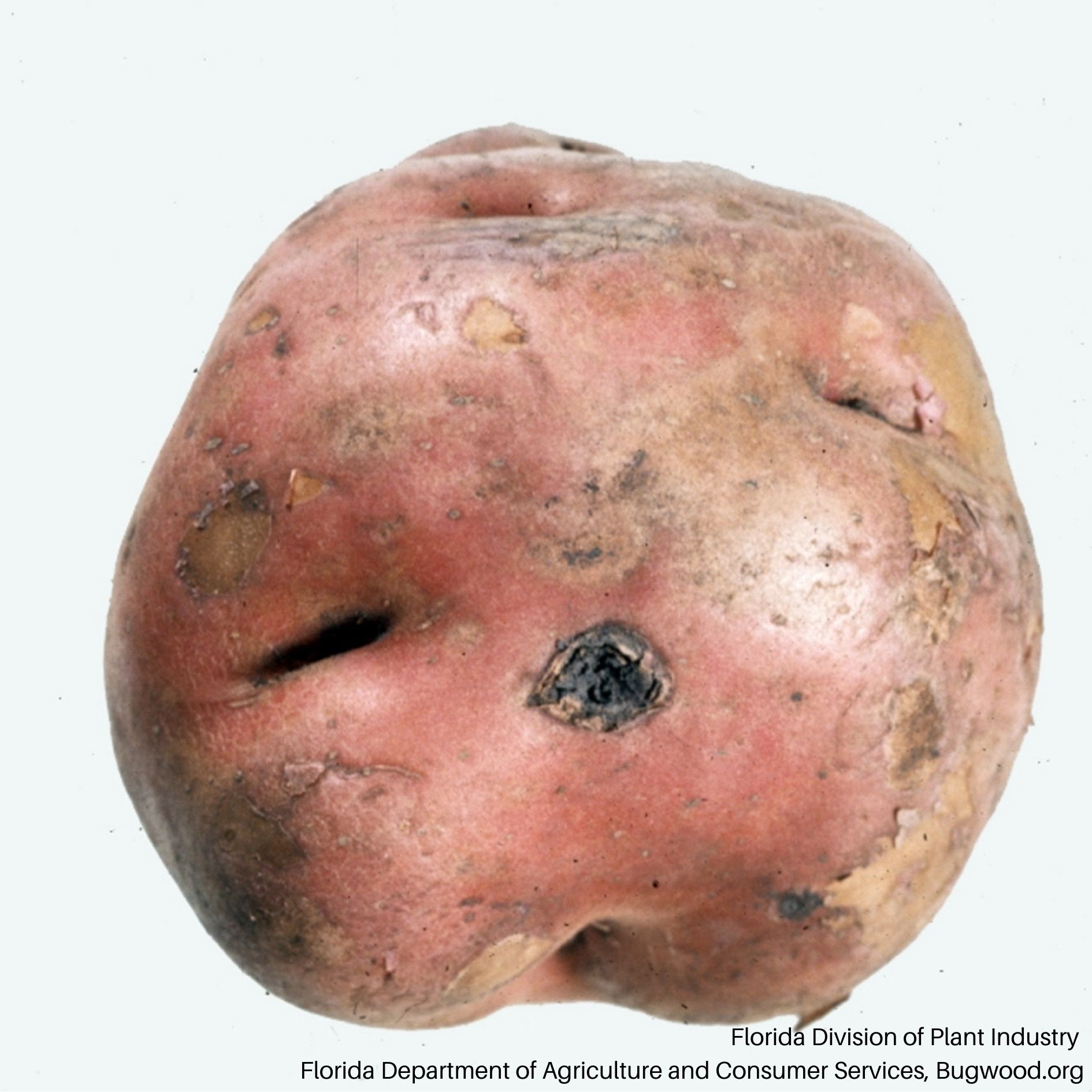
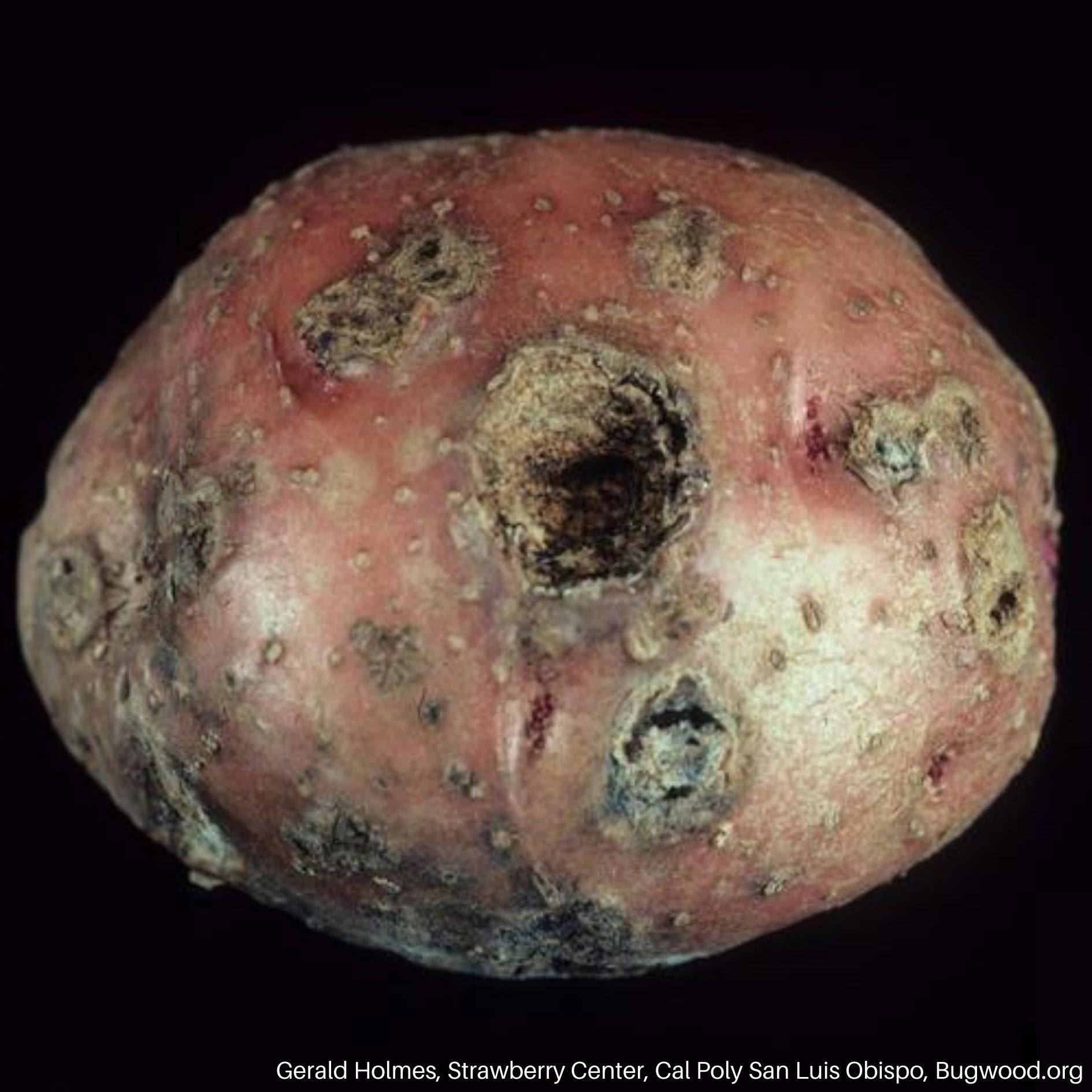
Scab
HOSTS
- Carrots
- Potatoes
- Root Crops
DESCRIPTION
Common scab is caused by the bacteria Streptomyces scabies.
Many soils naturally have a population of S. scabies, which feed on organic detritus in the soil. The bacterium can also be introduced through the use of infected seed stock. Regardless of the source of infection, the S. scabies population in the soil will increase after it has been used to grow potatoes or other susceptible crops.
BIOLOGY
S. scabies can overwinter in infected plant debris or tubers. When the weather warms, the bacterium releases spores that can spread through water, wind, and tools. When a spore comes in contact with a host it will penetrate through specialized pores in the potato skin called lenticels or through wounds. Once inside the host plant, the bacterium will grow through the outer tissue layers, using the dying host cells for nutrition. A compound secreted by the bacterium causes the host plant to produce a corky layer to cover the damaged area. This corky layer makes up the scabs on infected plants. The bacteria will continue to feed on the host plant and continue produce spores to infect additional hosts. Over time, the size and number of lesions will increase.
Crops with scab are more susceptible to further infections, such as bacterial soft rots.
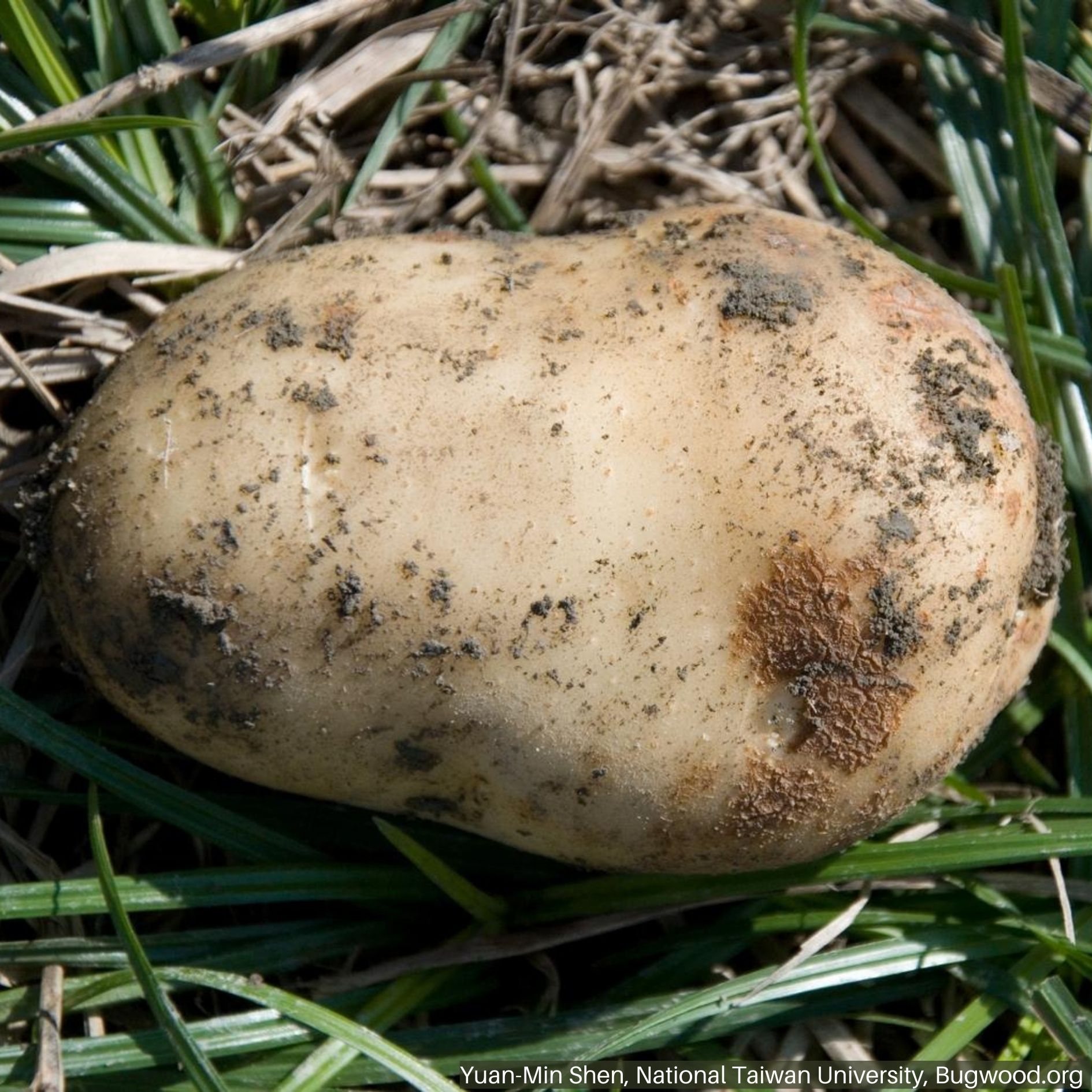
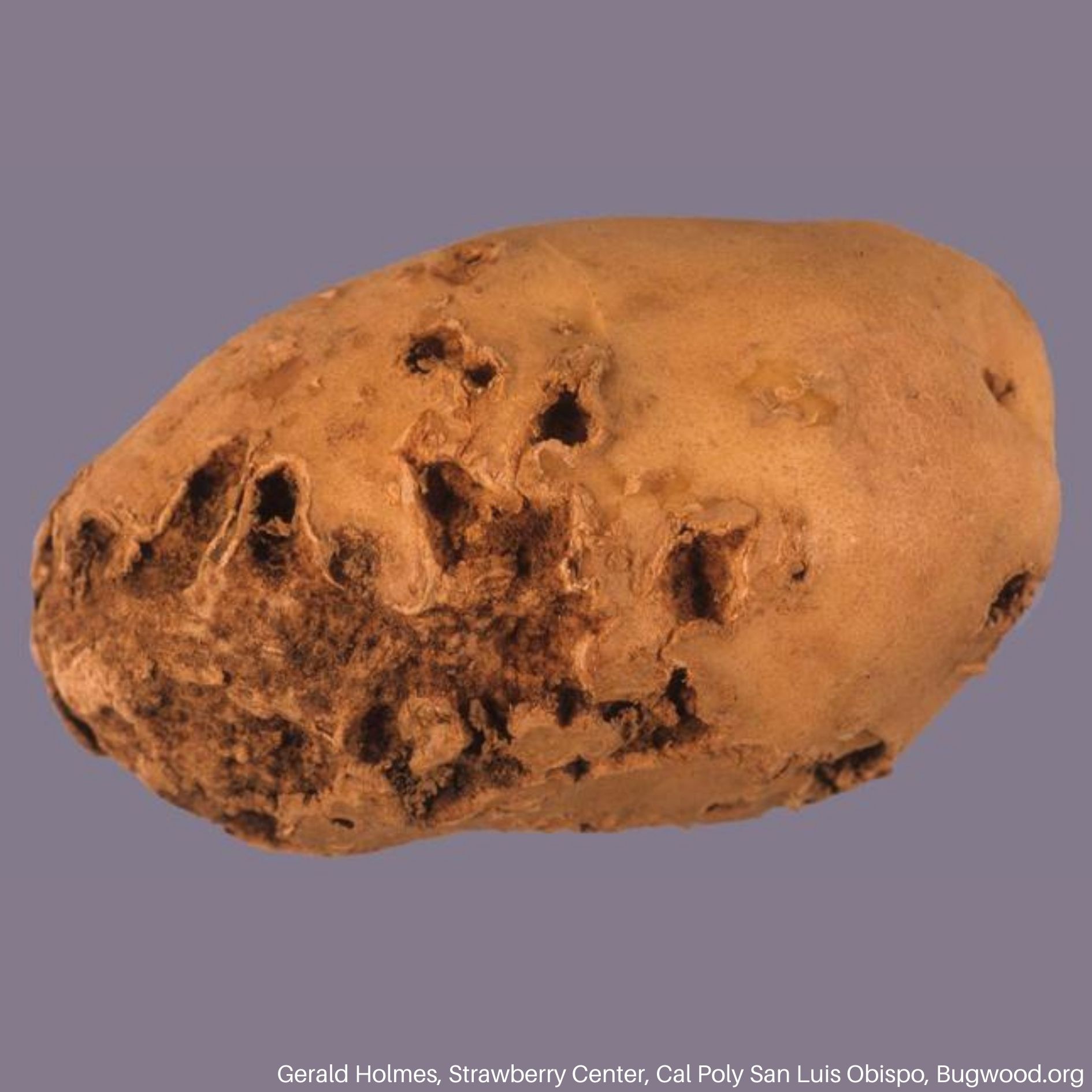
SYMPTOMS
- Rough, raised tissue that resemble scabs
- Pits or lesions
GENERAL MANAGEMENT
- Use certified disease-free seeds and seedstock
- Regularly rotate with non-susceptible crops
- Use crop varieties that are more resistant to scab
- Scab is less prevalent in acidic soils, keep soil pH below 7