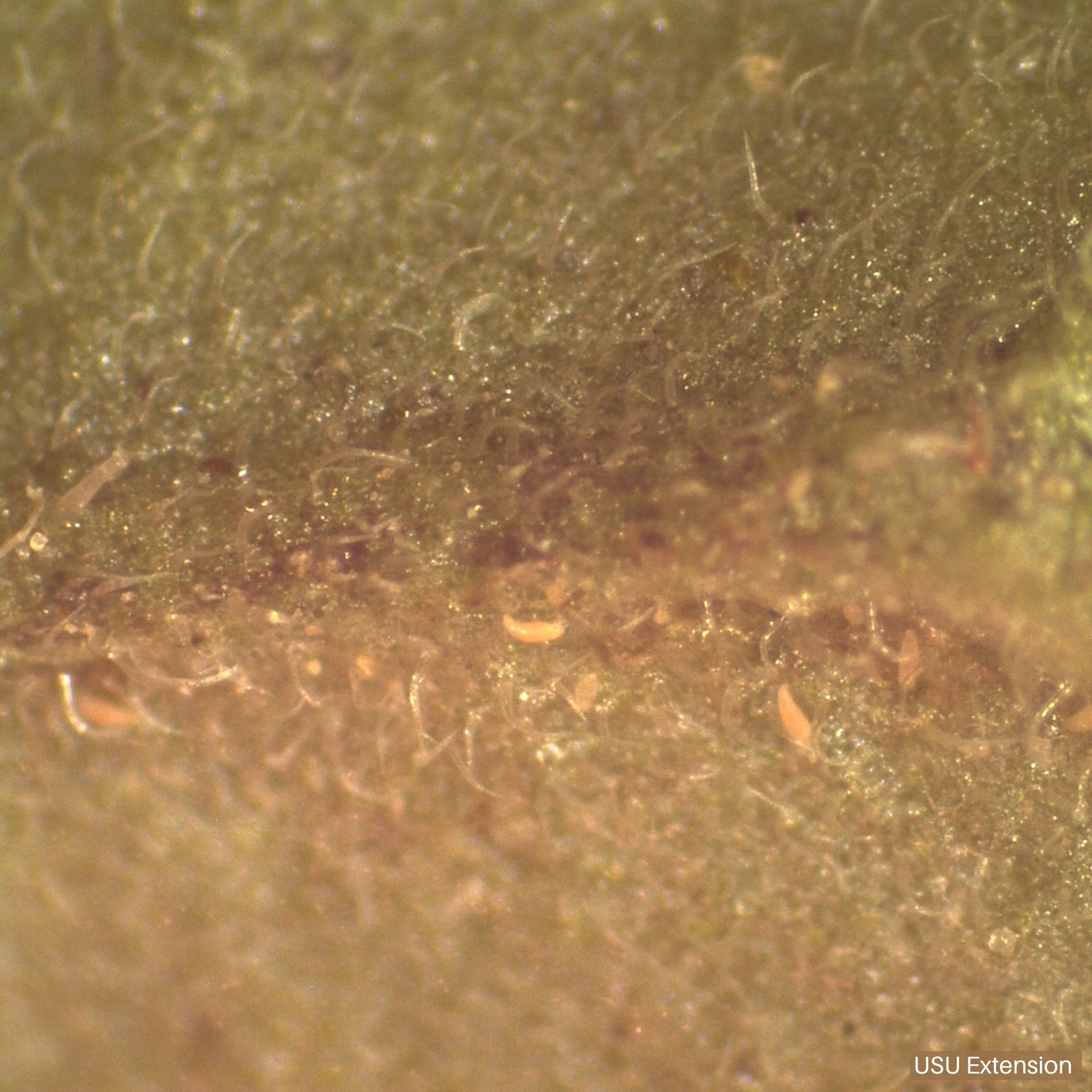
Tomato Russet Mite
HOSTS
- Potato
- Tomato
- Pepper
- Eggplant
DESCRIPTION
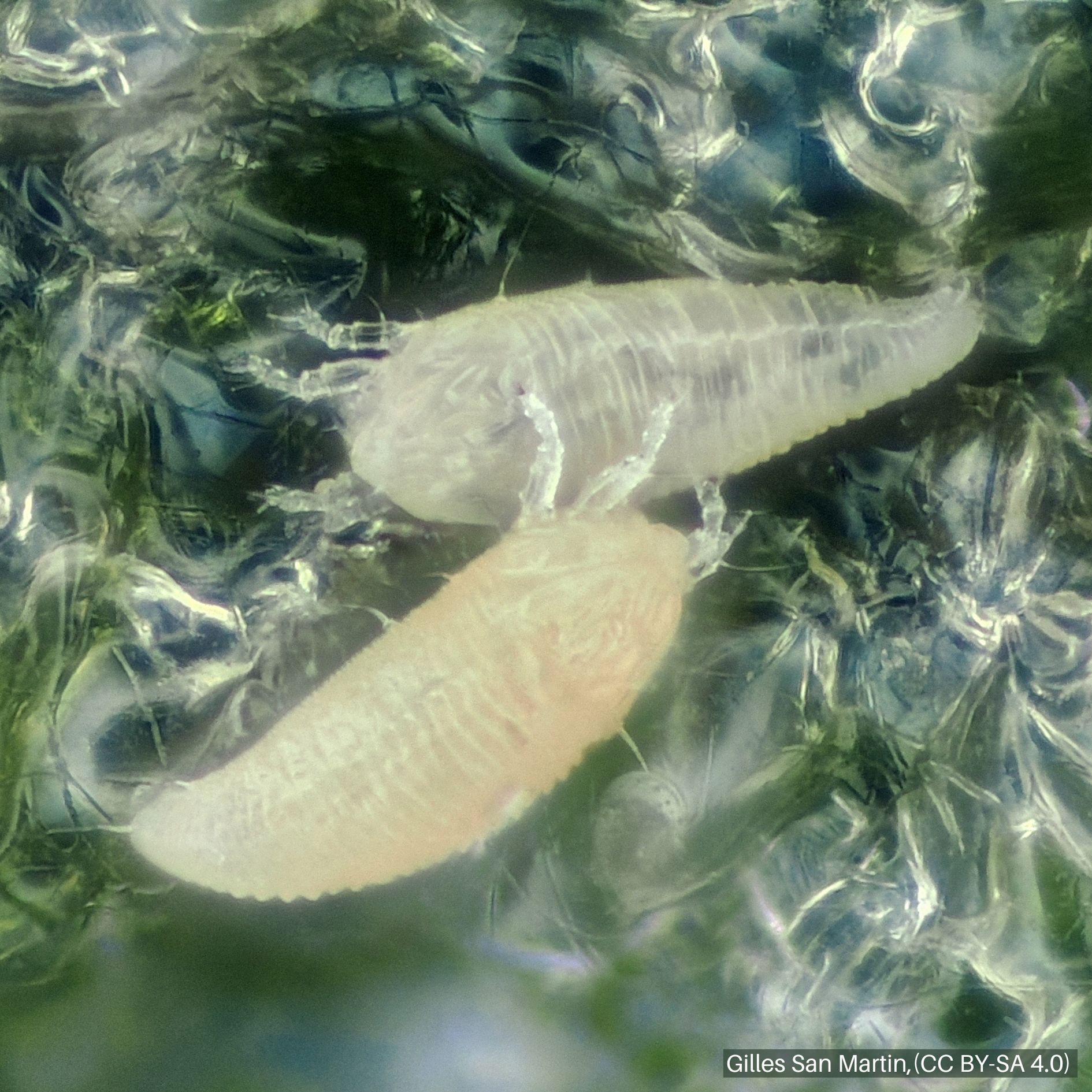
Adults and nymphs have cigar-shaped, yellowish-tan or pink bodies and require a microscope to observe.
BIOLOGY
Egg | Nymph | Adult
Tomato russet mites have multiple, overlapping generations per year. They overwinter as adults in crop debris. They are primarily a concern when weather conditions are hot and dry.
SYMPTOMS
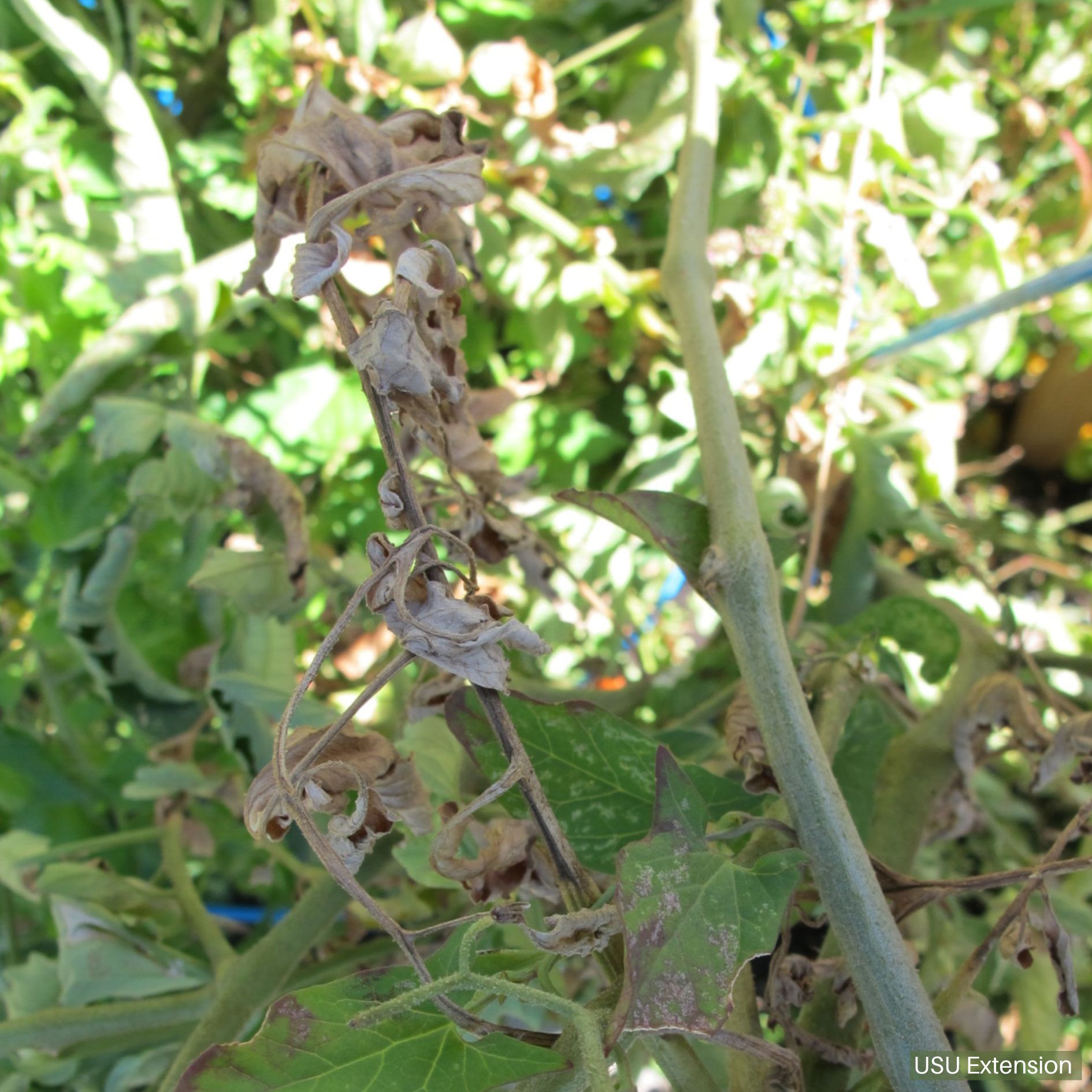
Adults and nymphs feed with piercing-sucking mouthparts causing bronzing or “russeting” of the surface of stems, leaves, and fruits. Damaged leaves may turn yellow, curl, wither, appear “deflated”, and fall from plants. Mite feeding on fruits can cause longitudinal cracks and bronze coloration.
SCOUTING
- The presence of tomato russet mites often goes unnoticed, due to their tiny size, until injury is evident.
- Watch for injury symptoms especially during hot, dry conditions.
- Look for bronzing on lower leaves and stems.
- Use a microscope to check damaged leaves and surrounding healthy leaves for mites.
GENERAL MANAGEMENT
If not controlled, this pest can kill plants. Tomatoes are most commonly affected, especially during hot, dry conditions.
- Use clean transplants.
- Avoid planting during hot, dry periods.
- Promptly remove or destroy infested plant debris.
- Clean tools used on infested plants before using on healthy plants.
INSECTICIDES
Once russet mites are present on plants, insecticide treatment (sulfur, abamectin) is the primary control option.
Click here to view insecticide options for commercial growers.
Click here to view insecticide options for home gardeners.