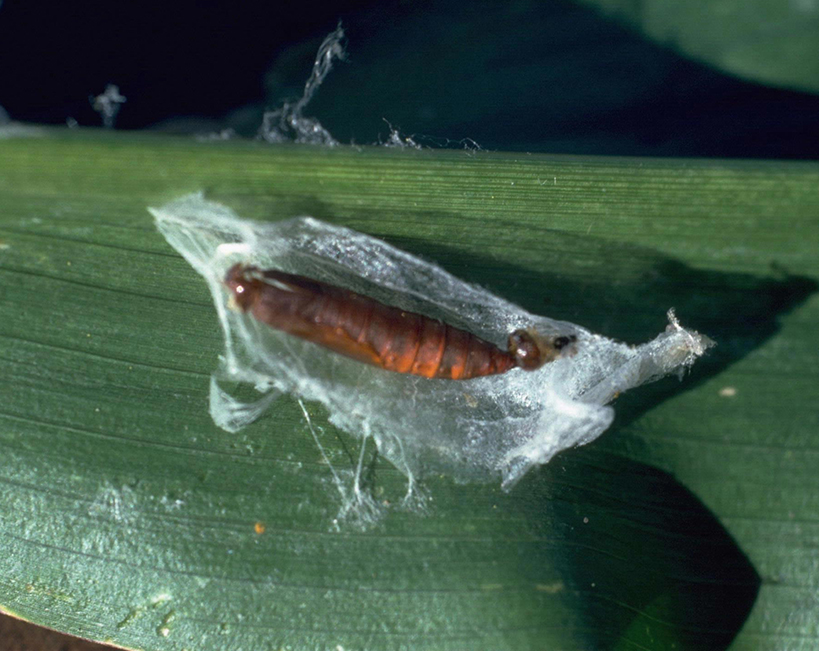
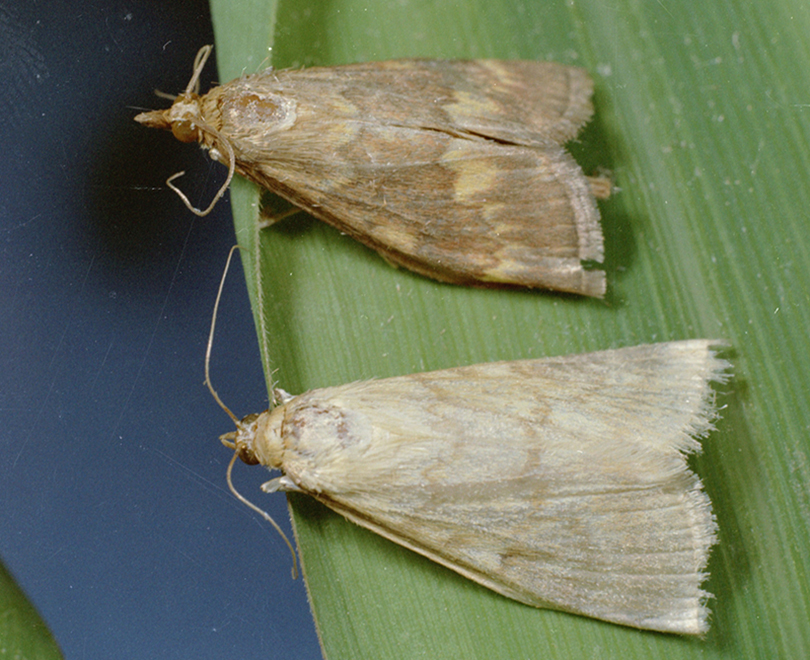
European Corn Borer
Ostrinia nubilalis
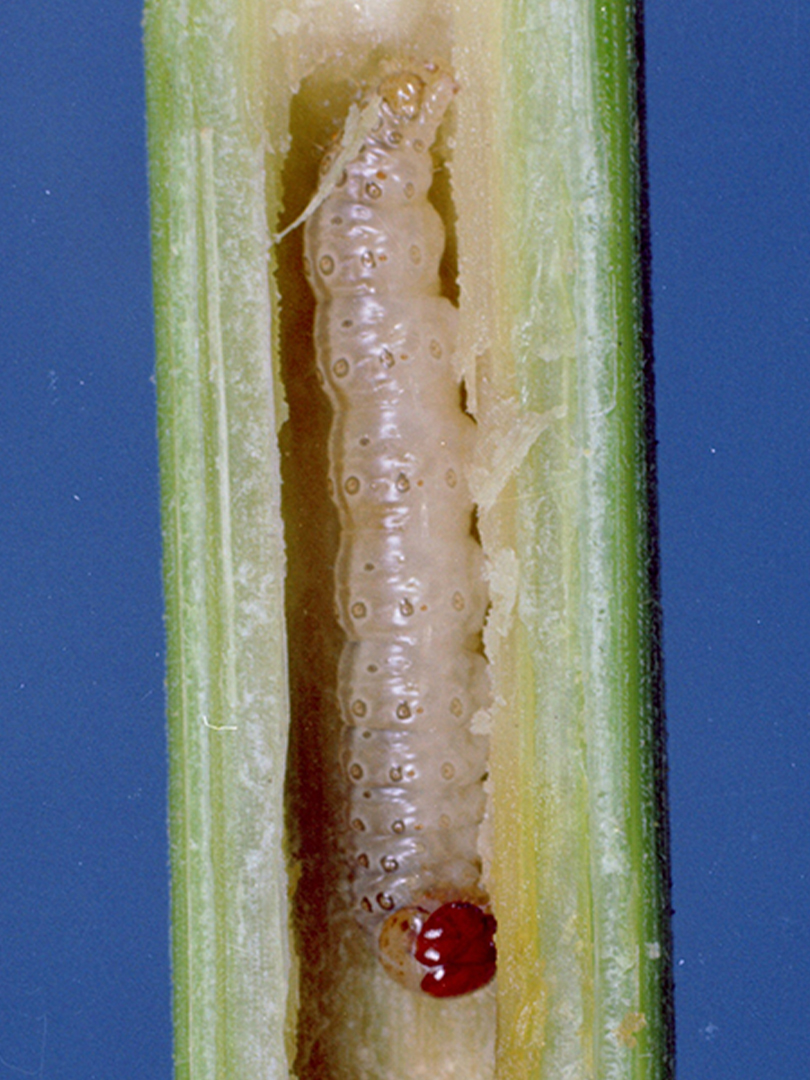 European corn borer larva inside corn.
European corn borer larva inside corn.
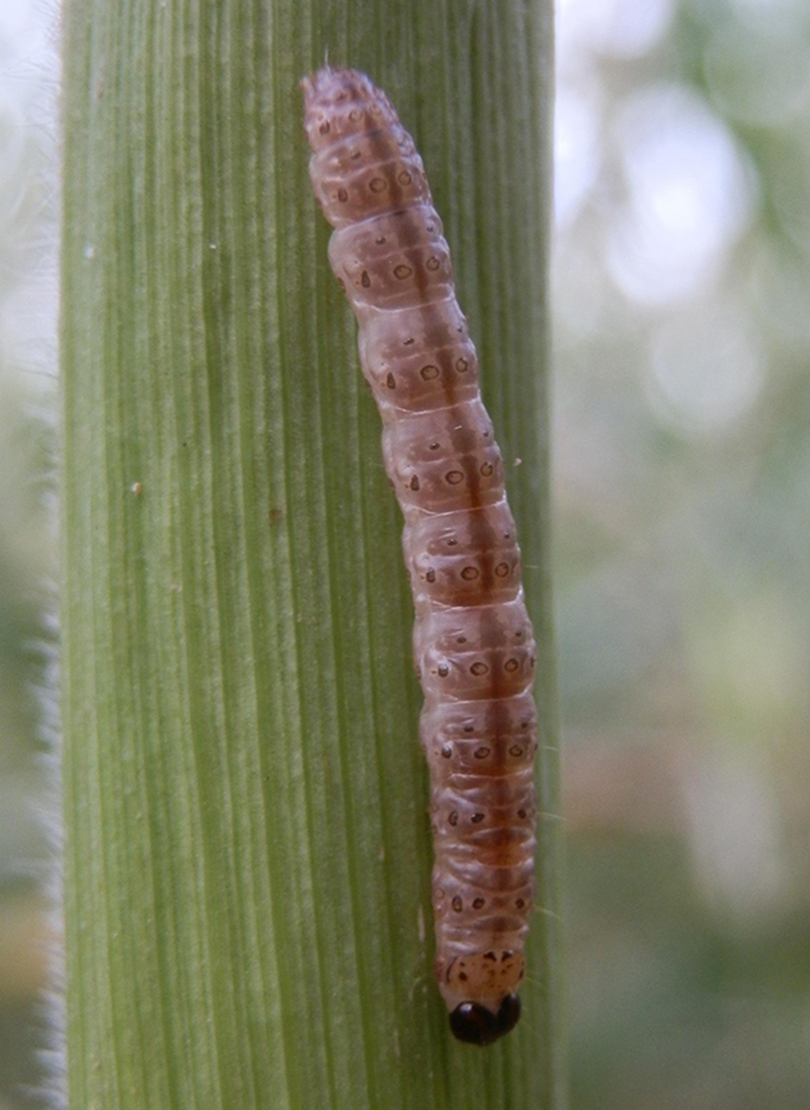

Mature European corn borer larva.
Hosts
- Field-grown hemp
- Corn
- Peppers
- Potato
- Snap beans
- Various ornamentals
Description
Larvae are creamy-white to gray with one row of small, round, brown spots in each body segment. Adults range in color from pale yellow-brown to light brown to dark brown with wavy markings on the wings. Eggs are clear-white and are laid in flat masses on the undersides of leaves.
Life Cycle
Egg | Larva | Pupa | Adult
- Likely 2-3 generations per year in Utah.
- Overwinter as caterpillars in stalks and debris of host plants.
- Pupation occurs inside stems.
- Adults fly from May-June (first generation) and in July-August (second generation).
- Eggs are laid in flat masses on the undersides of leaves.
- Young larvae feed on leaves, then bore into the stem to complete the life cycle.
Damaging Lifestage(s): Larva
Damage Symptoms
Newly hatched larvae feed in leaf whorls and then bore into the stems. Symptoms include significant structural damage along with wilting, dieback, and reduction of yield.
Time for Concern
Spring through harvest.
When and Where to Scout
- Monitor for adult moths in May-June and July-August using a pheromone trap.
- Adult moths indicate the need to scout for egg masses on plants.
- Look for egg masses laid on leaves, larvae inside stems, and damage symptoms such as plant wilting and dieback.
Threat Level
Medium if established.
Occurrence in Utah
This insect has not been identified as a pest in Utah hemp.
Management
- Remove overwintering larvae by removing crop debris, including stems and stalks.
- Management with insecticides can be difficult for this pest.
When to Consider Treatment
If there is a high population of moths and the signs of damage are seen consistently.
Look-alikes
None.
Caterpillar Insecticides
| Utah-Registered Product | Active Ingredient(s) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Agree WG | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. aizawa | |
| Aza-Direct Biological Insecticide | azadirachtin | |
| AzaGuard | azadirachtin | |
| AzaSol | azadirachtin | |
| Azatin O Biological Insecticide | azadirachtin | |
| Azatrol EC Insecticide | azadirachtin | |
| Azera Insecticide | azadirachtin | |
| BT Now | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | Greenhouse use only. |
| Bug Buster-O Extinguish Ant Bait | pyrethrins | Greenhouse use only. |
| Deadzone | diatomaceous earth | |
| Deliver Biological Insecticide | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | |
| DiPel DF Biological Insecticide | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | |
| DiPel DF Biological Insecticide Dry Flowable |
Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | |
| DiPel PRO DF Biological Insecticide | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | |
| Evergreen Crop Protection EC 60-6 | pyrethrins | |
| Ferti-Lome Dipel Dust Biological Insecticide (RTU) | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | |
| Ferti-lome Fruit Tree Spray | pyrethrins | |
| Grandevo CG;WDG | Chromobacterium sub strain PRAA4-1 cells | |
| Javelin WG Biological Insecticide | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | |
| Leprotec | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | |
| Molt-X | azadirachtin | |
| Neemix 4.5 Insect Growth Regulator | azadirachtin | |
| Prizefighter | ammonium nonanoate | |
| Pycana | pyrethrins | Greenhouse use only. |
| Pyganic Crop Protection EC 1.4 II; 5.0 II | pyrethrins | |
| SPEAR-LEP | gs-omega/kappahxtx-hv1a | Supression only; combine with a Bt product for greater efficacy. |
| Tersus Insecticide | pyrethrins | |
| Thuricide N/G | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | |
| Valent Professional Products DiPel Pro DF Biological Insecticide Dry Flowable |
Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. kurstaki | |
| Venerate CG | Burkholderia sp. strain A396 | |
| XenTari Biological Insecticide Dry Flowable | Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. aizawai |
Photo Credits
- Larva in stem/Adults - Clemson University - USDA Cooperative Extension Slide Series, Bugwood.org
- Mature larva - Mariusz Sobieski, Bugwood.org
- Recently hatched - Phil Sloderbeck, Kansas State University, Bugwood.org
- Pupa - Frank Peairs, Colorado State University, Bugwood.org