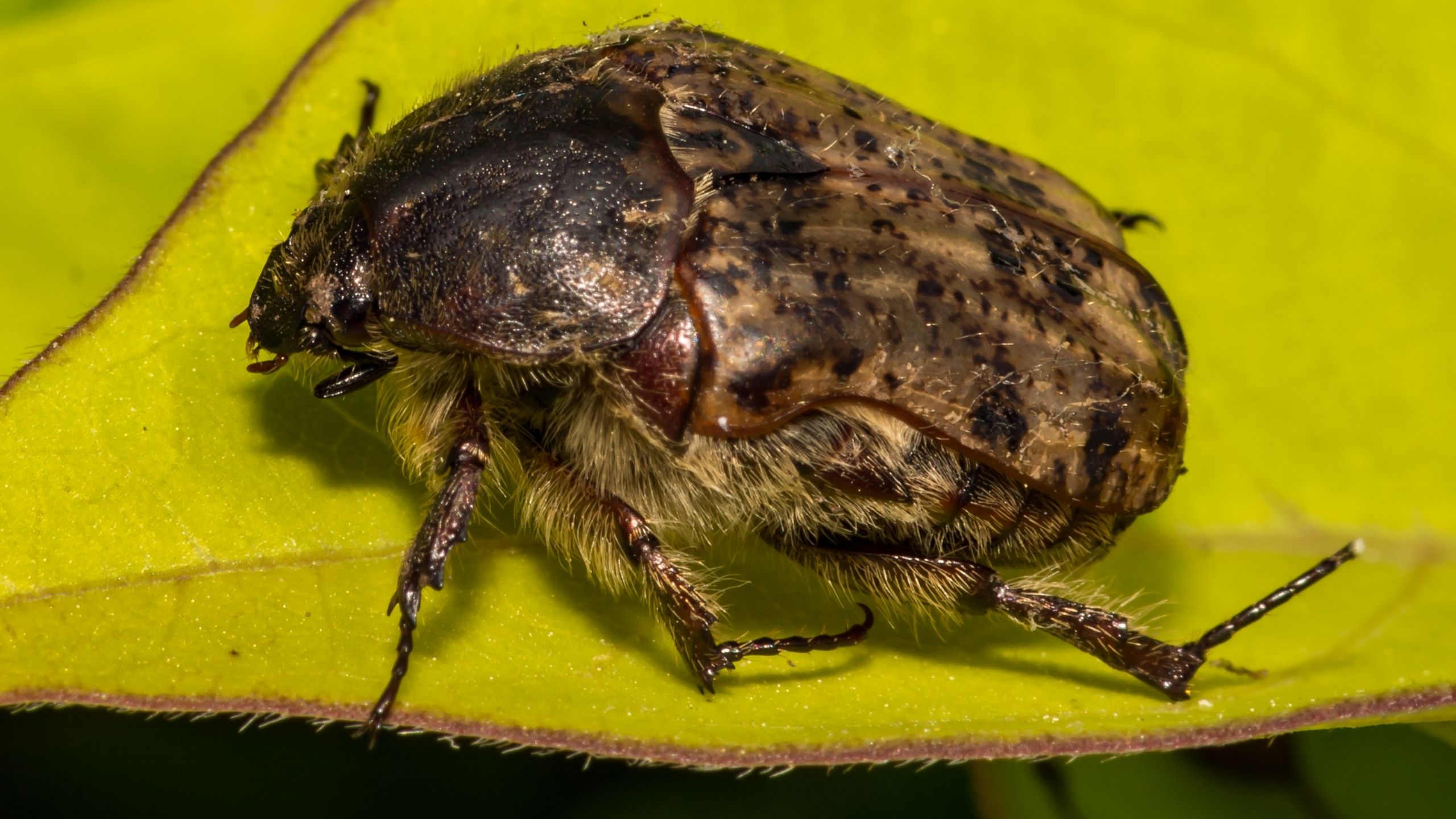

Bumble Flower Beetle
Bumble flower beetles are common throughout the growing season on flowers, oozing sap, and other sweet, overripe, or fermenting matter. Bumble flower beetles seldom warrant the use of chemicals for control. Control methods include removing organic materia
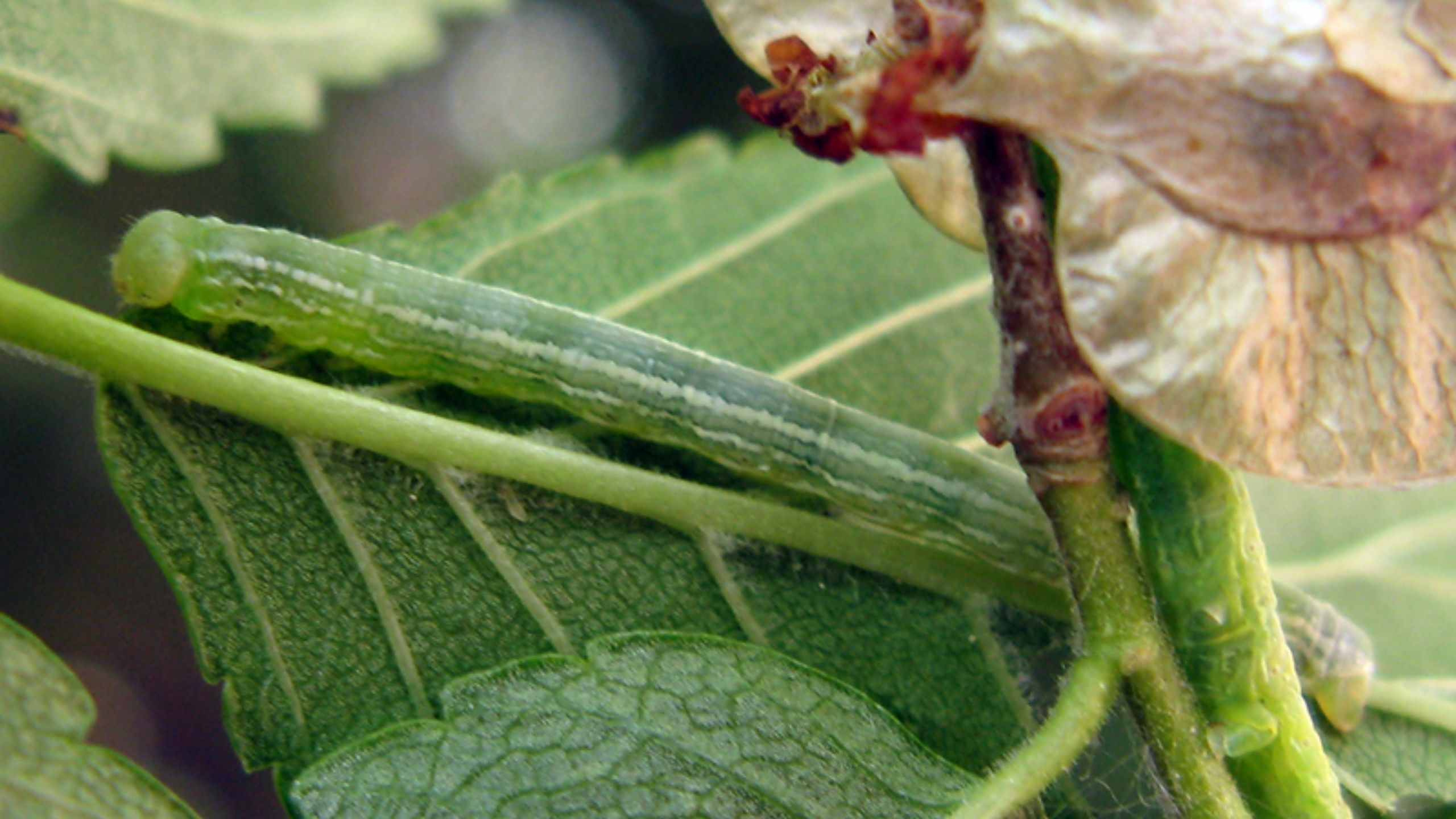

Cankerworms
Cankerworms, also known as inchworms, are in the order Lepidoptera and family Geometridae. Geometrid moth adults have slender bodies and relatively large, broad forewings. Both fall and spring cankerworms occur in Utah, with the fall cankerworm being most
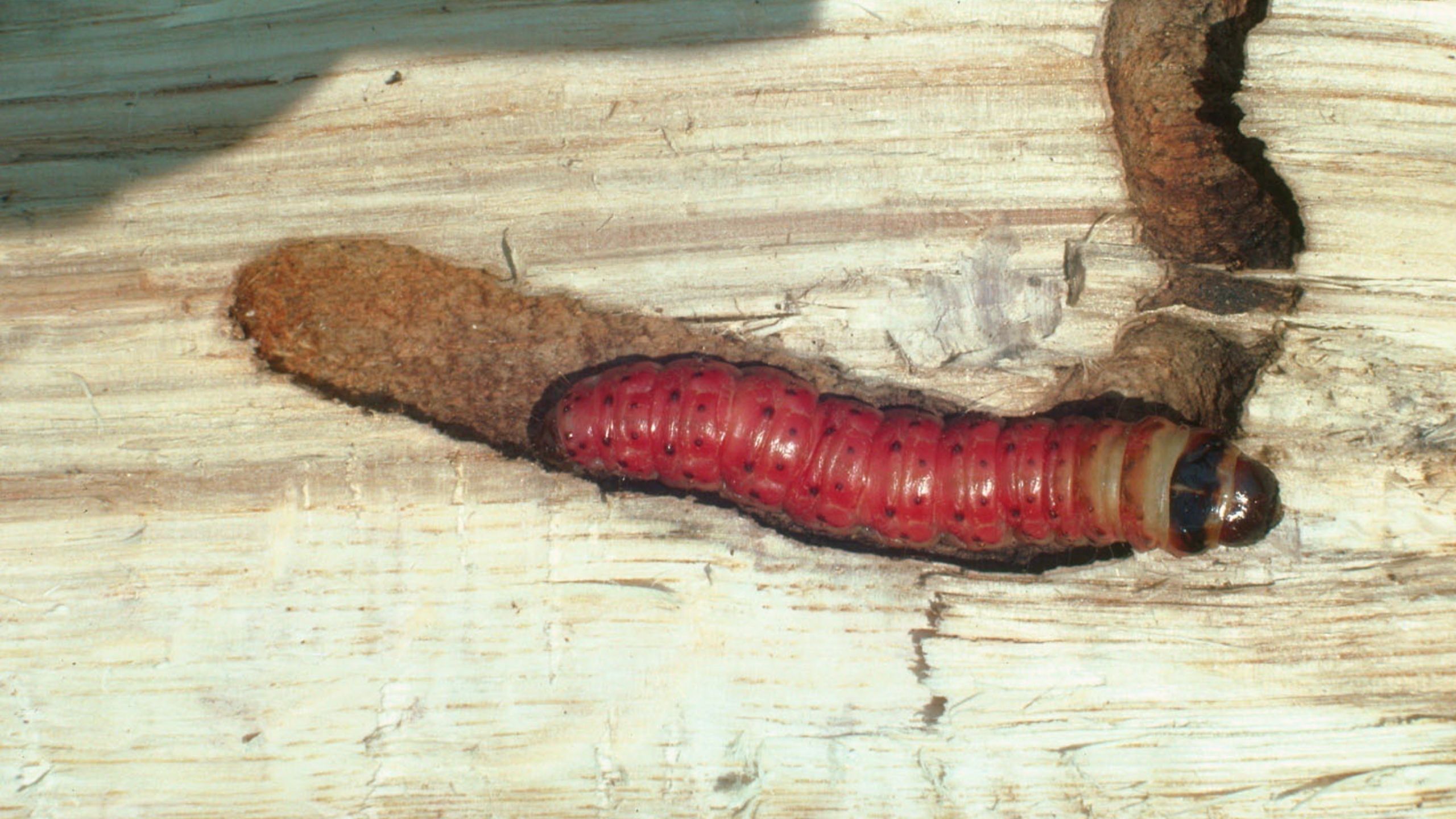

Carpenterworm
The larval stage of the carpenterworm, Prionoxystus robiniae is a wood-boring insect that affects various ornamental trees. Unlike most other wood-boring pests of ornamentals, which are mostly beetle larvae, the carpenterworm is a caterpillar belonging to
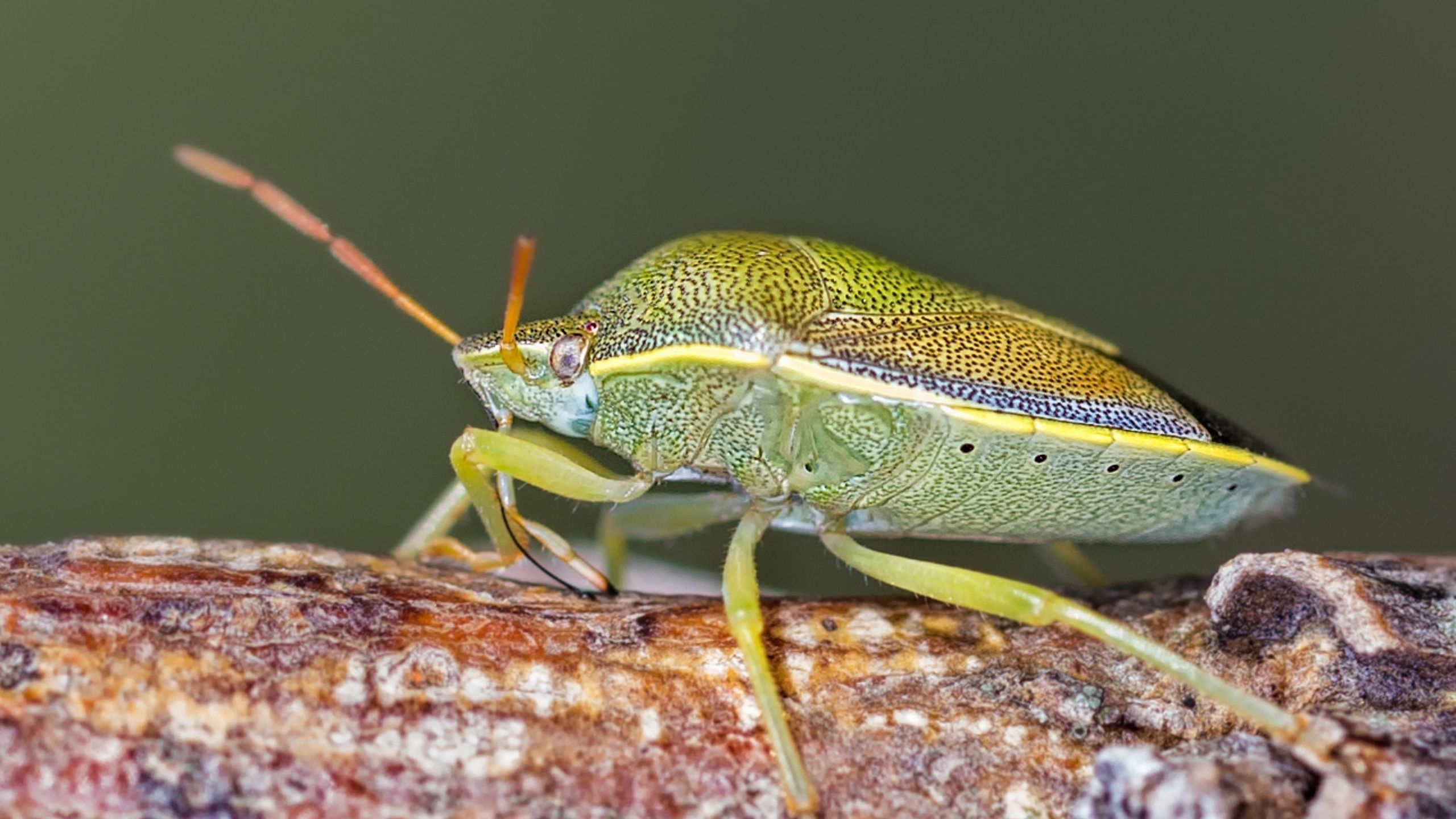

Common Stink Bugs of Utah
This fact sheet provides descriptions and images of stink bugs, including the adult and immature stages, that are commonly encountered in gardens and farms in Utah.
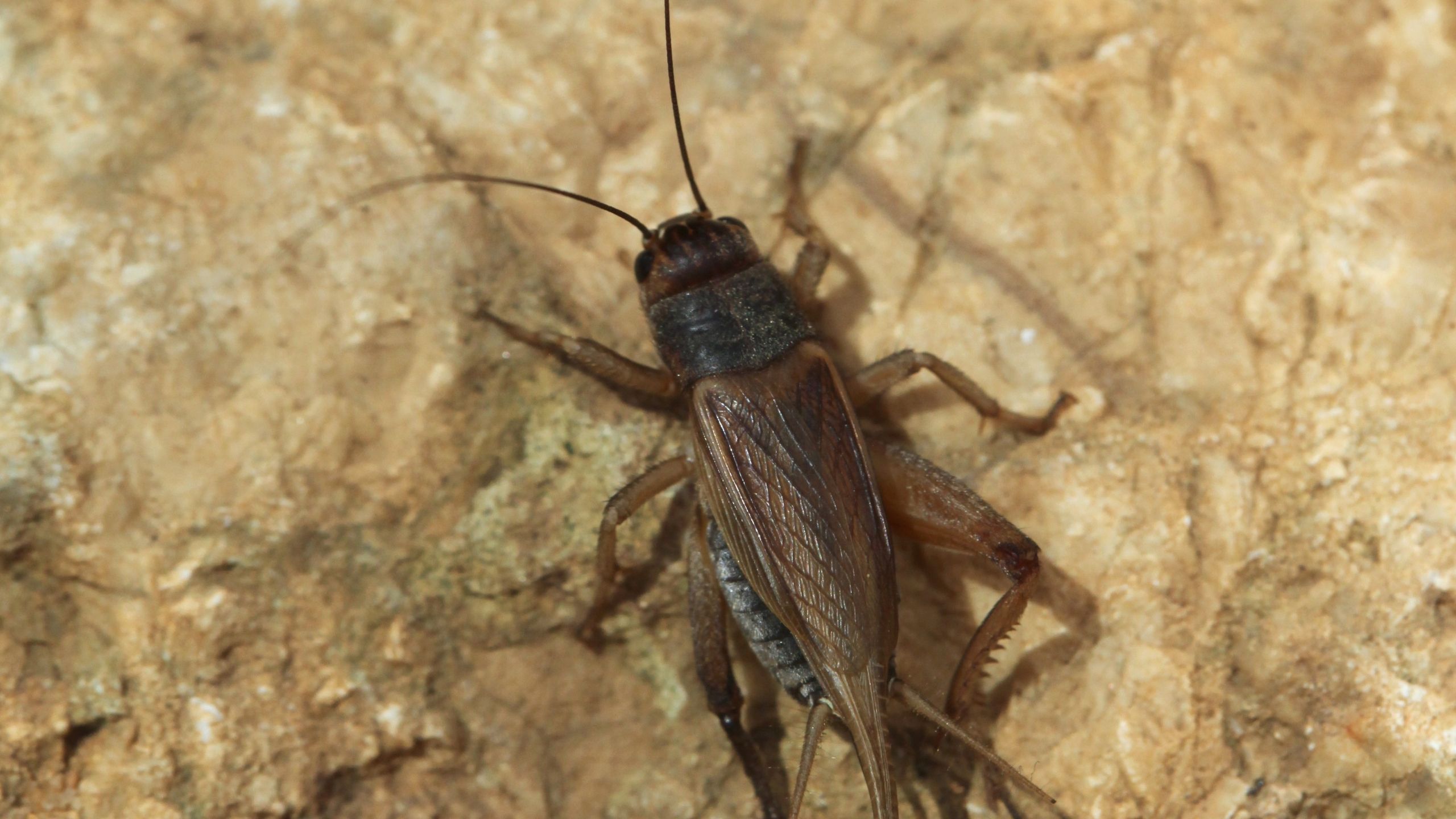

Crickets
Crickets will eat almost anything, including fabrics, other insects (dead or alive), food products, and furs. Occasionally crickets may enter the home or chirp near the home, and become a nuisance. Regular sanitation around the exterior of the home will d
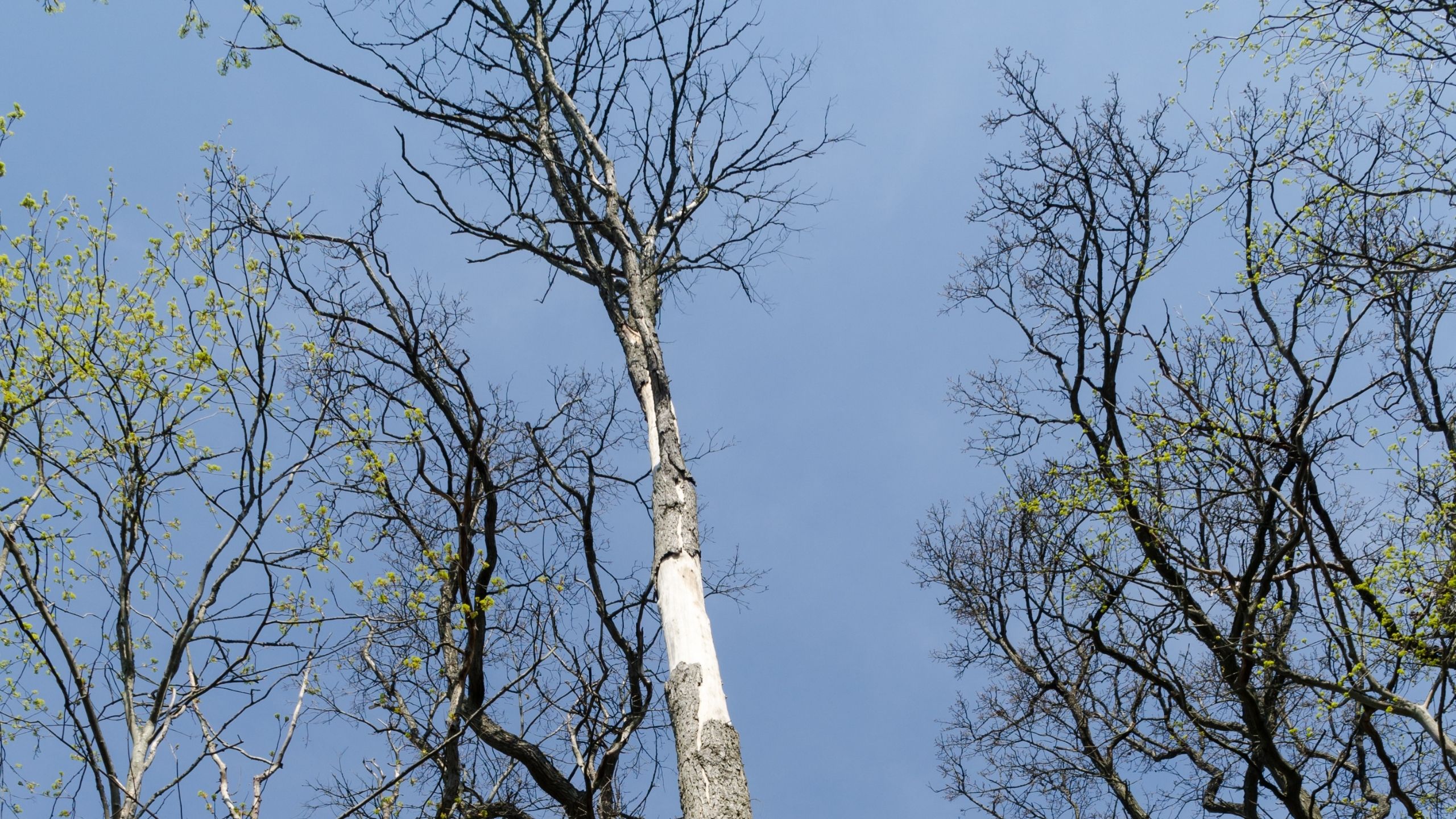

Elm Bark Beetles and Dutch Elm Disease
Two major bark beetle species attack elm trees in Utah; both can transmit Dutch Elm Disease (DED) , leading to tree death, decline, or chronic stress. Preventive treatments such as foliar insecticide applications, severing root graphs between trees, injec
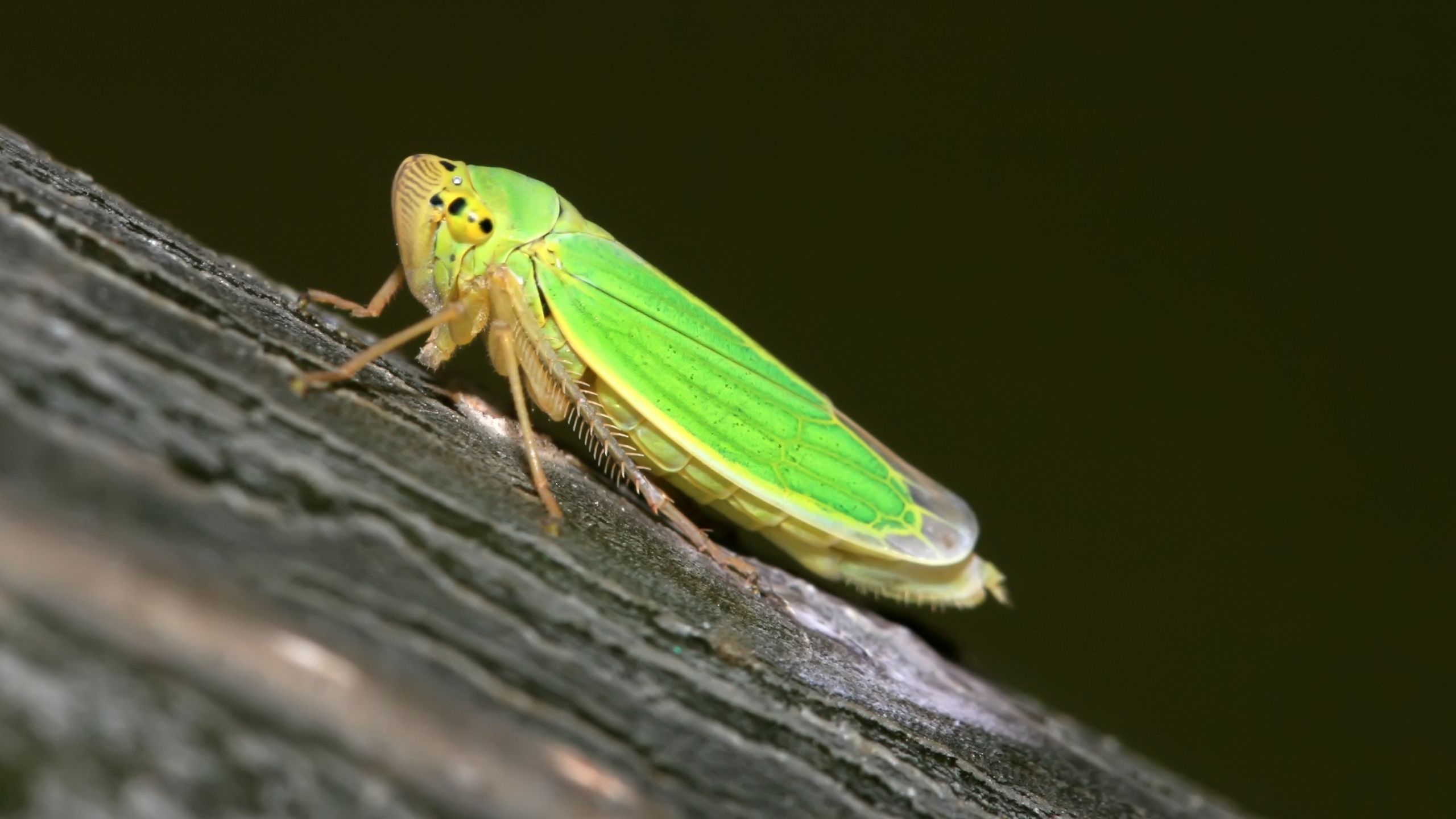

Leafhoppers in the Home Garden
Leafhoppers are common problems in home gardens and orchards throughout the state of Utah. There are many species of leafhoppers, several of which attack apples, roses, grapes, and potatoes. Most species overwinter in the egg stage in the bark of the host
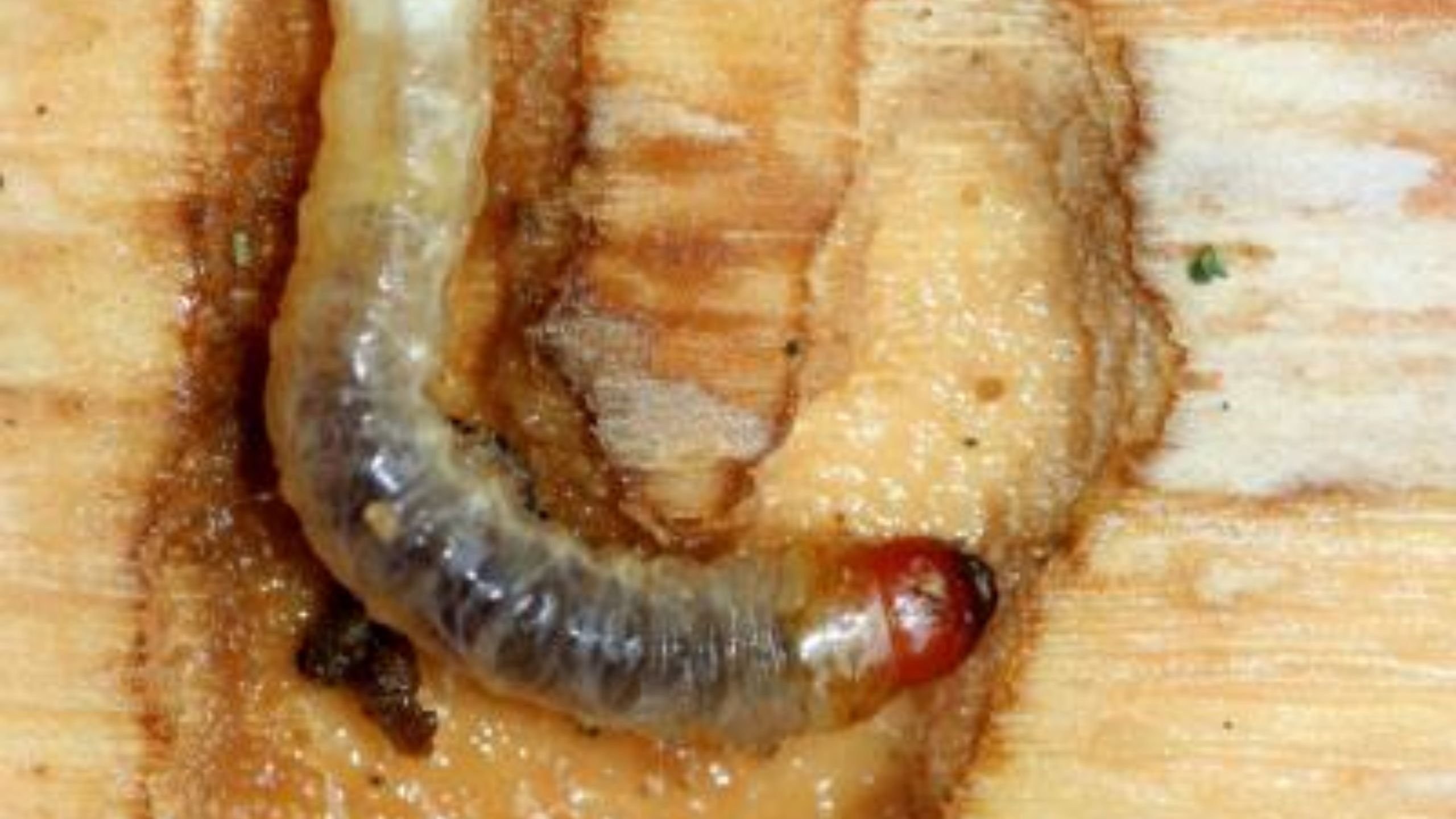
Lilac-Ash Borer
Lilac-ash borer, a clear-wing moth common in Utah, can be a destructive pest of many species of ash, privet, lilac, and related species. Adults emerge from host trees and lay eggs in the spring; larvae feed on wood within branches, overwinter in the heart
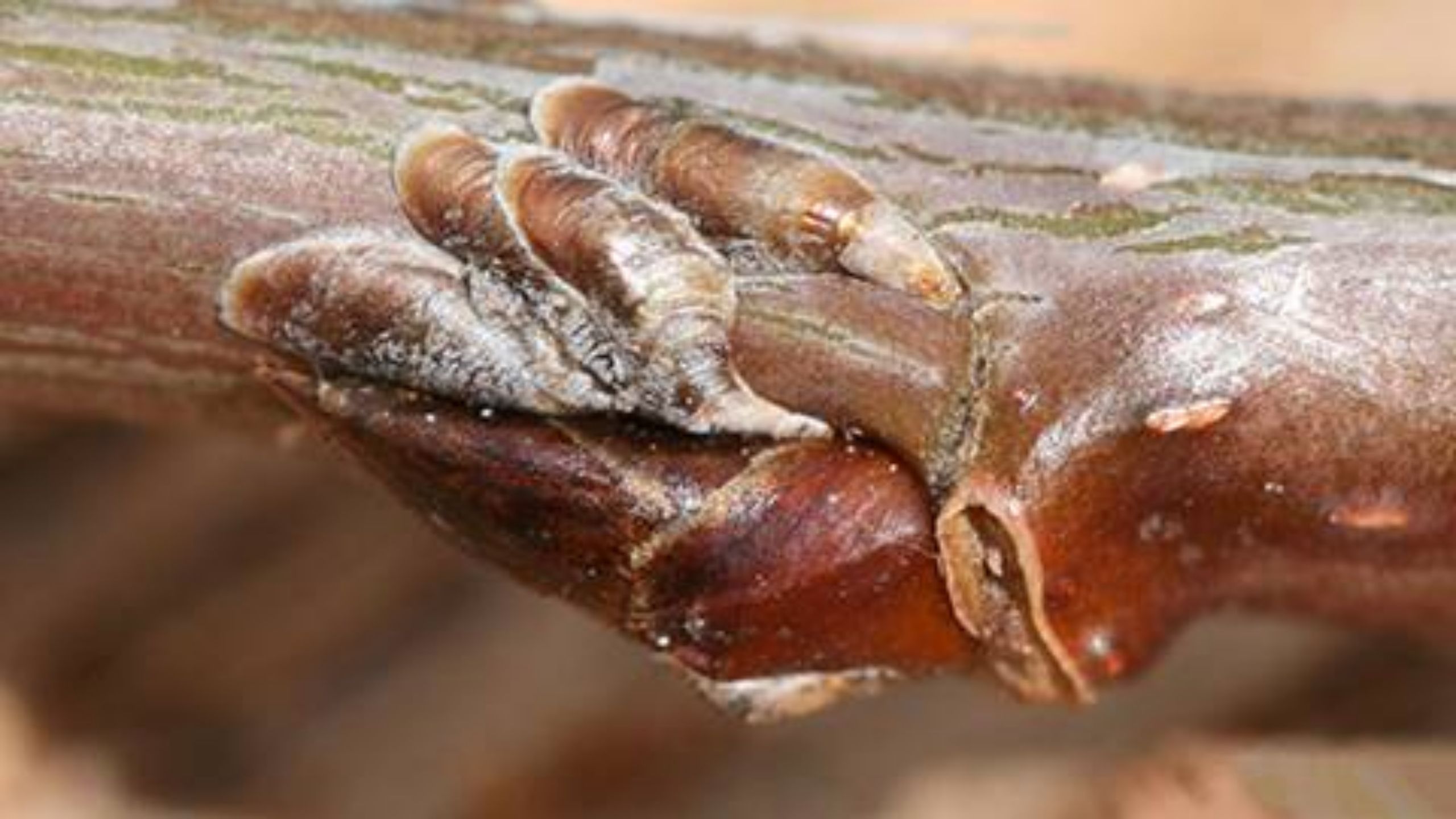

Oystershell Scale
The oystershell scale belongs to a group of insects called the armored scales. The adult insect is enclosed in a shell made up of its own shed skins and waxy secretions. Under this covering is a sac-like animal that is quite different in appearance from m
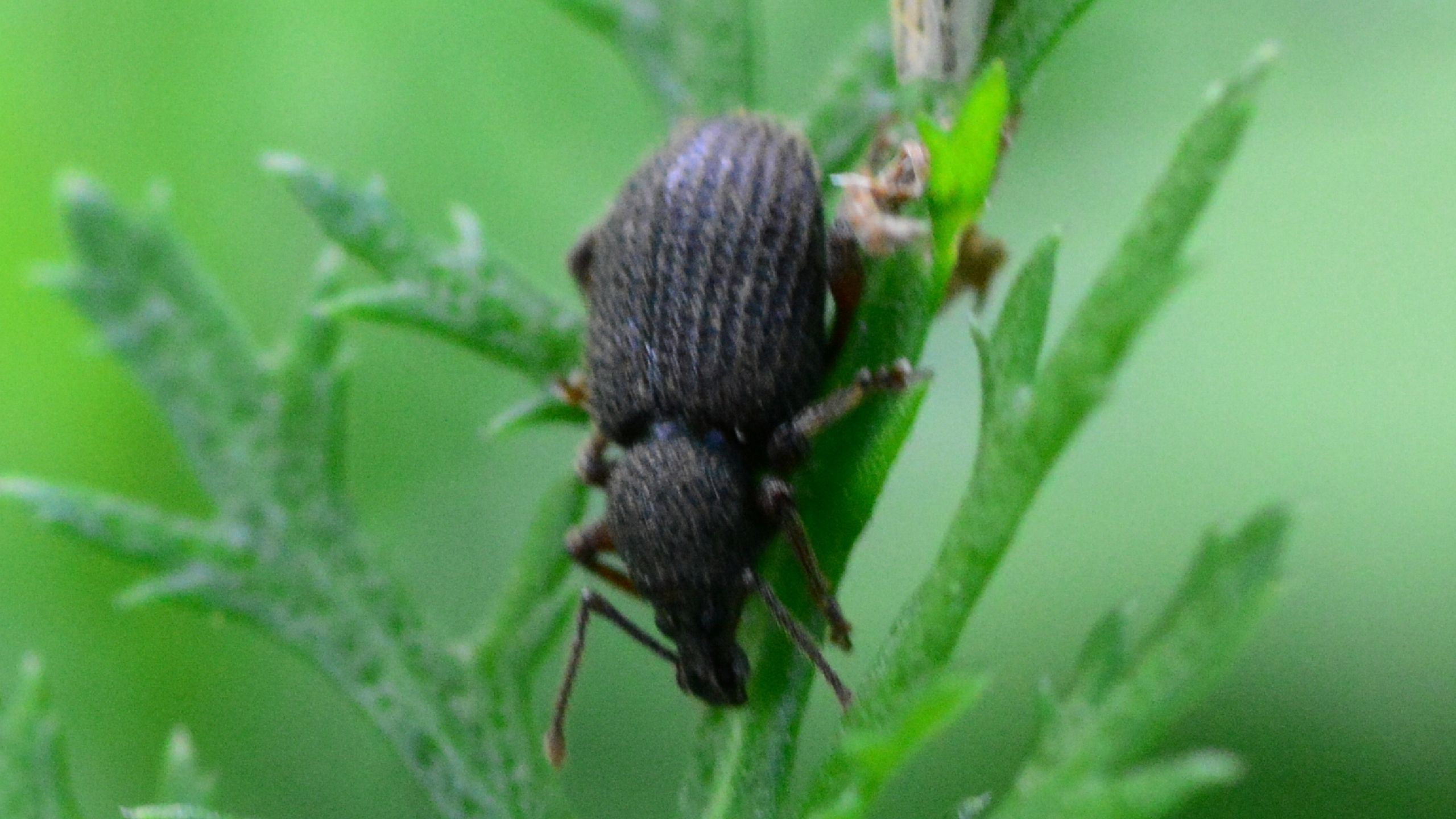

Root Weevils
Root weevils are common pests of landscape ornamentals and small fruits. Root weevils cause notching of leaf margins and root damage leading to canopy dieback or plant death.

Sequoia Pitch Moth in Pines
Sequoia pear moth is not typically considered a serious pest of pines, but may cause limb dieback, unsightly resin masses, tree stress, or even tree death in severe cases.
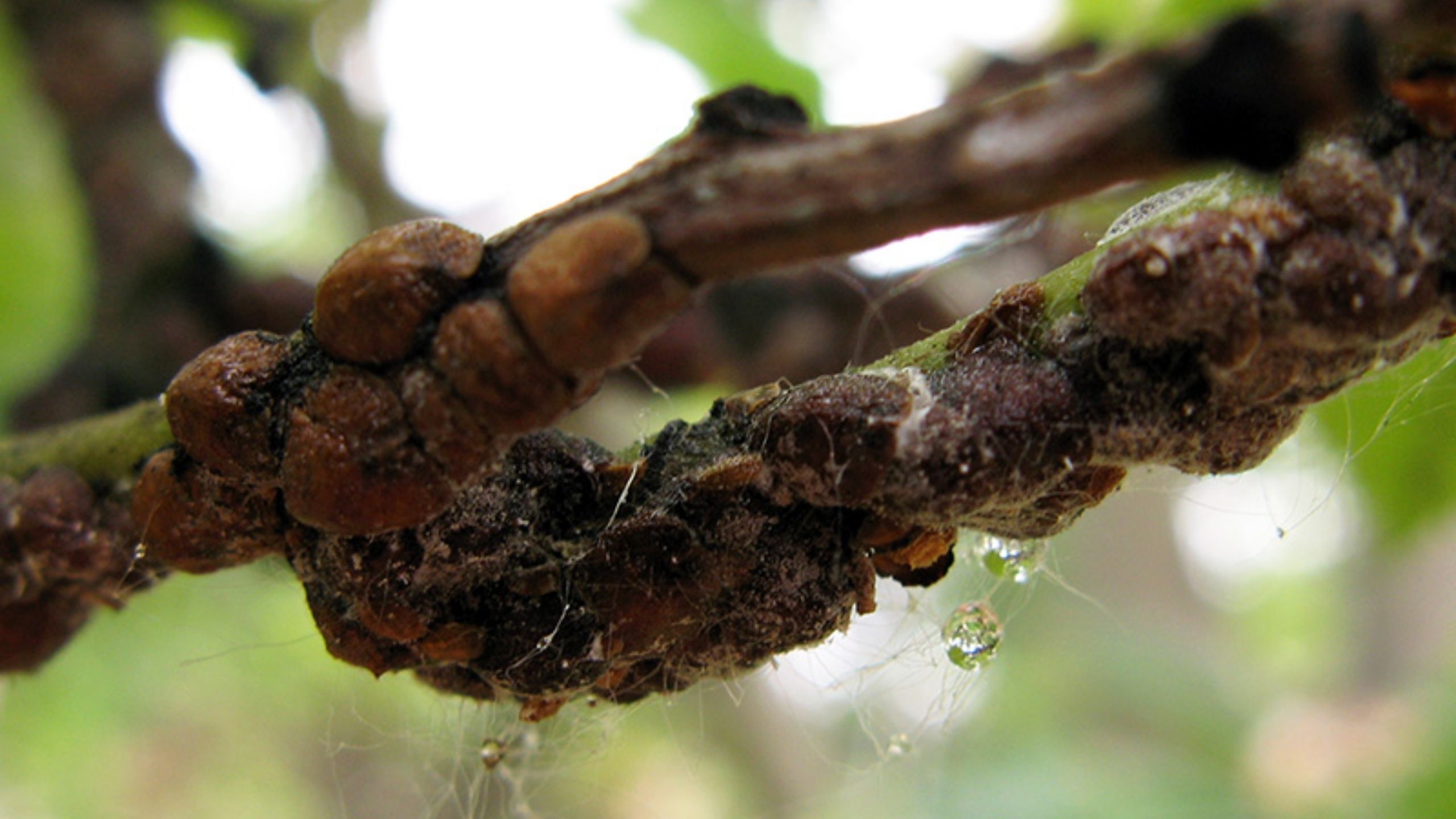

Soft Scales in Utah
There are more than 1,000 different species of soft scales found throughout the world. Less than 5% are considered serious pests. Soft scales feed on a wide range of woody ornamental plants and often go unnoticed until they stunt growth or cause severe pl
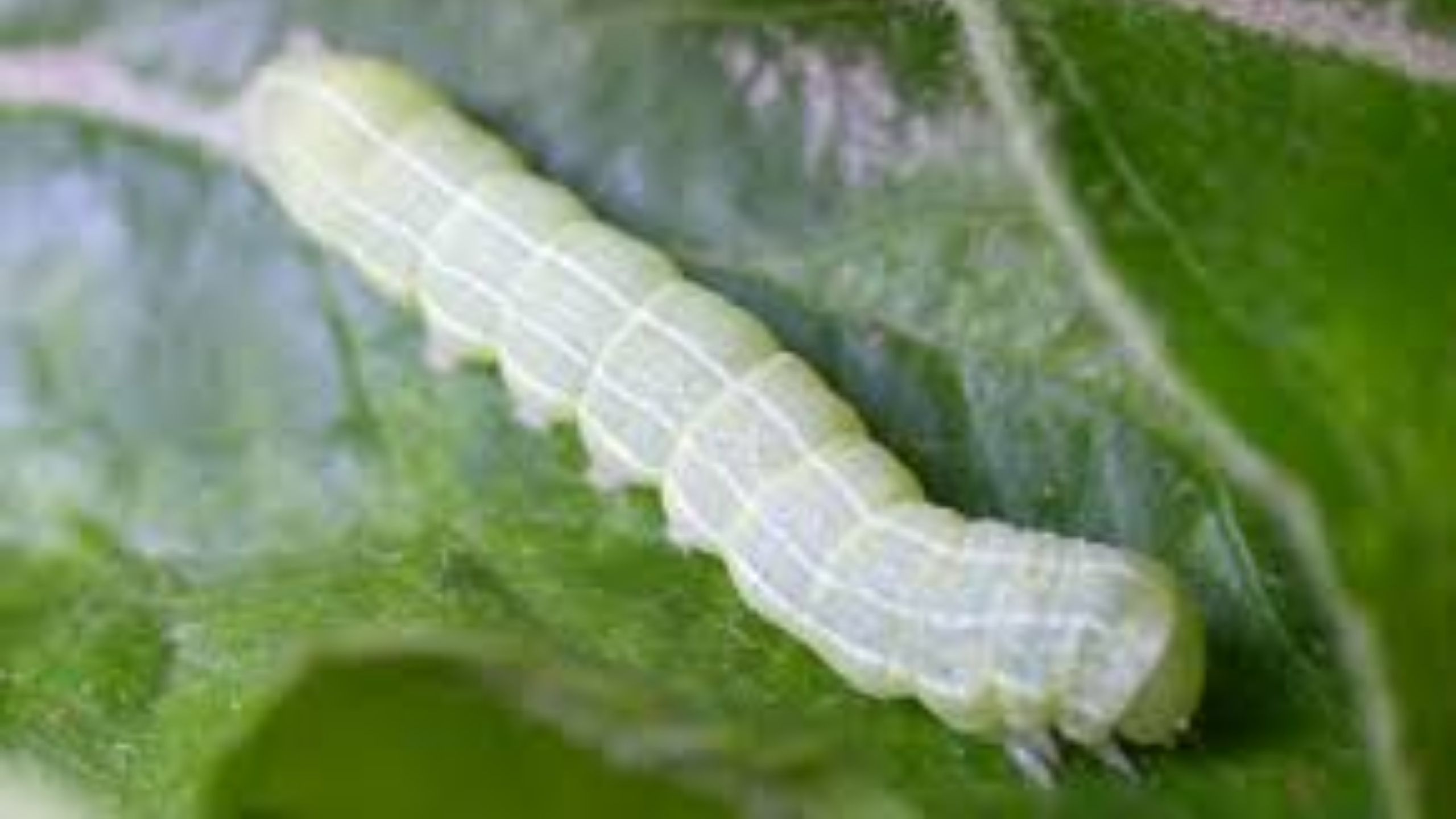

Speckled Green Fruitworm
Fruitworms chew holes in fruits and leaves, and can cause localized defoliation of fruit trees. Fruitworms can be monitored with beat-samples (abrupt shaking of tree branches over a tray). Applications of reduced-risk insecticides, such as Bacillus thurin

Balsam Woolly Adelgid
Invasive balsam woolly adelgid is a tiny sucking insect that was introduced to North America from Europe. In the U.S., it is a serious pest of true firs in forests, landscapes, and in seed and Christmas tree production.

Boxelder Leafroller
The boxelder leafroller is a pest of boxelder and other trees and shrubs in parts of the United States and Canada and is commonly found in Utah. Boxelder is the primary host, but damage can also occur on raspberry, birch, elderberry, white elm, and va
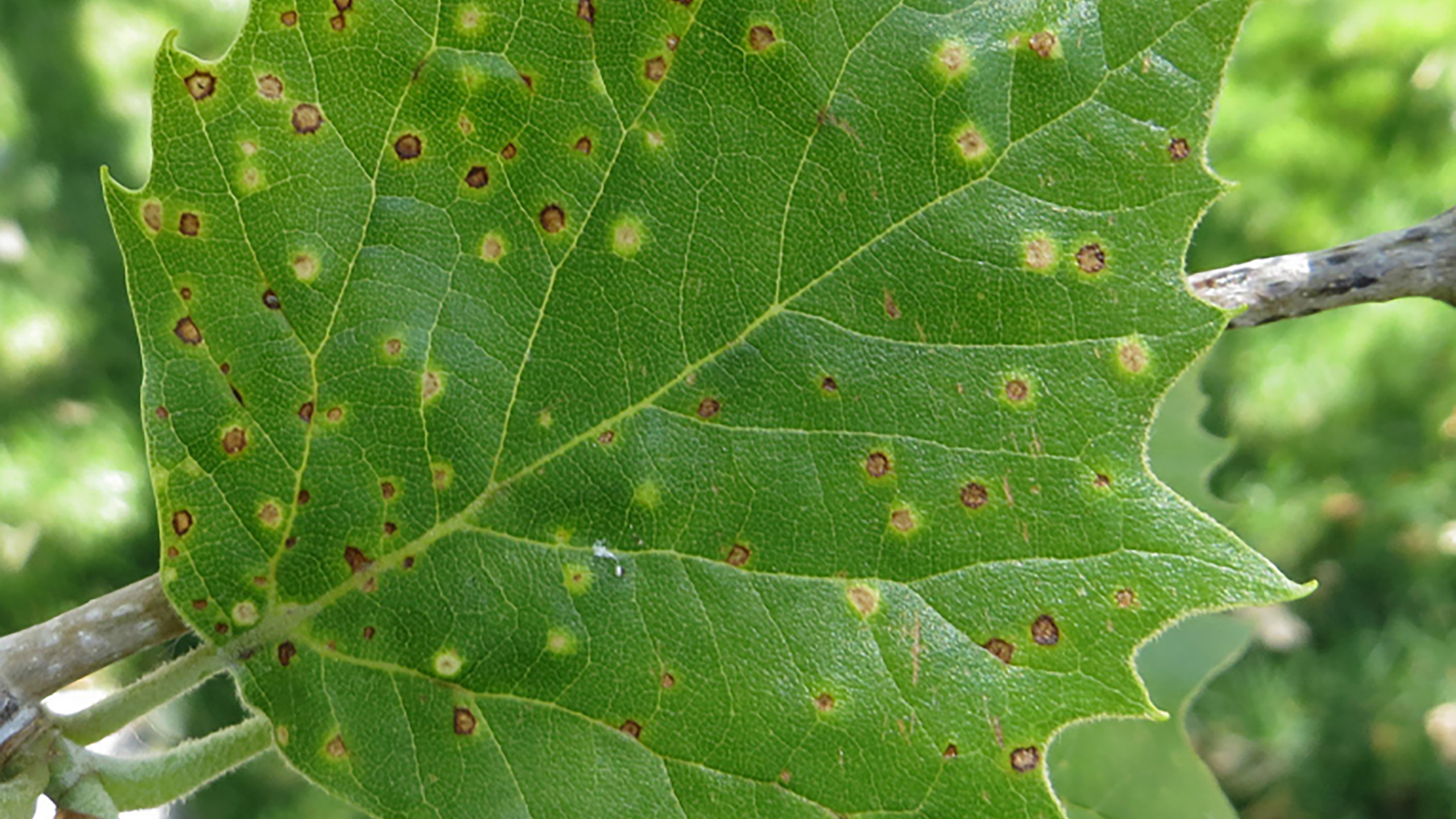

Sycamore Scale
Sycamore scale is a pest of sycamore trees (Platanus spp.), especially London planetree. Scale life stages are difficult to see with the naked eye, and therefore, symptoms of leaf damage are often noticed first. The primary symptom is yellow-to-brown leaf




































